
1. 编程: 匿名对象与匿名类的实现过程
<?php
//匿名类
// PHP 7.0+ 才支持
// 类似于匿名函数,就是没有名称的类
// 匿名类适合于一次性的创建与引用,总是与 new 配套使用
class BadPerson
{
private $name = '西门庆';
public function story($name)
{
return $this->name.'喜欢上了:'.'<span style="color:red">'.$name.'</span>';
}
}
//有三种方式来访问 story()
//方式1.对象
$badperson = new BadPerson();
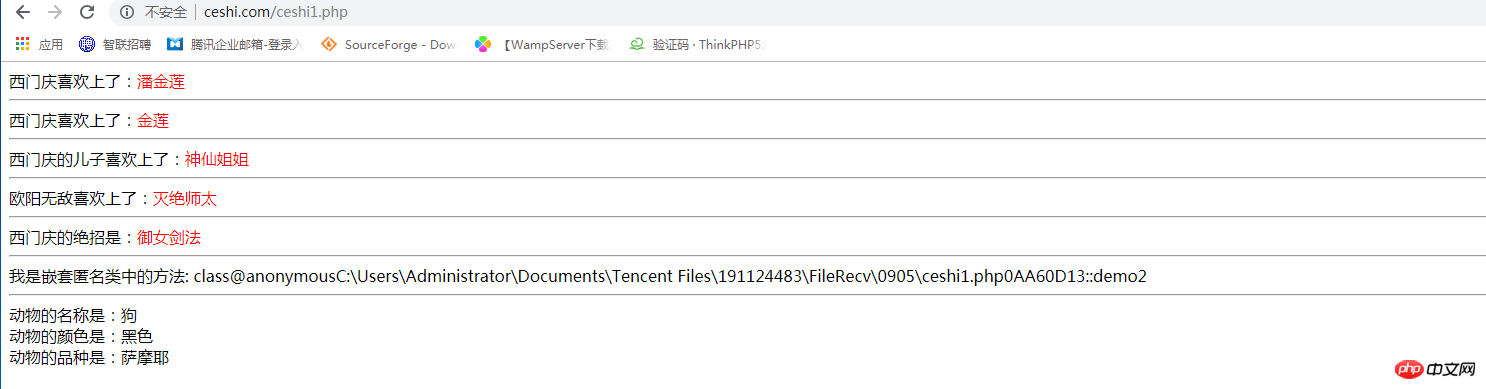
echo $badperson->story('潘金莲'), '<hr>';
//方式2:匿名对象
echo (new BadPerson())->story('金莲'), '<hr>';
//方式3:匿名类
echo (new class
{
private $name = '西门庆的儿子';
public function story($name)
{
return $this->name.'喜欢上了:'.'<span style="color:red">'.$name.'</span>';
}
})->story('神仙姐姐'), '<hr>';
//匿名类的三种应用场景
//场景1:匿名类中可以使用构造方法
echo (new class('欧阳无敌')
{
private $name;
//匿名类中的构造方法
public function __construct($name)
{
$this->name = $name;
}
public function story($name)
{
return $this->name.'喜欢上了:'.'<span style="color:red">'.$name.'</span>';
}
})->story('灭绝师太'), '<hr>';
//场景2:在匿名类汇中可以继承其他类中的成员
class KungFu
{
private $kill;//必杀技
public function __construct($art='')
{
$this->kill = $art;
}
public function show()
{
return $this->kill ?:'九阴白骨爪';
}
}
echo(new class('西门庆','御女剑法') extends KungFu //这里御女剑法也可以不写,为空的话会显示九阴白骨抓
{
private $name;
//匿名类中的构造方法
public function __construct($name,$art='')
{
parent::__construct($art);//继承了父类,所以必须对父类的$art进行引用
$this->name = $name;
}
public function story($name)
{
return $this->name.'喜欢上了:'.'<span style="color:red">'.$name.'</span>';
}
public function show()
{
return $this->name.'的绝招是:'.'<span style="color:red">'.parent::show().'</span>';
}
})->show(),'<hr>';
//场景3:可以在类声明中嵌套一个匿名类
class Animal //宿主类,父类的角色
{
public $name = '狗';
protected $color = '黑色';
private $type = '萨摩耶';
protected function info ()
{
return '市 场售价2000元';
}
public function demo1()
{
//宿主类中的私有成员不能在匿名类中直接使用
//可以通过在匿名类创建一个构造方法将宿主类中的私有成员进行注入
//将宿主类中的私有属性做为匿名类的构造方法的参数传入即可
return (new class ($this->type)extends Animal
{
//1.在匿名类中创建一个属性用来接收宿主类中的私有属性
private $type;
//2.创建一个构造方法
public function __construct($type)
{
$this->type = $type;
}
public function demo2()
{
return '我是嵌套匿名类中的方法: '. __METHOD__;
}
public function show()
{
return
'动物的名称是:'.$this->name.'<br>'.
