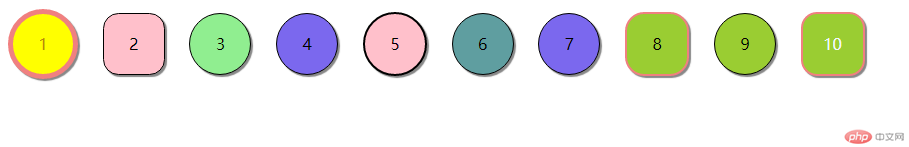
ID 选择器:#one { border-radius: 90%; } 选中的1号变为球型;
属性选择器:.three { background-color: lightgreen; border-radius: 90%; } 选中的3号变成球形并且颜色变成浅绿色;
群组选择器:.four, #seven { border-radius: 50%; background-color: mediumslateblue;} 同时选择4号和7号生成球型变成紫色;
属性选择器:li[id="five"] { border-radius: 40px; border: 2px solid;} 选中5号变成球型添加2px的黑色边框;
相邻选择器:#five+* { background-color: cadetblue; border-radius: 50%; } 与5号相邻的6号变成墨绿色4号不变色
兄弟选择器:#seven~* { background-color: yellowgreen;} 与7号后面同级的所有兄弟8,9,10号都变成黄绿色;
伪类选择器:根据位置和类型分成2种:
根据位置:
ul :first of child { border-radius: 40px; color: darkgoldenrod; background-color: yellow; }第一个li(1号球)颜色变成黄色
球型字体变成深黄色;
ul :last of child { background-color: lightseagreen;color: aliceblue; } 最后一个li(10号球)颜色变成黄色
球型字体变成深黄色
ul :nth-child(8) {border: 2px double lightcoral; border-radius: 30%; } 8号边框变成粉色
根据类型:
ul li:first-of-type {
border-radius: 40px;
color: darkgoldenrod;
background-color: yellow;
}
