Excel LAMBDA function: how to write, calculate and use
This tutorial simplifies the Excel LAMBDA function, providing practical examples to illustrate its use, behavior, and potential pitfalls. Before LAMBDA, user-defined functions were primarily for programmers. Now, LAMBDA empowers everyone to create custom functions within Excel's familiar formula language, eliminating the need for VBA expertise in many cases.
- Excel Versions Supporting LAMBDA
- Constructing LAMBDA Formulas in Excel
- Calculating with LAMBDA in Excel
- Custom LAMBDA Function Examples:
- Example 1: Streamlining Complex Formulas
- Example 2: Utilizing Multiple Parameters
- Example 3: LAMBDA and Dynamic Arrays
- Exporting/Importing LAMBDA Across Workbooks
- Advantages and Limitations of LAMBDA
- Troubleshooting LAMBDA Function Errors
The Excel LAMBDA Function
The LAMBDA function in Excel enables the creation of custom, reusable functions, callable by user-defined names. Any complex formula can be encapsulated within a LAMBDA function and assigned a user-friendly name (e.g., MyCustomFunction). This eliminates the need to repeatedly type lengthy formulas. LAMBDA operates without macros or scripting languages, making it accessible to all users.
Lambda's Meaning
The lambda symbol (λ) originates from lambda calculus, a computational model where functions are anonymous and created through abstraction. Microsoft's LAMBDA function makes Excel "Turing-complete," allowing for virtually any calculation using native formulas, thanks to its recursive capabilities (a function calling itself).
Syntax
The syntax is: LAMBDA([parameter1, parameter2, …], calculation)
- Parameter (optional): Input values (cell references, numbers, text). Up to 253 parameters are allowed.
- Calculation (required): The formula to execute; it must return a value.
A simple LAMBDA example:

Usage Notes
- Adhere to Excel's naming conventions for LAMBDA functions and parameters.
- Avoid periods (.) in parameter names.
- Prevent parameter names from clashing with cell references (e.g., use
val_1instead ofval1if you have a cell namedVAL1). - Follow standard formula best practices (correct argument count, matching parentheses).
Excel Versions with LAMBDA Support
LAMBDA is available in Microsoft 365 subscriptions (Windows, Mac, and web versions).
Creating LAMBDA Formulas in Excel
-
Develop a Core Formula: Start with the core formula producing the desired result. For example, a percentage variance formula:
=IFERROR(C2/B2-1, "-")

-
Create and Test a LAMBDA Formula: If the formula uses input values, add them as parameters to LAMBDA. For our example:
=LAMBDA(old, new, IFERROR(new/old-1, "-"))(B2, C2)This testing syntax allows immediate function evaluation before naming.

-
Name the LAMBDA Function:
- Copy the LAMBDA formula (excluding the function call).
- Open the Name Manager (Ctrl F3).
- Click "New."
- Enter a name (e.g.,
PercentVar), select "Workbook" scope, paste the formula into "Refers to," and click "OK."

Now, use the named LAMBDA like a built-in function: =PercentVar(B2, C2)

Excel LAMBDA Examples
Example 1: Compacting Long Formulas
LAMBDA excels at simplifying complex formulas. A formula to extract numbers from a string can be encapsulated in a LAMBDA function for easier readability and reuse.
Example 2: LAMBDA with Multiple Parameters
LAMBDA handles up to 253 parameters, but minimizing their number improves readability and usability. A compound annual growth rate (CAGR) function demonstrates this. Consider adding comments in the Name Manager to explain parameters.
Example 3: LAMBDA with Dynamic Arrays
LAMBDA works seamlessly with Excel 365's dynamic arrays. A function to sort a list by item count using SORTBY, COUNTIF, and UNIQUE illustrates this.
Exporting/Importing LAMBDA
LAMBDAs are workbook-specific. To transfer them, copy a sheet from the source workbook to the destination workbook. This transfers all LAMBDAs from the source.
Advantages and Limitations of LAMBDA
Advantages:
- Compact, readable functions.
- Centralized function editing.
- Formula-based solutions for tasks previously requiring VBA.
Limitations:
- Excel 365 only.
- Workbook-specific.
- No tooltips for arguments (use Name Manager comments as a workaround).
Troubleshooting LAMBDA Errors
Various errors (#NAME!, #VALUE!, #NUM!, #CALC!) can occur due to version incompatibility, typos, incorrect argument counts, circular references, or invalid parameter names. Ensure parameter names don't conflict with cell references.
This tutorial provides a foundation for using the powerful Excel LAMBDA function. Further exploration will reveal its extensive capabilities. A practice workbook is available for download.
The above is the detailed content of Excel LAMBDA function: how to write, calculate and use. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1656
1656
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1307
1307
 25
25
 1255
1255
 29
29
 1229
1229
 24
24
 How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to Excel's Flash Fill feature, a powerful tool for automating data entry tasks. It covers various aspects, from its definition and location to advanced usage and troubleshooting. Understanding Excel's Fla
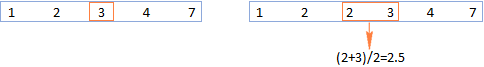 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
This tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
 How to spell check in Excel
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:10 AM
How to spell check in Excel
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:10 AM
This tutorial demonstrates various methods for spell-checking in Excel: manual checks, VBA macros, and using a specialized tool. Learn to check spelling in cells, ranges, worksheets, and entire workbooks. While Excel isn't a word processor, its spel
 Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to sharing Excel workbooks, covering various methods, access control, and conflict resolution. Modern Excel versions (2010, 2013, 2016, and later) simplify collaborative editing, eliminating the need to m
 Absolute value in Excel: ABS function with formula examples
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:12 AM
Absolute value in Excel: ABS function with formula examples
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:12 AM
This tutorial explains the concept of absolute value and demonstrates practical Excel applications of the ABS function for calculating absolute values within datasets. Numbers can be positive or negative, but sometimes only positive values are neede
 Excel: Group rows automatically or manually, collapse and expand rows
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:17 AM
Excel: Group rows automatically or manually, collapse and expand rows
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:17 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to streamline complex Excel spreadsheets by grouping rows, making data easier to analyze. Learn to quickly hide or show row groups and collapse the entire outline to a specific level. Large, detailed spreadsheets can be
 How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
This tutorial explores various methods for converting .xls files to .jpg images, encompassing both built-in Windows tools and free online converters. Need to create a presentation, share spreadsheet data securely, or design a document? Converting yo
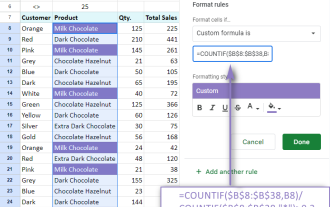 Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Master Google Sheets COUNTIF: A Comprehensive Guide This guide explores the versatile COUNTIF function in Google Sheets, demonstrating its applications beyond simple cell counting. We'll cover various scenarios, from exact and partial matches to han




