用Python解析XML的几种常见方法的介绍
一、简介
XML(eXtensible Markup Language)指可扩展标记语言,被设计用来传输和存储数据,已经日趋成为当前许多新生技术的核心,在不同的领域都有着不同的应用。它是web发展到一定阶段的必然产物,既具有SGML的核心特征,又有着HTML的简单特性,还具有明确和结构良好等许多新的特性。
python解析XML常见的有三种方法:一是xml.dom.*模块,它是W3C DOM API的实现,若需要处理DOM API则该模块很适合,注意xml.dom包里面有许多模块,须区分它们间的不同;二是xml.sax.*模块,它是SAX API的实现,这个模块牺牲了便捷性来换取速度和内存占用,SAX是一个基于事件的API,这就意味着它可以“在空中”处理庞大数量的的文档,不用完全加载进内存;三是xml.etree.ElementTree模块(简称 ET),它提供了轻量级的Python式的API,相对于DOM来说ET 快了很多,而且有很多令人愉悦的API可以使用,相对于SAX来说ET的ET.iterparse也提供了 “在空中” 的处理方式,没有必要加载整个文档到内存,ET的性能的平均值和SAX差不多,但是API的效率更高一点而且使用起来很方便。
二、详解
解析的xml文件(country.xml):
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<data>
<country name="Singapore">
<rank>4</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>59900</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/>
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank>68</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/>
<neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/>
</country>
</data>
1、xml.etree.ElementTree
ElementTree生来就是为了处理XML,它在Python标准库中有两种实现:一种是纯Python实现的,如xml.etree.ElementTree,另一种是速度快一点的xml.etree.cElementTree。注意:尽量使用C语言实现的那种,因为它速度更快,而且消耗的内存更少。
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
try:
import xml.etree.cElementTree as ET
except ImportError:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
这是一个让Python不同的库使用相同API的一个比较常用的办法,而从Python 3.3开始ElementTree模块会自动寻找可用的C库来加快速度,所以只需要import xml.etree.ElementTree就可以了。
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
#!/usr/bin/evn python
#coding:utf-8
try:
import xml.etree.cElementTree as ET
except ImportError:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import sys
try:
tree = ET.parse("country.xml") #打开xml文档
#root = ET.fromstring(country_string) #从字符串传递xml
root = tree.getroot() #获得root节点
except Exception, e:
print "Error:cannot parse file:country.xml."
sys.exit(1)
print root.tag, "---", root.attrib
for child in root:
print child.tag, "---", child.attrib
print "*"*10
print root[0][1].text #通过下标访问
print root[0].tag, root[0].text
print "*"*10
for country in root.findall('country'): #找到root节点下的所有country节点
rank = country.find('rank').text #子节点下节点rank的值
name = country.get('name') #子节点下属性name的值
print name, rank
#修改xml文件
for country in root.findall('country'):
rank = int(country.find('rank').text)
if rank > 50:
root.remove(country)
tree.write('output.xml')
运行结果:
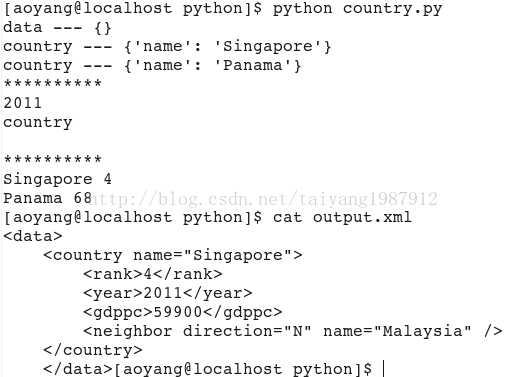
参考:https://docs.python.org/2/library/xml.etree.elementtree.html
2、xml.dom.*
文件对象模型(Document Object Model,简称DOM),是W3C组织推荐的处理可扩展置标语言的标准编程接口。一个 DOM 的解析器在解析一个XML文档时,一次性读取整个文档,把文档中所有元素保存在内存中的一个树结构里,之后你可以利用DOM 提供的不同的函数来读取或修改文档的内容和结构,也可以把修改过的内容写入xml文件。python中用xml.dom.minidom来解析xml文件,例子如下:
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding=utf-8
from xml.dom.minidom import parse
import xml.dom.minidom
# 使用minidom解析器打开XML文档
DOMTree = xml.dom.minidom.parse("country.xml")
Data = DOMTree.documentElement
if Data.hasAttribute("name"):
print "name element : %s" % Data.getAttribute("name")
# 在集合中获取所有国家
Countrys = Data.getElementsByTagName("country")
# 打印每个国家的详细信息
for Country in Countrys:
print "*****Country*****"
if Country.hasAttribute("name"):
print "name: %s" % Country.getAttribute("name")
rank = Country.getElementsByTagName('rank')[0]
print "rank: %s" % rank.childNodes[0].data
year = Country.getElementsByTagName('year')[0]
print "year: %s" % year.childNodes[0].data
gdppc = Country.getElementsByTagName('gdppc')[0]
print "gdppc: %s" % gdppc.childNodes[0].data
for neighbor in Country.getElementsByTagName("neighbor"):
print neighbor.tagName, ":", neighbor.getAttribute("name"), neighbor.getAttribute("direction")
运行结果:

参考:https://docs.python.org/2/library/xml.dom.html
3、xml.sax.*
SAX是一种基于事件驱动的API,利用SAX解析XML牵涉到两个部分:解析器和事件处理器。其中解析器负责读取XML文档,并向事件处理器发送事件,如元素开始跟元素结束事件;而事件处理器则负责对事件作出相应,对传递的XML数据进行处理。python中使用sax方式处理xml要先引入xml.sax中的parse函数,还有xml.sax.handler中的ContentHandler。常使用在如下的情况下:一、对大型文件进行处理;二、只需要文件的部分内容,或者只需从文件中得到特定信息;三、想建立自己的对象模型的时候。
ContentHandler类方法介绍
(1)characters(content)方法
调用时机:
从行开始,遇到标签之前,存在字符,content的值为这些字符串。
从一个标签,遇到下一个标签之前, 存在字符,content的值为这些字符串。
从一个标签,遇到行结束符之前,存在字符,content的值为这些字符串。
标签可以是开始标签,也可以是结束标签。
(2)startDocument()方法
文档启动的时候调用。
(3)endDocument()方法
解析器到达文档结尾时调用。
(4)startElement(name, attrs)方法
遇到XML开始标签时调用,name是标签的名字,attrs是标签的属性值字典。
(5)endElement(name)方法
遇到XML结束标签时调用。
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
#coding=utf-8
#!/usr/bin/python
import xml.sax
class CountryHandler(xml.sax.ContentHandler):
def __init__(self):
self.CurrentData = ""
self.rank = ""
self.year = ""
self.gdppc = ""
self.neighborname = ""
self.neighbordirection = ""
# 元素开始事件处理
def startElement(self, tag, attributes):
self.CurrentData = tag
if tag == "country":
print "*****Country*****"
name = attributes["name"]
print "name:", name
elif tag == "neighbor":
name = attributes["name"]
direction = attributes["direction"]
print name, "->", direction
# 元素结束事件处理
def endElement(self, tag):
if self.CurrentData == "rank":
print "rank:", self.rank
elif self.CurrentData == "year":
print "year:", self.year
elif self.CurrentData == "gdppc":
print "gdppc:", self.gdppc
self.CurrentData = ""
# 内容事件处理
def characters(self, content):
if self.CurrentData == "rank":
self.rank = content
elif self.CurrentData == "year":
self.year = content
elif self.CurrentData == "gdppc":
self.gdppc = content
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建一个 XMLReader
parser = xml.sax.make_parser()
# turn off namepsaces
parser.setFeature(xml.sax.handler.feature_namespaces, 0)
# 重写 ContextHandler
Handler = CountryHandler()
parser.setContentHandler(Handler)
parser.parse("country.xml")
运行结果:

4、libxml2和lxml解析xml
libxml2是使用C语言开发的xml解析器,是一个基于MIT License的免费开源软件,多种编程语言都有基于它的实现,python中的libxml2模块有点小不足的是:xpathEval()接口不支持类似模板的用法,但不影响使用,因libxml2采用C语言开发的,因此在使用API接口的方式上难免会有点不适应。
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding=utf-8
import libxml2
doc = libxml2.parseFile("country.xml")
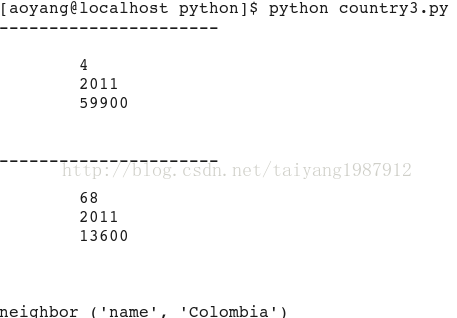
for book in doc.xpathEval('//country'):
if book.content != "":
print "----------------------"
print book.content
for node in doc.xpathEval("//country/neighbor[@name = 'Colombia']"):
print node.name, (node.properties.name, node.properties.content)
doc.freeDoc()
lxml是以libxml2为基础采用python语言开发的,从使用层面上说比lxml更适合python开发者,且xpath()接口支持类似模板的用法。
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding=utf-8
import lxml.etree
doc = lxml.etree.parse("country.xml")
for node in doc.xpath("//country/neighbor[@name = $name]", name = "Colombia"):
print node.tag, node.items()
for node in doc.xpath("//country[@name = $name]", name = "Singapore"):
print node.tag, node.items()

三、总结
(1)Python中XML解析可用的类库或模块有xml、libxml2 、lxml 、xpath等,需要深入了解的还需参考相应的文档。
(2)每一种解析方式都有自己的优点和缺点,选择前可以综合各个方面的性能考虑。
(3)若有不足,请留言,在此先感谢!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1426
1426
 52
52
 1328
1328
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1255
1255
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.