1号小球字体变黄,整体颜色变黄
ul li:last-of-type {
background-color: lightseagreen;
color: aliceblue;
}
最后一个10号小球 字体颜色变白,整体颜色变浅蓝
ul li:nth-of-type(9) {
background-color: lightslategray;
border-radius: 50%;
}
9号变成小球颜色变成浅灰
相邻选择器和兄弟选择器都可以选择后面的元素,但是相邻选择器之能选择相邻的一个元素,而兄弟选择器可以选择后面同级别的所有元素。
nth-of-child 和nth-of-type 可以选择相同的元素,但是它们的关注点不同,如果关注点在位置,用nth-of-child
如果既要关注位置还要关注类型 使用nth-of-type
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
/* 标签选择器 */
ul {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
ul li {
list-style: none;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background-color: pink;
border: 1px solid black;
/* 水平垂直 居中*/
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
/*将一个块级元素转为内联元素
内联元素是单行文本,多个元素在一行显示,
但是不支持宽高,而块级元素支持宽高却不再一行显示,
而内联块就是两者的综合*/
display: inline-block;
/* 加阴影
第一,二位表示左右 偏移量
第三位表示扩散范围
第四位表示颜色
*/
box-shadow: 2px 2px 1px #888;
border-radius: 25%;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
}
/* id 选择器 */
#one {
