Detailed explanation of the use of angular's scopel directive
This time I will bring you a detailed explanation of the use of angular's scopel instruction. What are the precautions for using angular's scopel instruction? The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
Let’s create a custom directive
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.primary{ background: red;
} </style></head><body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="mainCtrl">
<my-btn></my-btn>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
myApp.controller('mainCtrl',['$scope',function($scope){
$scope.myClass = 'primary';
}]);
myApp.directive('myBtn',function(){ return {
template:'<input type="button" value="按钮" class="{{myClass}}">'
}
}); </script></body></html>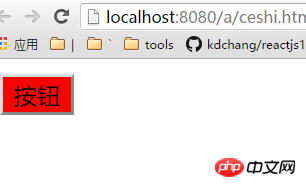
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.primary{ background: red;
} </style></head><body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="mainCtrl">
<my-btn></my-btn>
<my-btn></my-btn>
<my-btn></my-btn>
<my-btn></my-btn>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
myApp.controller('mainCtrl',['$scope',function($scope){
$scope.myClass = 'primary';
}]);
myApp.directive('myBtn',function(){ return {
template:'<input type="button" value="按钮" class="{{myClass}}">'
}
}); </script></body></html> ##One idea is to put these custom command buttons in different controllers, and then pass different values through the $scope context in the controller:
##One idea is to put these custom command buttons in different controllers, and then pass different values through the $scope context in the controller:
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.primary{ background: red;
} .success{ background: green;
} .default{ background: gray;
} </style></head><body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="aCtrl">
<my-btn></my-btn>
</div>
<div ng-controller="bCtrl">
<my-btn></my-btn>
</div>
<div ng-controller="cCtrl">
<my-btn></my-btn>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
myApp.controller('aCtrl',['$scope',function($scope){
$scope.myClass = 'primary';
}]);
myApp.controller('bCtrl',['$scope',function($scope){
$scope.myClass = 'success';
}]);
myApp.controller('cCtrl',['$scope',function($scope){
$scope.myClass = 'default';
}]);
myApp.directive('myBtn',function(){ return {
template:'<input type="button" value="按钮" class="{{myClass}}">'
}
}); </script></body></html> It’s too troublesome to write like this, so our angular provides a configuration item called scope for our custom instructions, so we can write it like this:
It’s too troublesome to write like this, so our angular provides a configuration item called scope for our custom instructions, so we can write it like this:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.primary{ background: red;
} .success{ background: green;
} .default{ background: gray;
} </style></head><body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="Controller">
<my-btn b="className1"></my-btn>
<my-btn b="className2"></my-btn>
<my-btn b="className3"></my-btn>
</div>
<script ></script>
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
myApp
.controller('Controller', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.className1 = 'primary';
$scope.className2 = 'success';
$scope.className3 = 'default';
}])
.directive('myBtn',function(){ return {
scope:{
a:'=b'
},
template:'<input type="button" value="按钮" class="{{a}}">'
}
}); </script></body></html>To understand the above, just pay attention to two points:
The a in the independent scope here represents the model a in the template
=b represents that Angular needs to find the view. The attribute b of the current directive
The value of attribute b needs to be found in the external scope
If you want to bind the name of the model in the directive scope and the attributes when used externally The names are the same and can be written as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.primary{ background: red;
} .success{ background: green;
} .default{ background: gray;
} </style></head><body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="Controller">
<my-btn a="className1"></my-btn>
<my-btn a="className2"></my-btn>
<my-btn a="className3"></my-btn>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
myApp
.controller('Controller', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.className1 = 'primary';
$scope.className2 = 'success';
$scope.className3 = 'default';
}])
.directive('myBtn',function(){ return {
scope:{
a:'='
},
template:'<input type="button" value="按钮" class="{{a}}">'
}
}); </script></body></html>Of course, the = sign above is two-way data binding:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.primary{ background: red;
} .success{ background: green;
} .default{ background: gray;
} </style></head><body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="Controller">
<my-btn a="abc"></my-btn>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
myApp
.controller('Controller', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.abc = '我是初始内容';
}])
.directive('myBtn',function(){ return {
scope:{
a:'='
},
template:'<input type="text" ng-model="a"><span>{{a}}</span>'
}
}); </script></body></html>If you only want one-way data communication, you can use the @ symbol:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.primary{ background: red;
} .success{ background: red;
} .default{ background: red;
} </style></head><body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="Controller">
<my-btn a="primary"></my-btn>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
myApp
.controller('Controller', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.mm = 'primary';
}])
.directive('myBtn',function(){ return {
scope:{
a:'@'
},
template:'<input type="button" value="按钮" class="{{a}}">'
}
}); </script></body></html>If you want to use ng-class, you can do it:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.primary{ background: red;
} .success{ background: red;
} .default{ background: red;
} </style></head><body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="Controller">
<my-btn a="primary"></my-btn>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
myApp
.controller('Controller', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.mm = true;
}])
.directive('myBtn',function(){ return {
scope:{
a:'@'
},
template:'<input type="button" value="按钮" ng-class="{primary:a}">'
}
