Nested IF in Excel – formula with multiple conditions
This tutorial demonstrates how to effectively use multiple IF functions in Microsoft Excel, showcasing nested IF formulas for various tasks. The core concept is using nested IF statements to evaluate multiple conditions and return different results based on those evaluations.
While a single IF function handles one condition, nested IFs extend this capability, allowing for more complex logical tests within a single formula. Excel versions 2007 and later support up to 64 nested IF functions, while older versions (2003 and earlier) limit this to 7.
Example 1: Grading Student Exam Scores
This example classifies student exam scores (in column B) based on predefined ranges:
- Excellent: Over 249
- Good: 200-249
- Satisfactory: 150-199
- Poor: Under 150
The nested IF formula is:
=IF(B2>249, "Excellent", IF(B2>=200, "Good", IF(B2>=150, "Satisfactory", "Poor")))
The formula proceeds sequentially. If the first condition (B2>249) is true, it returns "Excellent". Otherwise, it moves to the next IF statement, and so on.

Example 2: Calculating Total Price Based on Quantity
This example calculates the total price based on a quantity (in cell B8) and a tiered pricing structure:
| Unit Quantity | Price per unit |
|---|---|
| 1 to 10 | $20 |
| 11 to 19 | $18 |
| 20 to 49 | $16 |
| 50 to 100 | $13 |
| Over 101 | $12 |
The formula is:
=B8*IF(B8>=101, 12, IF(B8>=50, 13, IF(B8>=20, 16, IF(B8>=11, 18, IF(B8>=1, 20, "")))))
This formula multiplies the quantity by the appropriate price per unit determined by the nested IF structure. A more refined version references cell values for prices, allowing for easier price updates:
=B8*IF(B8>=101,B6, IF(B8>=50, B5, IF(B8>=20, B4, IF( B8>=11, B3, IF(B8>=1, B2, "")))))

Tips and Tricks:
- Order Matters: The order of IF statements significantly impacts the result. The formula stops at the first TRUE condition.
- Parentheses: Carefully balance parentheses to avoid errors. Excel's color-coding helps with this.
- Data Types: Enclose text values in double quotes, but not numbers.
- Readability: Use spaces and line breaks (Alt Enter) to improve formula readability.
-
Alternatives: For very complex scenarios, consider alternatives like
CHOOSE,VLOOKUP, or VBA functions.
Alternatives to Nested IFs:
For formulas with numerous nested IFs, consider using more efficient methods such as CHOOSE, VLOOKUP (with approximate match), logical functions (OR/AND), array formulas, or VBA custom functions. These alternatives often provide better performance and readability.
This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for mastering nested IF functions in Excel, enabling users to create powerful and flexible formulas for various data analysis tasks. A practice workbook is available for download to further enhance understanding.
The above is the detailed content of Nested IF in Excel – formula with multiple conditions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1658
1658
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1309
1309
 25
25
 1257
1257
 29
29
 1231
1231
 24
24
 If You Don't Rename Tables in Excel, Today's the Day to Start
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:58 AM
If You Don't Rename Tables in Excel, Today's the Day to Start
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:58 AM
Quick link Why should tables be named in Excel How to name a table in Excel Excel table naming rules and techniques By default, tables in Excel are named Table1, Table2, Table3, and so on. However, you don't have to stick to these tags. In fact, it would be better if you don't! In this quick guide, I will explain why you should always rename tables in Excel and show you how to do this. Why should tables be named in Excel While it may take some time to develop the habit of naming tables in Excel (if you don't usually do this), the following reasons illustrate today
 You Need to Know What the Hash Sign Does in Excel Formulas
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:55 AM
You Need to Know What the Hash Sign Does in Excel Formulas
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:55 AM
Excel Overflow Range Operator (#) enables formulas to be automatically adjusted to accommodate changes in overflow range size. This feature is only available for Microsoft 365 Excel for Windows or Mac. Common functions such as UNIQUE, COUNTIF, and SORTBY can be used in conjunction with overflow range operators to generate dynamic sortable lists. The pound sign (#) in the Excel formula is also called the overflow range operator, which instructs the program to consider all results in the overflow range. Therefore, even if the overflow range increases or decreases, the formula containing # will automatically reflect this change. How to list and sort unique values in Microsoft Excel
 How to Format a Spilled Array in Excel
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
How to Format a Spilled Array in Excel
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
Use formula conditional formatting to handle overflow arrays in Excel Direct formatting of overflow arrays in Excel can cause problems, especially when the data shape or size changes. Formula-based conditional formatting rules allow automatic formatting to be adjusted when data parameters change. Adding a dollar sign ($) before a column reference applies a rule to all rows in the data. In Excel, you can apply direct formatting to the values or background of a cell to make the spreadsheet easier to read. However, when an Excel formula returns a set of values (called overflow arrays), applying direct formatting will cause problems if the size or shape of the data changes. Suppose you have this spreadsheet with overflow results from the PIVOTBY formula,
 How to change Excel table styles and remove table formatting
Apr 19, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to change Excel table styles and remove table formatting
Apr 19, 2025 am 11:45 AM
This tutorial shows you how to quickly apply, modify, and remove Excel table styles while preserving all table functionalities. Want to make your Excel tables look exactly how you want? Read on! After creating an Excel table, the first step is usual
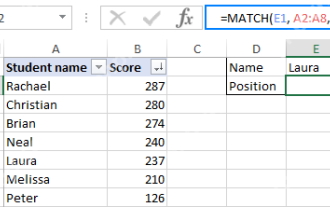 Excel MATCH function with formula examples
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Excel MATCH function with formula examples
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
This tutorial explains how to use MATCH function in Excel with formula examples. It also shows how to improve your lookup formulas by a making dynamic formula with VLOOKUP and MATCH. In Microsoft Excel, there are many different lookup/ref
 How to Use Excel's AGGREGATE Function to Refine Calculations
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:54 AM
How to Use Excel's AGGREGATE Function to Refine Calculations
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:54 AM
Quick Links The AGGREGATE Syntax
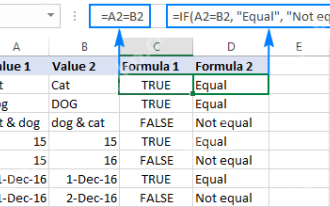 Excel: Compare strings in two cells for matches (case-insensitive or exact)
Apr 16, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Excel: Compare strings in two cells for matches (case-insensitive or exact)
Apr 16, 2025 am 11:26 AM
The tutorial shows how to compare text strings in Excel for case-insensitive and exact match. You will learn a number of formulas to compare two cells by their values, string length, or the number of occurrences of a specific character, a