border-radius: 90%;
}
/* class 选择器 */
.three {
background-color: lightgreen;
border-radius: 90%;
}
/* 群组选择器 */
.four,
#seven {
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: mediumslateblue;
}
/* 属性选择器 */
li[id="five"] {
border-radius: 40px;
border: 2px solid;
}
/* 相邻选择器 */
#five+* {
background-color: cadetblue;
border-radius: 50%;
}
/* 兄弟选择器 */
#seven~* {
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
/* 伪类选择器 根据位置和类型来选择*/
/* 根据位置来选择 */
ul :first-child {
border: 5px solid lightcoral;
}
ul :last-child {
border: 2px double lightcoral;
}
ul :nth-child(8) {
border: 2px double lightcoral;
border-radius: 30%;
}
/* 根据类型来选择 */
ul li:first-of-type {
border-radius: 40px;
color: darkgoldenrod;
background-color: yellow;
}
ul li:last-of-type {
background-color: lightseagreen;
color: aliceblue;
}
ul li:nth-of-type(9) {
background-color: lightslategray;
border-radius: 50%;
}
</style>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li id="one">1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li class="three">3</li>
<li class="four">4</li>
<li id="five">5</li>
<li>6</li>
<li id="seven">7</li>
<li>8</li>
<li>9</li>
<li>10</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
1padding 对盒子大小的影响与解决
![]()
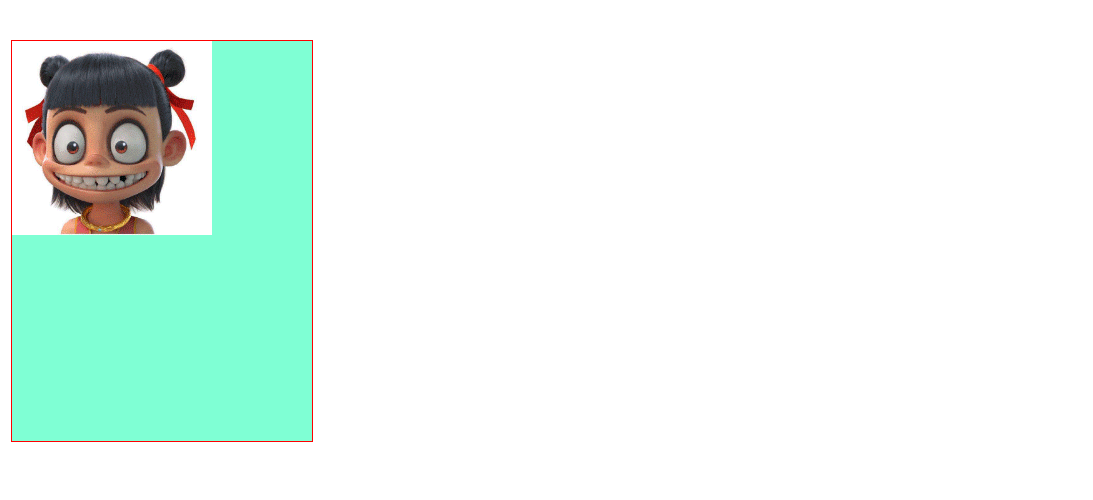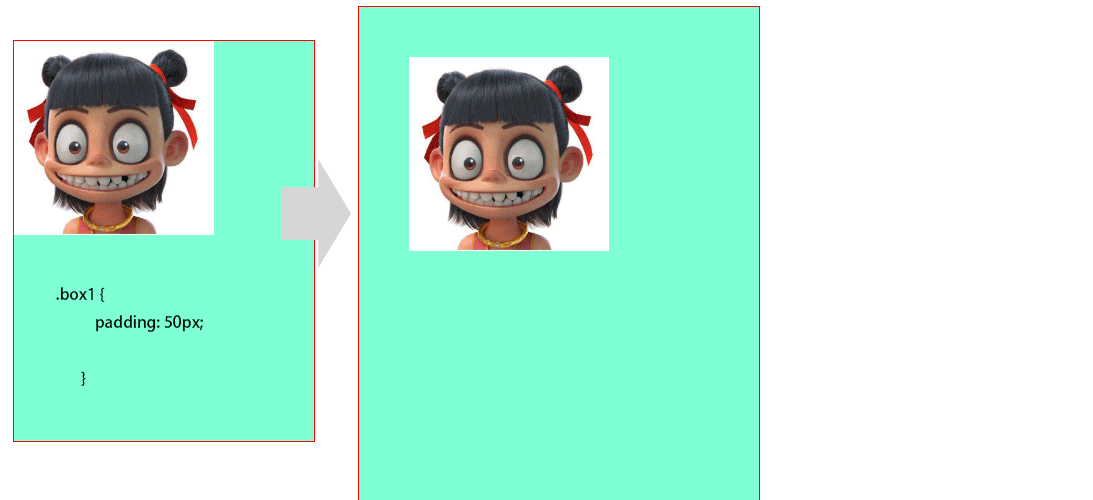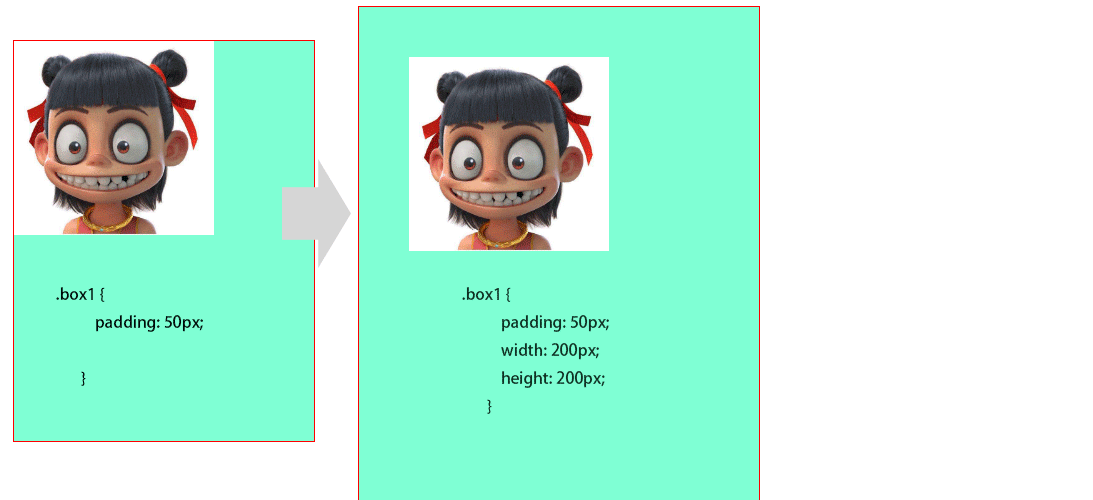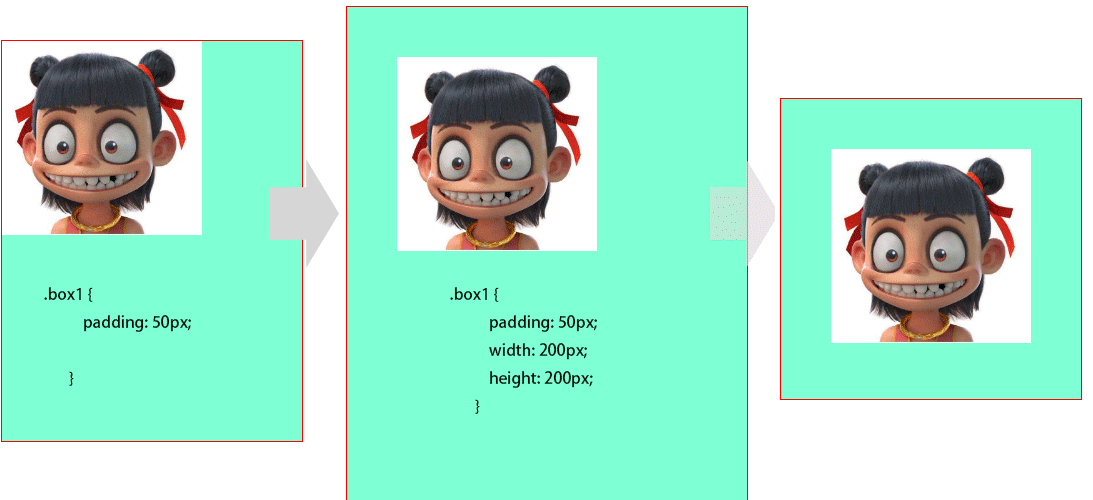
![]()
在盒子上添加padding50px后盒子会被撑开,需要再重新设置box的高度和宽度,这样才能使图片居中显示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
.box1,
.box2,
.box3 {
width: 300px;
height: 400px;
background-color: aquamarine;
border: 1px solid red;
margin: 20px;
}
.box1 {
padding: 50px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}
/* .box2 {} */
</style>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<img src="images/2.jpeg" width="200" alt="">
</div>
<!-- <div class="box2">
<img src="images/1.jpeg" width="200" alt="">
