My first open source contribution
Filing an issue
For my first contribution, I filed an issue to add a new feature to another project which is to add a new flag option to display the tokens used for the prompt and the completion generation.
 Feat: chat completion token info flag option
#8
Feat: chat completion token info flag option
#8

Description
A flag option that gives the user a count of tokens sent and received. I think that it is an important feature that guides the user to stay within the token budget when making a chat completions request!
Implementation
To do this, we would need to add another option flag which could be -t and --token-usage. When a user includes this flag to their command, it should display in clear detail how many tokens were used in the generation of the completion, and how many tokens were used in the prompt.
I chose to contribute to fadingNA's open source project, chat-minal, a CLI tool written in Python that allows you to leverage OpenAI to do various things, such as using it to generate a code review, file conversion, generating markdown from text, and summarizing text.
My pull request
I have written code in Python before, but it is not my strongest skill. So contributing to this project provides a challenging but good learning experience for me.
The challenge is that I would have to read and understand someone else's code, and provide a proper solution in a way that it does not break the design of the code. Understanding the flow is crucial so that I can efficiently add the feature without having to make big changes in the code and keep the code consistent.
 FEAT: Token usage flag
#9
FEAT: Token usage flag
#9

Feature
Added the feature to include a --token_usage flag option for the user. This option gives the user the information of how many tokens were used for the prompt and generated completion.
Implementation
The solution I came up with based on the code design is to check for the existence of the token_usage flag. I do not want the code to check any unnecessary if statements if the token_usage flag was not used, so I made two separate identical loop logic, with the difference of checking the the existence of usage_metadata inside chunk.
if token_usage:
for chunk in runnable.stream({"input_text": input_text}):
print(chunk.content, end="", flush=True)
answer.append(chunk.content)
if chunk.usage_metadata:
completion_tokens = chunk.usage_metadata.get('output_tokens')
prompt_tokens = chunk.usage_metadata.get('input_tokens')
else:
for chunk in runnable.stream({"input_text": input_text}):
print(chunk.content, end="", flush=True)
answer.append(chunk.content)Display
At the end of the execution of get_completions() method, a check for the flag token_usage is added, which then displays the token usage details to stderr if the flag was used.
if token_usage:
logger.error(f"Tokens used for completion: <span class="pl-s1"><span class="pl-kos">{completion_tokens}</span>"</span>)
logger.error(f"Tokens used for prompt: <span class="pl-s1"><span class="pl-kos">{prompt_tokens}</span>"</span>)My solution
Retrieving the token usage
if token_usage:
for chunk in runnable.stream({"input_text": input_text}):
print(chunk.content, end="", flush=True)
answer.append(chunk.content)
if chunk.usage_metadata:
completion_tokens = chunk.usage_metadata.get('output_tokens')
prompt_tokens = chunk.usage_metadata.get('input_tokens')
else:
for chunk in runnable.stream({"input_text": input_text}):
print(chunk.content, end="", flush=True)
answer.append(chunk.content)
Originally, the code only had one for loop which retrieves the content from a stream and appends it to an array which forms the response of the completion.
Why did I write it this way?
My reasoning behind duplicating the for while adding the distinct if block is to prevent the code from repeatedly checking the if block even if the user is not using the newly added --token_usage flag. So instead, I check for the existence of the flag firstly, and then decide which for loop to execute.
Realization
Even though my pull request has been accepted by the project owner, I realized late that this way adds complexity to the code's maintainability. For example, if there are changes required in the for loop for processing the stream, that means modifying the code twice since there are two identical for loops.
What I think I could do as an improvement for it is to make it into a function so that any changes required can be done in one function only, keeping the maintainability of the code. This just proves that even if I wrote the code with optimization in mind, there are still other things that I can miss which is crucial to a project, which in this case, is maintainability.
Receiving a pull request
My tool, genereadme, also received a contribution. I received a PR from Mounayer, which is to add the same feature to my project.
 feat: added a new flag that displays the number of tokens sent in prompt and received in completion
#13
feat: added a new flag that displays the number of tokens sent in prompt and received in completion
#13

