Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulas
This tutorial clarifies the function of Excel names and demonstrates how to define names for cells, ranges, constants, or formulas. It also covers editing, filtering, and deleting defined names.
Excel names, while incredibly useful, are often overlooked. This tutorial not only explains how to create named ranges but also shows how they simplify formula creation, readability, and reusability.
Understanding Excel Names
In everyday life, names simplify referencing. Similarly, Excel names provide human-readable identifiers for cells and ranges, replacing complex cell references. For example, instead of =SUMIF($A$2:$A$10, $E$1, $B$2:$B$10), use =SUMIF(items_list, item, sales). The latter is significantly clearer.

Excel Name Types:
- Defined Names: Names assigned to single cells, ranges, constants, or formulas (including named ranges). This tutorial focuses on defined names.
- Table Names: Automatically generated names for Excel tables (created using Ctrl T).
Creating Named Ranges
Three methods exist for defining names:
1. Name Box:
- Select the cell(s) or range.
- Type the name in the Name Box.
- Press Enter.

2. Define Name Option:
- Select the cell(s).
- Go to the Formulas tab, click Define Name.
- In the dialog box, enter the name, scope (workbook is default), and reference.
- Click OK.

3. Name Manager:
- Go to Formulas tab > Name Manager (or Ctrl F3).
- Click New….
- Configure the name as in method 2.
Creating Named Constants and Formulas
You can define names for constant values (e.g., =0.93 for USD_EUR) and formulas (e.g., =COUNTA(Sheet5!$A:$A)-1 for Items_count). These enhance formula clarity and maintainability.


Naming Columns and Rows
Select the table including headers, go to Formulas > Create from Selection, and choose the header rows or columns to create names automatically.


Dynamic Named Ranges
For expanding datasets, use dynamic named ranges (using OFFSET or INDEX functions) to automatically include new data.
Excel Naming Rules and Scope
- Names are case-insensitive and under 255 characters.
- They must start with a letter, underscore, or backslash.
- Spaces and most punctuation are not allowed.
- Scope can be worksheet-level or workbook-level. Workbook-level names are accessible throughout the workbook.
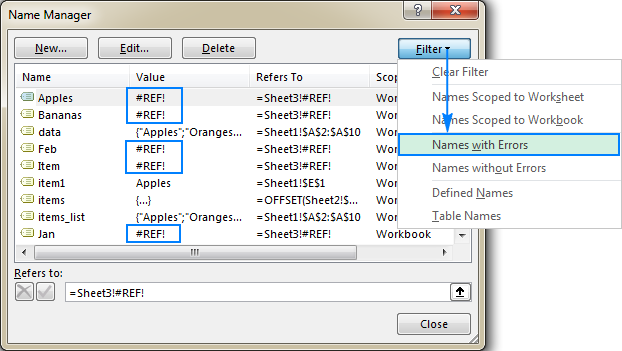
Excel Name Manager
The Name Manager (Ctrl F3) allows editing, filtering (by scope, errors, type), and deleting names. Filtering for names with errors helps identify and correct invalid references.


Benefits of Using Excel Names
- Improved formula readability and creation.
- Creation of expandable formulas using dynamic ranges.
- Easier formula reuse across sheets and workbooks.
- Simplified navigation to named ranges.
- Enables creation of dynamic dropdown lists.
Tips and Tricks
- Use
Paste Names…(F3) to list all names. - Understand the difference between absolute and relative names. Relative names adjust based on the active cell's position.
- Use Apply Names… to apply defined names to existing formulas.
- Utilize keyboard shortcuts (Ctrl F3, Ctrl Shift F3, F3).
- Be aware of
#REF!(deleted range) and#NAME?(invalid name) errors.
This enhanced summary retains the core information while improving clarity and flow. Remember to include all images as requested in the original format.
The above is the detailed content of Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulas. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1655
1655
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1306
1306
 25
25
 1252
1252
 29
29
 1226
1226
 24
24
 How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to Excel's Flash Fill feature, a powerful tool for automating data entry tasks. It covers various aspects, from its definition and location to advanced usage and troubleshooting. Understanding Excel's Fla
 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
This tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
 Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to sharing Excel workbooks, covering various methods, access control, and conflict resolution. Modern Excel versions (2010, 2013, 2016, and later) simplify collaborative editing, eliminating the need to m
 How to spell check in Excel
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:10 AM
How to spell check in Excel
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:10 AM
This tutorial demonstrates various methods for spell-checking in Excel: manual checks, VBA macros, and using a specialized tool. Learn to check spelling in cells, ranges, worksheets, and entire workbooks. While Excel isn't a word processor, its spel
 Excel: Group rows automatically or manually, collapse and expand rows
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:17 AM
Excel: Group rows automatically or manually, collapse and expand rows
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:17 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to streamline complex Excel spreadsheets by grouping rows, making data easier to analyze. Learn to quickly hide or show row groups and collapse the entire outline to a specific level. Large, detailed spreadsheets can be
 Absolute value in Excel: ABS function with formula examples
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:12 AM
Absolute value in Excel: ABS function with formula examples
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:12 AM
This tutorial explains the concept of absolute value and demonstrates practical Excel applications of the ABS function for calculating absolute values within datasets. Numbers can be positive or negative, but sometimes only positive values are neede
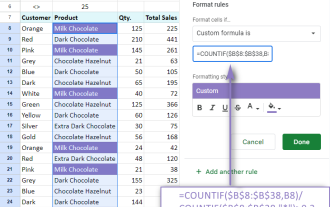 Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Master Google Sheets COUNTIF: A Comprehensive Guide This guide explores the versatile COUNTIF function in Google Sheets, demonstrating its applications beyond simple cell counting. We'll cover various scenarios, from exact and partial matches to han
 How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
This tutorial explores various methods for converting .xls files to .jpg images, encompassing both built-in Windows tools and free online converters. Need to create a presentation, share spreadsheet data securely, or design a document? Converting yo