'动物的颜色是:'.$this->color.'<br>'.
'动物的品 种是:'.$this->type.'<br>';
}
});
}
}
// 访问匿名类中的 demo2()
echo (new Animal())->demo1()->demo2();
echo '<hr>';
echo (new Animal())->demo1()->show();点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
2. 编程: Trait类的声明与工作原理
<?php
//trait 是什么?
//1.PHP 只能实现单继承,trait打破了限制
//2.trait 是代码复用机制(函数,类的继承)
//3.trait 使用类的语法,但不是类,所以不能实例化
//4.trait 相当于方法集
//trait 类位于 父类 与 子类 之间
//如果Person类不存在的情况下创建Person类
if (!class_exists('Person'))
{
class Person
{
protected $name;
public function __construct($name='小明')
{
$this->name = $name;
}
public function study($course='php')
{
return $this->name . '在学习: ' . $course;
}
}
}
//创建一个trait特性类
trait Course
{
public $student1 = '小华';
public function study($name='踢足球')
{
return $this->name.'在学习'.$name;
}
}
trait Recreation
{
public $student2 = '小军';
public function study($name='打篮球')
{
return $this->name.'在和'.$this->student2.$name;
}
}
//trait 类位于 Person 与 Student 之间
class Student extends Person
{
//use Course; 导入了一个trait 类
use Course,Recreation
{
Course::study insteadof Recreation;//A instead of B 则表示A代替B
Recreation::study as MYSport;
}
}
$student = new Student();
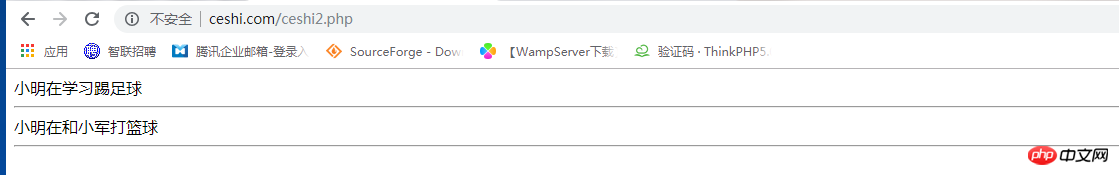
echo $student->study(),'<hr>';//小明在学习踢足球
echo $student->MYSport(),'<hr>';//小明在和小军打篮球点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
3. 编程: 类的自动加载函数的写法
<?php
//类的自动加载
//spl_autoload_register(); 将函数注册到SPL __autoload函数队列中。如果该队列中的函数尚未激活,则激活它们。
//成功时返回 TRUE, 或者在失败时返回 FALSE。
spl_autoload_register(function ($className)
{
require './class/'.$className.'.php';
//存在命名空间的情况下 需要这样操作
// $className = str_replace("\\","/", $className);
// require './class/'.$className.'.php';