</div>
<div class="box3">
<img src="images/3.jpeg" width="200" alt="">
</div> -->
</body>
</html>;点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
2.padding 对盒子大小的影响与解决

宽度分离:在盒子(box2)的外面再增加一个父级(wrap),设置父级的宽度,在box2上使用padding
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
/* .box1, */
.box2,
.box3 {
/* width: 400px; */
background-color: aquamarine;
border: 1px solid red;
}
/* .box1 {
padding: 50px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
} */
/* 高度分离 */
.wrap {
width: 400px;
}
.box2 {
padding: 50px;
}
/* .box3 {
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 50px;
width: 400px;
} */
</style>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <div class="box1">
<img src="images/2.jpeg" width="200" alt="">
</div> -->
<div class="wrap">
<div class="box2">
<img src="images/1.jpeg" width="300" alt="">
</div>
</div>
<!-- <div class="box3">
<img src="images/3.jpeg" width="300" alt="">
</div> -->
</body>
</html>;点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
box-sizing
作用于边框上 border-box包含了margin+padding

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
/* .box1, */
.box2,
.box3 {
/* width: 400px; */
background-color: aquamarine;
border: 1px solid red;
}
/* .box1 {
padding: 50px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
} */
/* 高度分离 */
/*
.wrap {
width: 400px;
}
.box2 {
padding: 50px;
} */
.box3 {
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 50px;
width: 400px;
}
</style>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <div class="box1">
<img src="images/2.jpeg" width="200" alt="">
</div> -->
<!-- <div class="wrap">
<div class="box2">
<img src="images/1.jpeg" width="300" alt="">
</div>
</div> -->
<div class="box3">
<img src="images/3.jpeg" width="300" alt="">
</div>
</body>
</html>;点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
margin中的同级塌陷, 嵌套传递与自动挤压
同级塌陷:两个相邻的元素之间的外边距会相互塌陷,塌陷后的间距等于两个元素外边距较大的一个(不受浮动影响)