}); </script></body></html>Finally, there is a scope that can be set to refer to the external scope method
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.primary{ background: red;
} .success{ background: red;
} .default{ background: red;
} </style></head><body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="Controller">
<my-btn fn2="fn()"></my-btn>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
myApp
.controller('Controller', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.fn = function(){
alert(11);
}
}])
.directive('myBtn',function(){ return {
scope:{
fn1:'&fn2'
},
template:'<input type="button" value="按钮" ng-click="fn1()">'
}
}); </script></body></html>I believe you have read the case in this article You have mastered the method. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the php Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
Detailed explanation of the use of Angular MaterialWhat are the naming rules for id selectors in cssUnpopular method of centering elements horizontally and verticallyThe above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the use of angular's scopel directive. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Windows operating system is one of the most popular operating systems in the world, and its new version Win11 has attracted much attention. In the Win11 system, obtaining administrator rights is an important operation. Administrator rights allow users to perform more operations and settings on the system. This article will introduce in detail how to obtain administrator permissions in Win11 system and how to effectively manage permissions. In the Win11 system, administrator rights are divided into two types: local administrator and domain administrator. A local administrator has full administrative rights to the local computer
 Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++ In statistics, the mode refers to the value that appears most frequently in a set of data. In C++ language, we can find the mode in any set of data by writing a mode function. The mode function can be implemented in many different ways, two of the commonly used methods will be introduced in detail below. The first method is to use a hash table to count the number of occurrences of each number. First, we need to define a hash table with each number as the key and the number of occurrences as the value. Then, for a given data set, we run
 How to install Angular on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
How to install Angular on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
Angular.js is a freely accessible JavaScript platform for creating dynamic applications. It allows you to express various aspects of your application quickly and clearly by extending the syntax of HTML as a template language. Angular.js provides a range of tools to help you write, update and test your code. Additionally, it provides many features such as routing and form management. This guide will discuss how to install Angular on Ubuntu24. First, you need to install Node.js. Node.js is a JavaScript running environment based on the ChromeV8 engine that allows you to run JavaScript code on the server side. To be in Ub
 Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operation is a common and important mathematical operation, used to calculate the result of dividing two numbers. Division is often used in database queries, so understanding the division operation and its usage in OracleSQL is one of the essential skills for database developers. This article will discuss the relevant knowledge of division operations in OracleSQL in detail and provide specific code examples for readers' reference. 1. Division operation in OracleSQL
 Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of the remainder function in C++ In C++, the remainder operator (%) is used to calculate the remainder of the division of two numbers. It is a binary operator whose operands can be any integer type (including char, short, int, long, etc.) or a floating-point number type (such as float, double). The remainder operator returns a result with the same sign as the dividend. For example, for the remainder operation of integers, we can use the following code to implement: inta=10;intb=3;
 Angular components and their display properties: understanding non-block default values
Mar 15, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
Angular components and their display properties: understanding non-block default values
Mar 15, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
The default display behavior for components in the Angular framework is not for block-level elements. This design choice promotes encapsulation of component styles and encourages developers to consciously define how each component is displayed. By explicitly setting the CSS property display, the display of Angular components can be fully controlled to achieve the desired layout and responsiveness.
 Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Authentication is one of the most important parts of any web application. This tutorial discusses token-based authentication systems and how they differ from traditional login systems. By the end of this tutorial, you will see a fully working demo written in Angular and Node.js. Traditional Authentication Systems Before moving on to token-based authentication systems, let’s take a look at traditional authentication systems. The user provides their username and password in the login form and clicks Login. After making the request, authenticate the user on the backend by querying the database. If the request is valid, a session is created using the user information obtained from the database, and the session information is returned in the response header so that the session ID is stored in the browser. Provides access to applications subject to
 Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
The modulo operator (%) in PHP is used to obtain the remainder of the division of two numbers. In this article, we will discuss the role and usage of the modulo operator in detail, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand. 1. The role of the modulo operator In mathematics, when we divide an integer by another integer, we get a quotient and a remainder. For example, when we divide 10 by 3, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is 1. The modulo operator is used to obtain this remainder. 2. Usage of the modulo operator In PHP, use the % symbol to represent the modulus