});
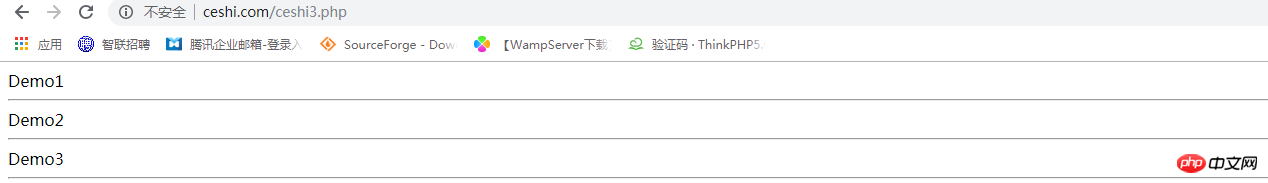
echo Demo1::CLASS_NAME, '<hr>';
echo Demo2::CLASS_NAME, '<hr>';
echo Demo3::CLASS_NAME, '<hr>';点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
4. 编程: 对象的序列化与反序列化的原理与应用
<?php
//对象的序列化与反序列化
//
//对象序列化的特点
//1.只保存对象中的属性,不保存方法
//2.只保存类名,不保存对象名
// serialize 产生一个可存储的值的表示
//unserialize 对单一的已序列化的变量进行操作,将其转换回 PHP 的值。
class Db
{
//连接参数与返回值
public $db = null;
public $host;
public $user;
public $pass;
//构造方法
public function __construct($host='127.0.0.1',$user='root',$pass='root')
{
$this->host = $host;
$this->user = $user;
$this->pass = $pass;
//确保实例化对象的时候能自动连接上数据库
$this->connect();
}
//数据库连接
private function connect()
{
$this->db = mysqli_connect($this->host,$this->user,$this->pass);
}
//对象序列化的时候调用
public function __sleep()
{
return ['host','user','pass'];
}
//反序列化
public function __wakeup()
{
$this->connect();
}
}
$obj = new Db();
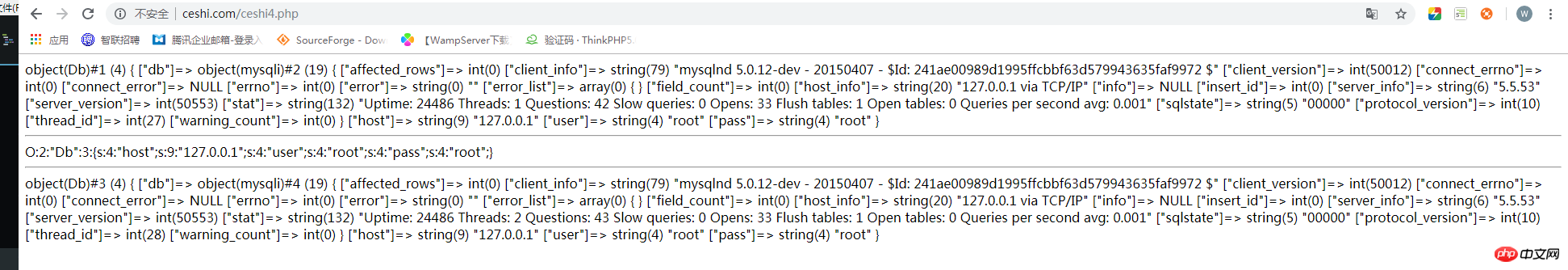
var_dump($obj);
echo '<hr>';
echo serialize($obj),'<hr>';
$tmp = serialize($obj);
var_dump(unserialize($tmp));点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
5. 问答:谈谈你对面向对象编程的基本理解(不少于200字)
面向对象的编程是以对象为中心的。所有的功能的实现都有自己的模板类,通过类的实例化进行扩展延伸,来实现各种各样的个性化功能。
记得老师上课讲过面向对象有三大特性,封装、继承和多态。
封装就是将一类事物的属性和行为抽象成一个类,使其属性私有化,行为公开化,提高了数据的隐秘性的同时,使代码模块化。这样做使得代码的复用性更高。
继承则是进一步将一类事物共有的属性和行为抽象成一个父类,而每一个子类是一个特殊的父类--有父类的行为和属性,也有自己特有的行为和属性。这样做扩展了已存在的代码块,进一步提高了代码的复用性。
如果说封装和继承是为了使代码重用,那么多态则是为了实现接口重用。多态的一大作用就是为了解耦--为了解除父子类继承的耦合度。多态就是允许父类引用(或接口)指向子类(或实现类)对象。很多的设计模式都是基于面向对象的多态性设计的。
总结一下,如果说封装和继承是面向对象的基础,那么多态则是面向对象最精髓的理论。掌握多态必先了解接口,只有充分理解接口才能更好的应用多态。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号