只作用于垂直方向,
解决的办法就是按照需要的边距进行一方的设置。

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
.box1 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lawngreen;
text-align: center;
line-height: 200px;
opacity: 0.5;
margin-bottom: 40px;
}
.box2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightseagreen;
text-align: center;
line-height: 200px;
opacity: 0.5;
margin-top: 80px;
}
</style>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">box1</div>
<div class="box2">box2</div>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
嵌套传递:当子元素外面有个父元素时,父元素没有margin padding 等边距设定时,子元素如果设置边距就会传递给父元素是父元素的边框也会被撑开(父元素不能浮动)。
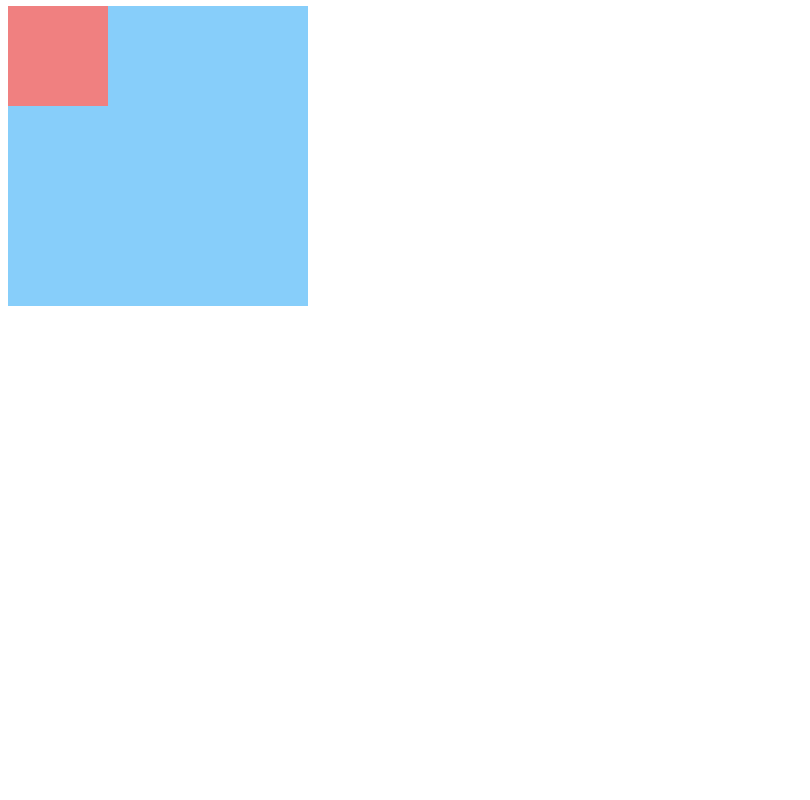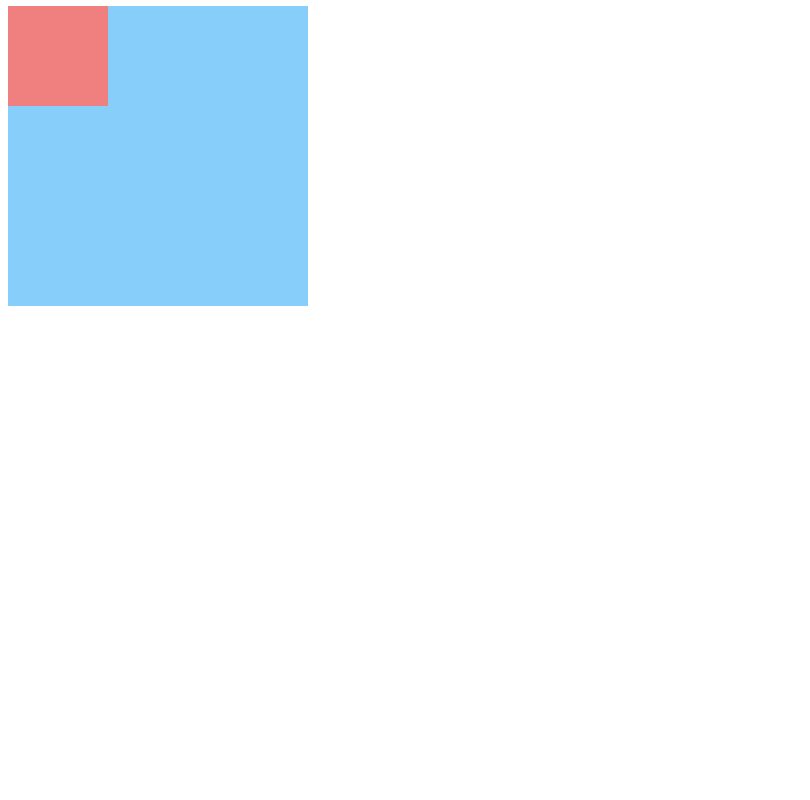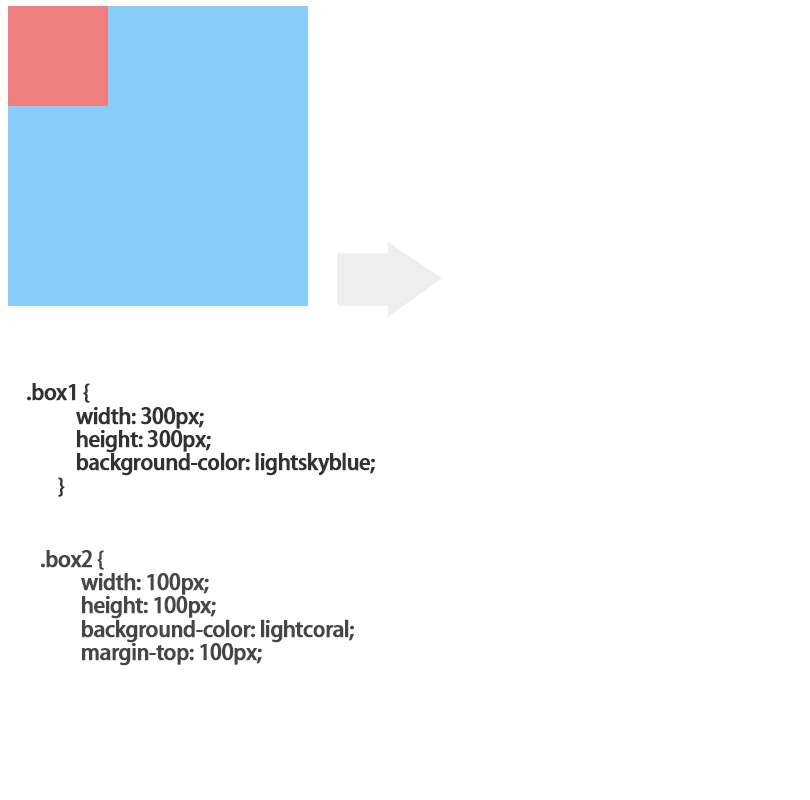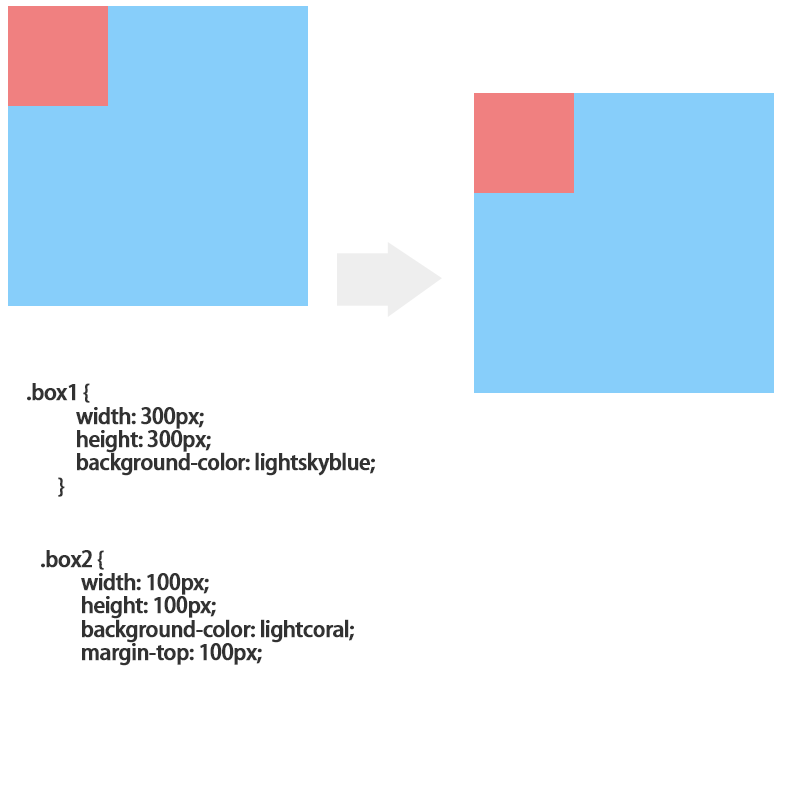
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
.box1 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightskyblue;
}
/* .box1 {