Description
Closes #12.
- Added a new flag --token-usage which when given, prints the number of tokens that were sent in the prompt and the number of tokens that were returned in the completion to `stderr.
This simply required the addition for another flag check --token-usage:
.option("--token-usage", "Show prompt and completion token usage")I've also made sure to keep your naming conventions/formatting style consistent, in the for loop that does the chat completion for each file processed, I have accumulated the total tokens sent and received:
promptTokens += response.usage.prompt_tokens;
completionTokens += response.usage.completion_tokens;which I then display at the end of program run-time if the --token-usage flag is provided as such:
if (program.opts().tokenUsage) {
console.error(`Prompt tokens: <span class="pl-s1"><span class="pl-kos">${promptTokens}</span>`</span>);
console.error(`Completion tokens: <span class="pl-s1"><span class="pl-kos">${completionTokens}</span>`</span>);
}- Updated README.md to explain the new flag.
Testing
Test 1
genereadme examples/sum.js --token-usage
This should display something like:
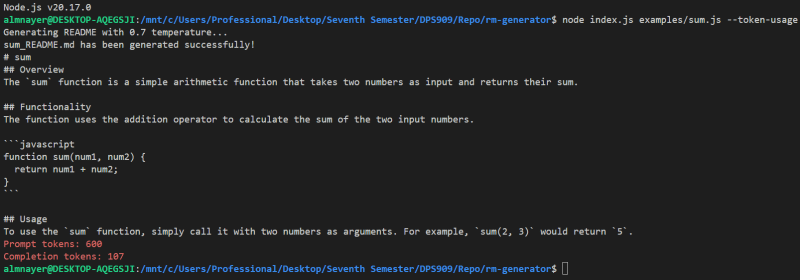
Test 2
You can try it out with multiple files too, i.e.:
genereadme examples/sum.js examples/createUser.js --token-usage
This time, instead of having to read someone else's code, someone had to read mine and contribute to it. It is nice knowing that someone is able to contribute to my project. To me, it means that they understood how my code works, so they were able to add the feature without breaking anything or adding any complexity to the code base.
With that being mentioned, reading code is also a skill that is not to be underestimated. My code is nowhere near perfect and I know there are still places I can improve on, so credit is also due to being able to read and understand code.
This specific pull request did not really require any back and forth changes as the code that was written by Mounayer is what I would have written myself.
The above is the detailed content of My first open source contribution. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1304
1304
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is suitable for data science, web development and automation tasks, while C is suitable for system programming, game development and embedded systems. Python is known for its simplicity and powerful ecosystem, while C is known for its high performance and underlying control capabilities.
 How Much Python Can You Learn in 2 Hours?
Apr 09, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
How Much Python Can You Learn in 2 Hours?
Apr 09, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
You can learn the basics of Python within two hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control structures such as if statements and loops, 3. Understand the definition and use of functions. These will help you start writing simple Python programs.
 Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in gaming and GUI development. 1) Game development uses Pygame, providing drawing, audio and other functions, which are suitable for creating 2D games. 2) GUI development can choose Tkinter or PyQt. Tkinter is simple and easy to use, PyQt has rich functions and is suitable for professional development.
 The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
You can learn basic programming concepts and skills of Python within 2 hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control flow (conditional statements and loops), 3. Understand the definition and use of functions, 4. Quickly get started with Python programming through simple examples and code snippets.
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.
 Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python is widely used in the fields of web development, data science, machine learning, automation and scripting. 1) In web development, Django and Flask frameworks simplify the development process. 2) In the fields of data science and machine learning, NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn and TensorFlow libraries provide strong support. 3) In terms of automation and scripting, Python is suitable for tasks such as automated testing and system management.
 Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
To maximize the efficiency of learning Python in a limited time, you can use Python's datetime, time, and schedule modules. 1. The datetime module is used to record and plan learning time. 2. The time module helps to set study and rest time. 3. The schedule module automatically arranges weekly learning tasks.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.




 Feat: chat completion token info flag option
#8
Feat: chat completion token info flag option
#8
