基于wxpython开发的简单gui计算器实例
本文实例讲述了基于wxpython开发的简单gui计算器。分享给大家供大家参考。具体如下:
# wxCalc1 a simple GUI calculator using wxPython
# created with the Boa Constructor which generates all the GUI components
# all I had to do is add some code for each button click event
# Boa free from: http://boa-constructor.sourceforge.net/
# note that boa-constructor-0.3.1.win32.exe
# still uses wxPythonWIN32-2.4.2.4-Py23.exe
# but is expected to work with wxPython version 2.5 soon
# tested with Python23 vegaseat 26feb2005
from wxPython.wx import *
# some Boa generated global IDs ...
[wxID_WXFRAME1, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN0, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN1, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN2,
wxID_WXFRAME1BTN3, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN4, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN5, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN6,
wxID_WXFRAME1BTN7, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN8, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN9,
wxID_WXFRAME1BTNCLEAR, wxID_WXFRAME1BTNDIV, wxID_WXFRAME1BTNDOT,
wxID_WXFRAME1BTNEQUAL, wxID_WXFRAME1BTNMINUS, wxID_WXFRAME1BTNMULTI,
wxID_WXFRAME1BTNPLUS, wxID_WXFRAME1EDIT,
] = map(lambda _init_ctrls: wxNewId(), range(19))
class wxFrame1(wxFrame):
#startregion, below this marker is Boa generated code do not edit!!!
def _init_ctrls(self, prnt):
# generated method, don't edit
wxFrame.__init__(self, id=wxID_WXFRAME1, name='', parent=prnt,
pos=wxPoint(306, 270), size=wxSize(266, 265),
style=wxDEFAULT_FRAME_STYLE, title='Calculator1')
self.SetClientSize(wxSize(258, 225))
self.SetBackgroundColour(wxColour(0, 128, 0))
self.btn1 = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTN1, label='1', name='btn1',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(16, 136), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btn1, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN1, self.OnBtn1Button)
self.btn2 = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTN2, label='2', name='btn2',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(64, 136), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btn2, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN2, self.OnBtn2Button)
self.btn3 = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTN3, label='3', name='btn3',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(112, 136), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btn3, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN3, self.OnBtn3Button)
self.btn4 = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTN4, label='4', name='btn4',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(16, 96), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btn4, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN4, self.OnBtn4Button)
self.btn5 = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTN5, label='5', name='btn5',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(64, 96), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btn5, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN5, self.OnBtn5Button)
self.btn6 = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTN6, label='6', name='btn6',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(112, 96), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btn6, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN6, self.OnBtn6Button)
self.btn7 = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTN7, label='7', name='btn7',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(16, 56), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btn7, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN7, self.OnBtn7Button)
self.btn8 = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTN8, label='8', name='btn8',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(64, 56), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btn8, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN8, self.OnBtn8Button)
self.btn9 = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTN9, label='9', name='btn9',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(112, 56), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btn9, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN9, self.OnBtn9Button)
self.btn0 = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTN0, label='0', name='btn0',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(16, 176), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btn0, wxID_WXFRAME1BTN0, self.OnBtn0Button)
self.btnDot = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTNDOT, label='.', name='btnDot',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(64, 176), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btnDot, wxID_WXFRAME1BTNDOT, self.OnBtnDotButton)
self.btnEqual = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTNEQUAL, label='=',
name='btnEqual', parent=self, pos=wxPoint(112, 176),
size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btnEqual, wxID_WXFRAME1BTNEQUAL, self.OnBtnEqualButton)
self.edit = wxTextCtrl(id=wxID_WXFRAME1EDIT, name='edit', parent=self,
pos=wxPoint(16, 16), size=wxSize(224, 24), style=0, value='')
self.btnPlus = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTNPLUS, label='+',
name='btnPlus', parent=self, pos=wxPoint(160, 56), size=wxSize(32,
32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btnPlus, wxID_WXFRAME1BTNPLUS, self.OnBtnPlusButton)
self.btnMinus = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTNMINUS, label='-',
name='btnMinus', parent=self, pos=wxPoint(160, 96),
size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btnMinus, wxID_WXFRAME1BTNMINUS, self.OnBtnMinusButton)
self.btnMulti = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTNMULTI, label='*',
name='btnMulti', parent=self, pos=wxPoint(160, 136),
size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btnMulti, wxID_WXFRAME1BTNMULTI, self.OnBtnMultiButton)
self.btnDiv = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTNDIV, label='/', name='btnDiv',
parent=self, pos=wxPoint(160, 176), size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
EVT_BUTTON(self.btnDiv, wxID_WXFRAME1BTNDIV, self.OnBtnDivButton)
self.btnClear = wxButton(id=wxID_WXFRAME1BTNCLEAR, label='C',
name='btnClear', parent=self, pos=wxPoint(208, 56),
size=wxSize(32, 32), style=0)
self.btnClear.SetToolTipString('btnClear')
EVT_BUTTON(self.btnClear, wxID_WXFRAME1BTNCLEAR, self.OnBtnClearButton)
def __init__(self, parent):
self._init_ctrls(parent)
#endregion, above this marker is Boa generated code, do not edit!!!
