Excel COUNTIF and COUNTIFS with OR logic
This tutorial demonstrates how to use Excel's COUNTIF and COUNTIFS functions to count cells meeting multiple OR conditions (e.g., if a cell contains X, Y, or Z).
While COUNTIF handles single criteria and COUNTIFS uses AND logic, this tutorial provides solutions for OR logic scenarios. It assumes familiarity with the basic syntax and usage of both functions.
Counting Cells with OR Conditions
The simplest case involves counting cells satisfying at least one of several conditions.
Method 1: COUNTIF COUNTIF
This adds the results of individual COUNTIF functions for each criterion. For example, to count cells in column A containing "apples" or "bananas":
=COUNTIF(A:A, "apples") COUNTIF(A:A, "bananas")
Using cell references (e.g., criteria in F1 and G1) improves efficiency and maintainability:
=COUNTIF(A2:A10, F1) COUNTIF(A2:A10, G1)

Method 2: COUNTIF with Array Constant
This offers a more compact approach:
SUM(COUNTIF(*range*, {*criterion1*, *criterion2*, *criterion3*, …}))
The criteria are enclosed in an array constant {"apples","bananas","lemons"}. COUNTIF returns multiple counts, which SUM adds.
=SUM(COUNTIF(A2:A10,{"apples","bananas","lemons"}))

Using cell references (F1:H1) requires an array formula (Ctrl Shift Enter):
=SUM(COUNTIF(A2:A10,F1:H1))

Method 3: SUMPRODUCT
SUMPRODUCT(1\*(*range* ={*criterion1*, *criterion2*, *criterion3*, …})) or SUMPRODUCT((*range*=*criterion1*) (*range*=*criterion2*) …)
This tests each cell against each criterion, summing the resulting TRUE/FALSE array (converted to 1/0).
=SUMPRODUCT(1*(A2:A10={"apples","bananas","lemons"}))
or
=SUMPRODUCT((A2:A10="apples") (A2:A10="bananas") (A2:A10="lemons"))
Using cell references (F1:H1):
=SUMPRODUCT(1*( A2:A10=F1:H1))

Note: SUMPRODUCT can be slower than COUNTIF for large datasets.
Counting Cells with OR and AND Logic
This extends the concept to include both OR and AND conditions. For example, counting "apples," "bananas," or "lemons" that are "delivered" (column A and column C):
Method 1: COUNTIFS COUNTIFS
This adds multiple COUNTIFS functions, each checking one OR condition and the AND condition.
=COUNTIFS(A2:A10, "apples", C2:C10, "delivered") COUNTIFS(A2:A10, "bananas", C2:C10, "delivered") COUNTIFS(A2:A10, "lemons", C2:C10, "delivered")

Method 2: COUNTIFS with Array Constant
A more concise version using an array constant for OR criteria:
=SUM(COUNTIFS(A2:A10, {"apples","bananas","lemons"}, C2:C10, "delivered"))
With cell references (F1:H1 and F2), an array formula (Ctrl Shift Enter) is needed:
=SUM(COUNTIFS(A2:A10,F1:H1,C2:C10,F2))

Wildcards are supported (e.g., "*bananas*"). Additional AND conditions can be added to COUNTIFS.
Counting Cells with Multiple OR Conditions
For multiple sets of OR criteria, COUNTIFS with array constants (limited to two sets) or SUMPRODUCT with ISNUMBER and MATCH (handles more sets) are used.
For two sets, use horizontal and vertical arrays within COUNTIFS:
=SUM(COUNTIFS(A2:A10, {"apples", "bananas", "lemons"}, B2:B10, {"delivered"; "in transit"}))

For multiple sets, SUMPRODUCT with MATCH is more versatile:
=SUMPRODUCT(ISNUMBER(MATCH(A2:A10,{"apples","bananas","lemons"},0))*ISNUMBER(MATCH(B2:B10,{"bag","tray"},0))*ISNUMBER(MATCH(C2:C10,{"delivered","in transit"},0)))