# now respond to all the button click events ...
def OnBtn0Button(self, event):
val = '0'
# get existing edit box text
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
# append text
txt = txt + val
# update edit box text
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtn1Button(self, event):
val = '1'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtn2Button(self, event):
val = '2'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtn3Button(self, event):
val = '3'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtn4Button(self, event):
val = '4'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtn5Button(self, event):
val = '5'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtn6Button(self, event):
val = '6'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtn7Button(self, event):
val = '7'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtn8Button(self, event):
val = '8'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtn9Button(self, event):
val = '9'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtnDotButton(self, event):
val = '.'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtnEqualButton(self, event):
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
# needs to contain a float so eg. 3/5 is 3/5.0
# otherwise division 3/5 would result in zero
if '/' in txt:
if '.' not in txt:
txt = txt + '.0'
# now evaluate the math string
txt = repr(eval(txt))
# and show result in edit box
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtnPlusButton(self, event):
val = '+'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtnMinusButton(self, event):
val = '-'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtnMultiButton(self, event):
val = '*'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtnDivButton(self, event):
val = '/'
txt = self.edit.GetValue()
txt = txt + val
self.edit.SetValue(txt)
def OnBtnClearButton(self, event):
self.edit.SetValue('')
# -------------------- end of class wxFrame1 ----------------------
def create(parent):
return wxFrame1(parent)
class BoaApp(wxApp):
def OnInit(self):
wxInitAllImageHandlers()
self.main = create(None)
self.main.Show()
self.SetTopWindow(self.main)
return True
def main():
application = BoaApp(0)
application.MainLoop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
希望本文所述对大家的Python程序设计有所帮助。

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use ttkbootstrap to create a beautiful interface for Python GUI?
May 07, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
How to use ttkbootstrap to create a beautiful interface for Python GUI?
May 07, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
These two pictures are screenshots of the display renderings provided on the official website: theme switching is a simple theme switching. Since there are few components on the current window, the effect is not obvious, but it will look good when there are many components in the layout. importttkbootstrapasttkfromttkbootstrap.constantsimport*root=ttk.Window()style=ttk.Style()theme_names=style.theme_names()#Return multiple theme names in the form of a list theme_selection=ttk.Frame(root,padding=(10,10
 What key is ac on the calculator?
Feb 24, 2023 am 10:19 AM
What key is ac on the calculator?
Feb 24, 2023 am 10:19 AM
The ac key on the calculator is the "all clear" key. The full English name of ac is "All Clear", which means "all clear key"; pressing the ac key means clearing the values in all registers; during number input, the first press Pressing the ac key will clear all values except the memory contents.
 Python text terminal GUI framework, so cool
Apr 12, 2023 pm 12:52 PM
Python text terminal GUI framework, so cool
Apr 12, 2023 pm 12:52 PM
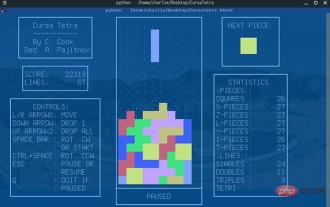
Curses The first one to appear is Curses[1]. CurseCurses is a dynamic library that provides text-based terminal window functionality. It can: Create and manage a window using the entire screen Use 8 different colors Provide mouse support for programs Use function keys on the keyboard Curses can be used in any ANSI/POSIX-compliant Runs on standard Unix/Linux systems. It can also run on Windows, but you need to install the windows-curses library additionally: pip install windows-curses. The picture above was written by a buddy using Curses. Russia
 What is e in the calculator
Oct 19, 2022 am 11:23 AM
What is e in the calculator
Oct 19, 2022 am 11:23 AM
The e in the calculator represents the power of 10, which means the exponent with base 10. For example, 1.99714E13 is equal to 19971400000000; expressing a number in the form of a multiplied by the nth power of 10 is called scientific notation. Notation: When we want to mark or operate something larger or smaller with a large number of digits, we can use scientific notation to avoid wasting a lot of space and time.
 Python tips can still implement graphical interface without using Gui
Apr 12, 2023 pm 04:43 PM
Python tips can still implement graphical interface without using Gui
Apr 12, 2023 pm 04:43 PM
If there is anything that programmers are afraid of, then I think it might be that the needs have changed again! No, after the author developed a browser-based Web application, the customer said: The program needs to be internal (no) internal (network) ) environment... This means that the Python environment cannot be installed! Who calls us programmers? Why don't we just develop a GUI version? It's not a problem for me... But after hearing the time given, I couldn't calm down... ...In order not to affect the customer's evaluation, we can only give one week! Although it is not difficult to conceive the GUI, it needs to sort out the service and the interactive interface with the user. If not, you will have to write a separate interface for the GUI, which is obviously not enough time. ah. No, let’s think of another way...otherwise we can just use the Web
 Who said writing GUI programs in Python is ugly? That's because you don't know how to beautify it!
Apr 11, 2023 pm 01:52 PM
Who said writing GUI programs in Python is ugly? That's because you don't know how to beautify it!
Apr 11, 2023 pm 01:52 PM
In our daily work and study, we often write some simple Python GUI tools to complete various automated tasks, such as batch processing of files, batch processing of pictures, etc. When we write these tools, we often only focus on the implementation of functions and ignore the beautification of the page. This also makes the GUI programs built in Python relatively low in people's eyes. Today we will ignore the functions first. , focusing on page beautification, let’s see how beautiful GUI programs written in pure Python can be! Page Layout We first complete a basic GUI layout. Suppose we want to make a hexadecimal conversion tool, then the general layout is as follows: The above picture is
 How to use Python GUI layout tool Tkinter
May 09, 2023 pm 02:16 PM
How to use Python GUI layout tool Tkinter
May 09, 2023 pm 02:16 PM
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Graphical User Interface (GUI) is nothing but a desktop application that helps us interact with the computer. A GUI application like a text editor can create, read, update, and delete a number of different types of files. Applications such as Solitaire, Chess, and Solitaire are game versions of GUI programs, and GUI applications such as Google Chrome, Firefox, and Microsoft Edge are used to browse the Internet. These are some of the different types of GUIs we use on our computers every day. Application, in fact, we can also build simple similar applications through Tkinter. Today, as an introduction to GUI, we will create a very simple
 How to implement Frame switching in Python Tkinter GUI programming
May 11, 2023 pm 04:25 PM
How to implement Frame switching in Python Tkinter GUI programming
May 11, 2023 pm 04:25 PM
1. Introduction to the tkraise() method of Frame Usually, a Tkinter application consists of multiple Frames. And you often need to switch between Frames to display the Frame relevant to the user's selection. Tkinter allows stacking Frames on top of each other. To display a specific Frame, just place one on top of another in stacking order. The top Frame will be visible. To put the Frame on top, you can use the tkraise() method of the Frame widget, as shown below: frame.tkraise() 2. tkraise usage example The following will implement a small temperature conversion application, using two for Fahrenheit and Celsius. Different frames