This tutorial provides various methods for handling OR conditions in Excel's counting functions, catering to different complexity levels and dataset sizes. A sample workbook is available for further practice.
The above is the detailed content of Excel COUNTIF and COUNTIFS with OR logic. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
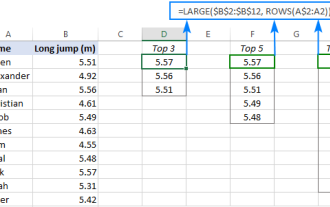 Excel formula to find top 3, 5, 10 values in column or row
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:09 AM
Excel formula to find top 3, 5, 10 values in column or row
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:09 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to efficiently locate the top N values within a dataset and retrieve associated data using Excel formulas. Whether you need the highest, lowest, or those meeting specific criteria, this guide provides solutions. Findi
 Add a dropdown list to Outlook email template
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:13 AM
Add a dropdown list to Outlook email template
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:13 AM
This tutorial shows you how to add dropdown lists to your Outlook email templates, including multiple selections and database population. While Outlook doesn't directly support dropdowns, this guide provides creative workarounds. Email templates sav
 How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to Excel's Flash Fill feature, a powerful tool for automating data entry tasks. It covers various aspects, from its definition and location to advanced usage and troubleshooting. Understanding Excel's Fla
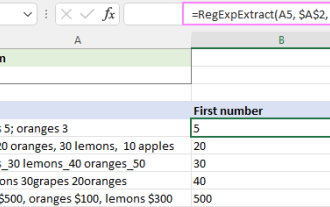 Regex to extract strings in Excel (one or all matches)
Mar 28, 2025 pm 12:19 PM
Regex to extract strings in Excel (one or all matches)
Mar 28, 2025 pm 12:19 PM
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to use regular expressions in Excel to find and extract substrings matching a given pattern. Microsoft Excel provides a number of functions to extract text from cells. Those functions can cope with most
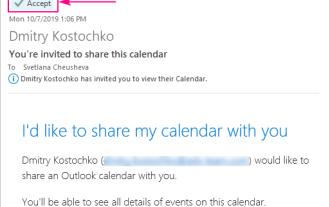 How to add calendar to Outlook: shared, Internet calendar, iCal file
Apr 03, 2025 am 09:06 AM
How to add calendar to Outlook: shared, Internet calendar, iCal file
Apr 03, 2025 am 09:06 AM
This article explains how to access and utilize shared calendars within the Outlook desktop application, including importing iCalendar files. Previously, we covered sharing your Outlook calendar. Now, let's explore how to view calendars shared with
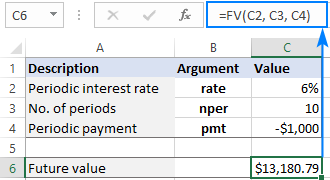 FV function in Excel to calculate future value
Apr 01, 2025 am 04:57 AM
FV function in Excel to calculate future value
Apr 01, 2025 am 04:57 AM
This tutorial explains how to use Excel's FV function to determine the future value of investments, encompassing both regular payments and lump-sum deposits. Effective financial planning hinges on understanding investment growth, and this guide prov
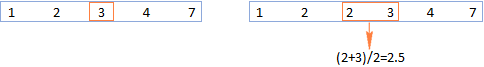 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
This tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
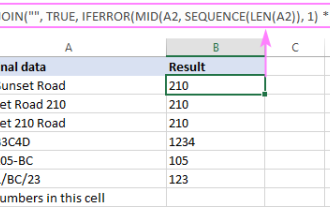 How to remove / split text and numbers in Excel cell
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:07 AM
How to remove / split text and numbers in Excel cell
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:07 AM
This tutorial demonstrates several methods for separating text and numbers within Excel cells, utilizing both built-in functions and custom VBA functions. You'll learn how to extract numbers while removing text, isolate text while discarding numbers