padding-top: 100px;
height: 200px;
} */
.box2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightcoral;
margin-top: 100px;
}
</style>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
解决的办法1.父元素设置padding;
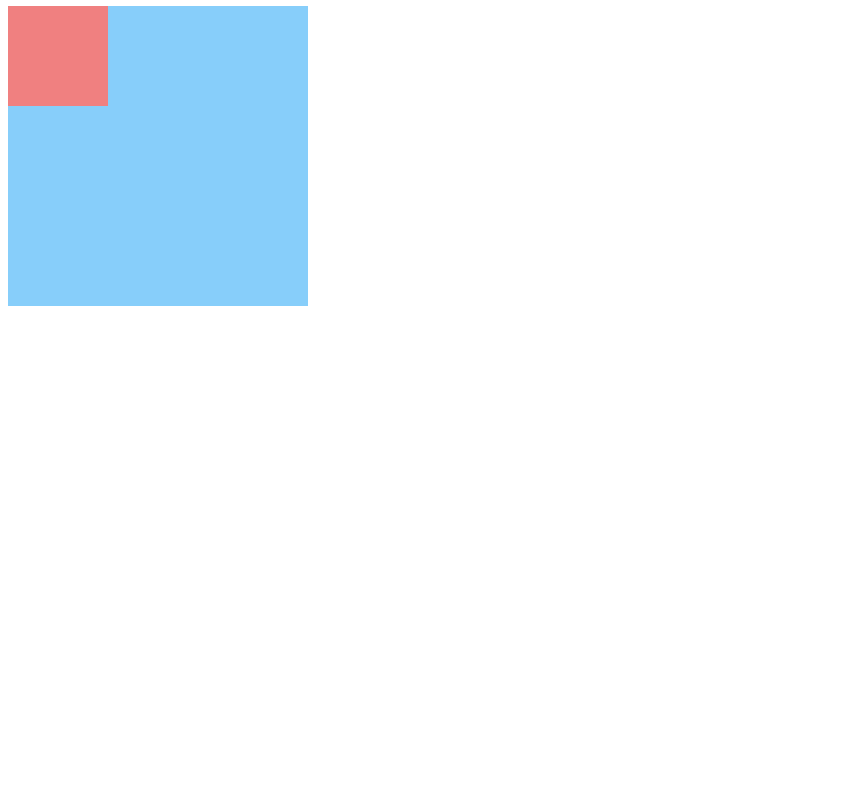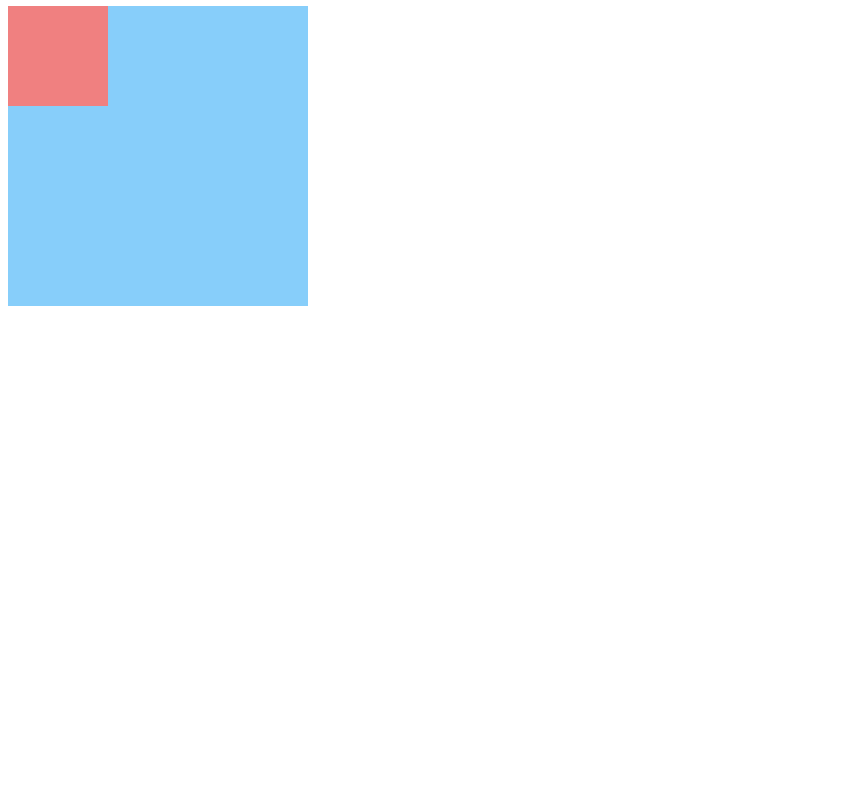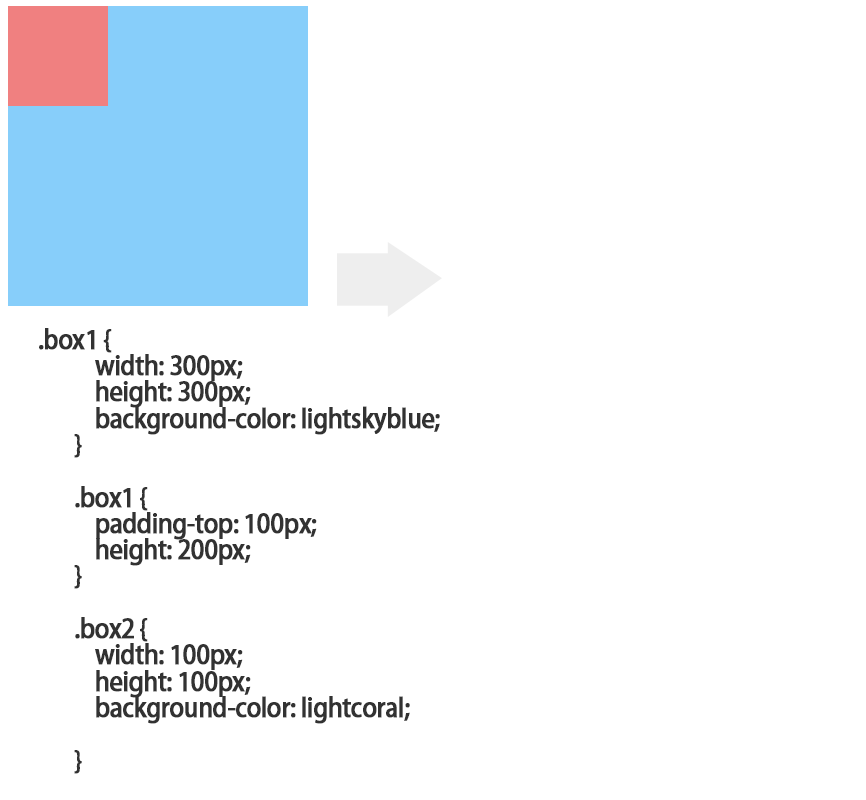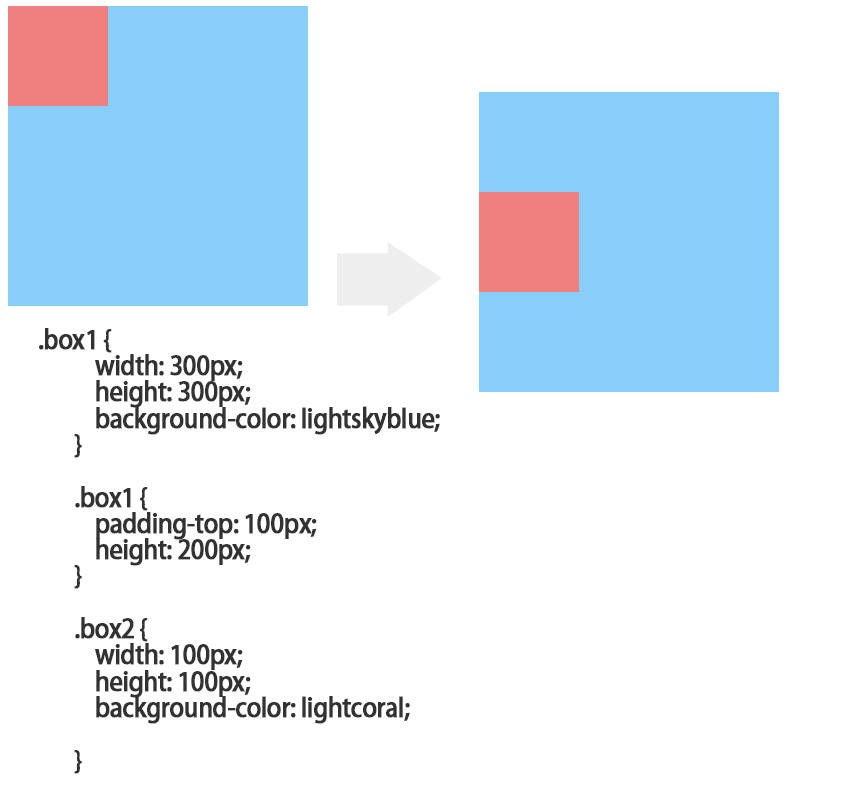
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
.box1 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightskyblue;
}
.box1 {
padding-top: 100px;
height: 200px;
}
.box2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightcoral;
/* margin-top: 100px; */
}
</style>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
2.box-sizing:border-box;
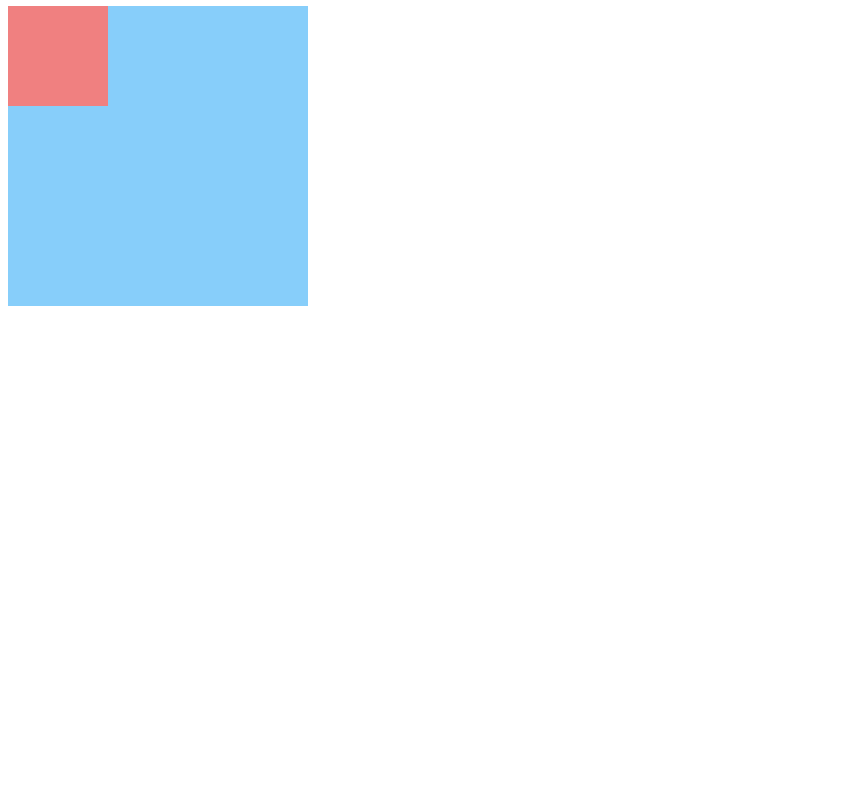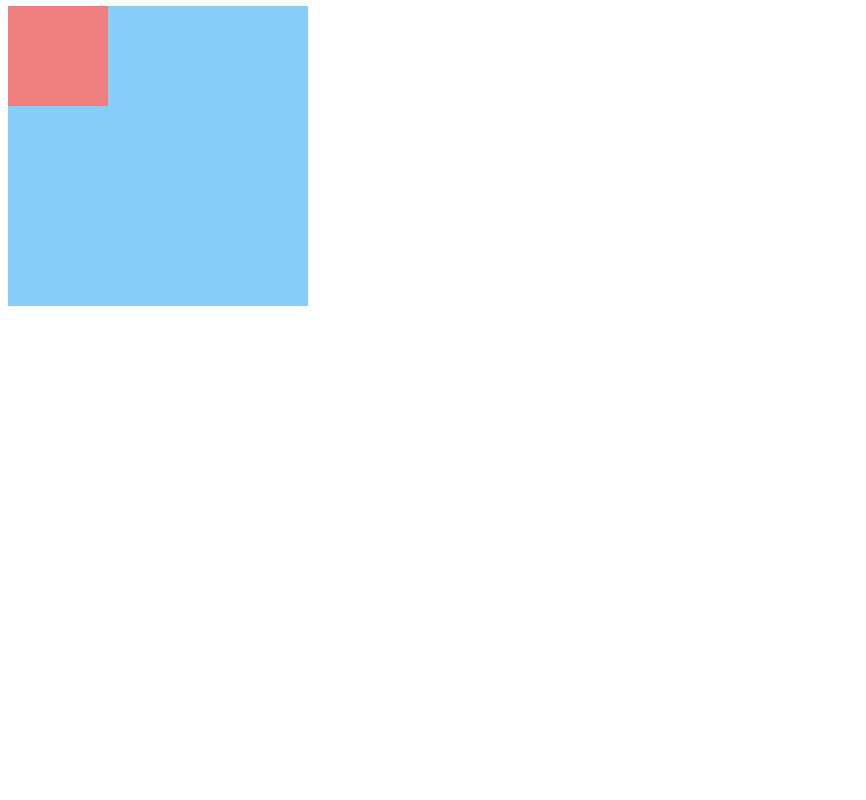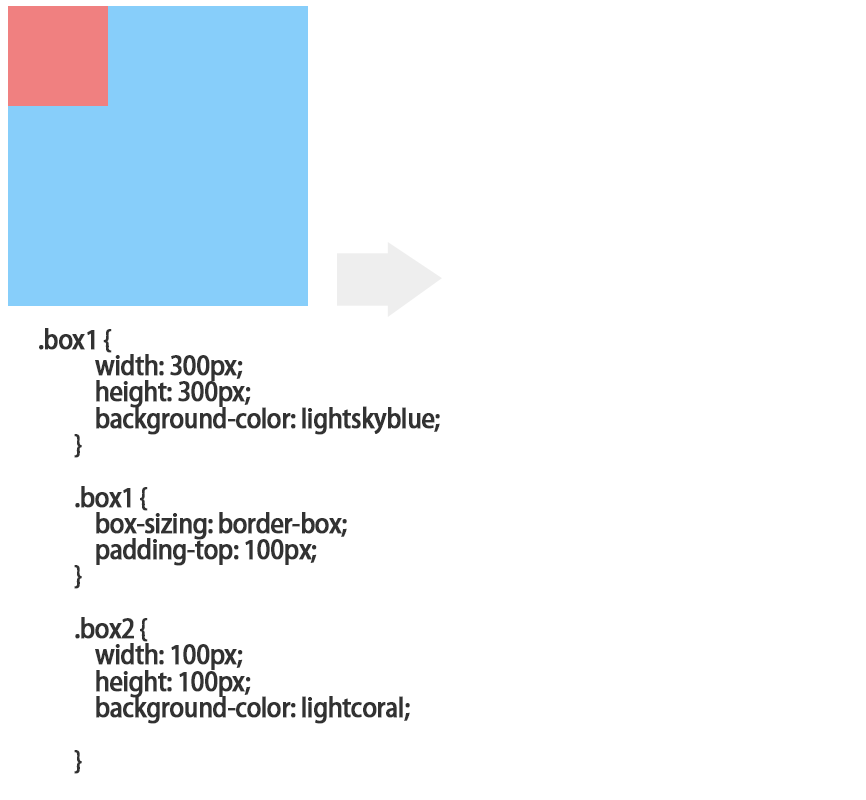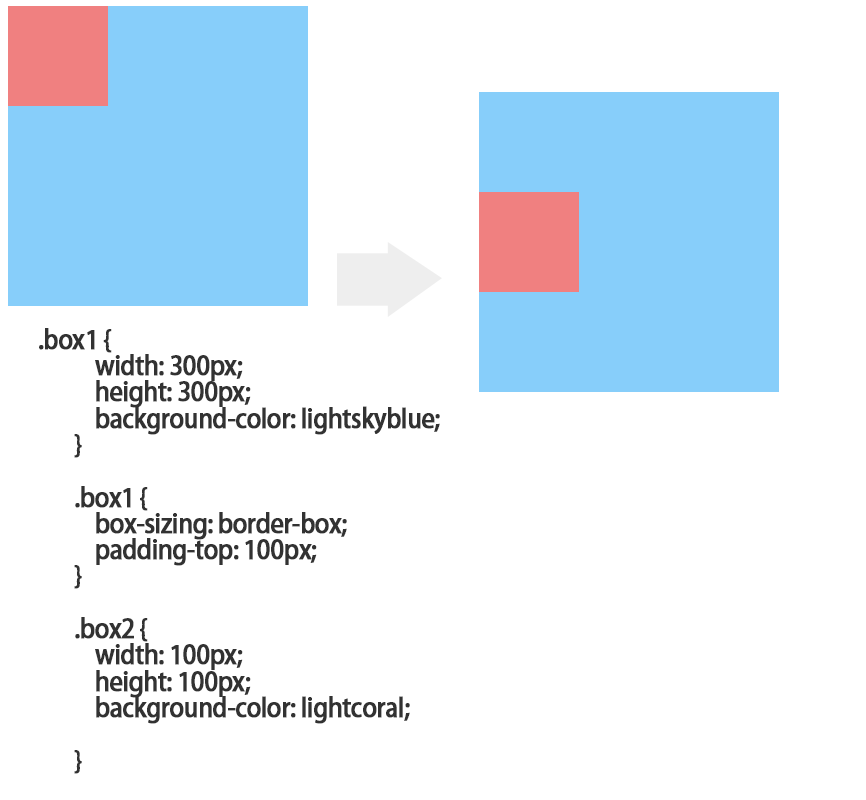
3,父级设置overflow:hidden
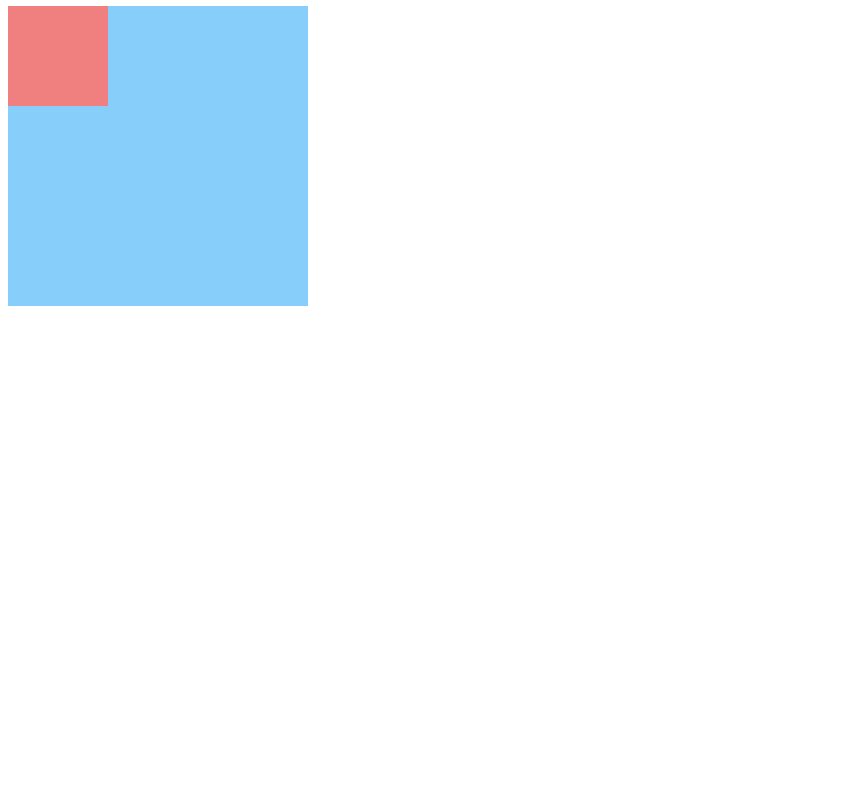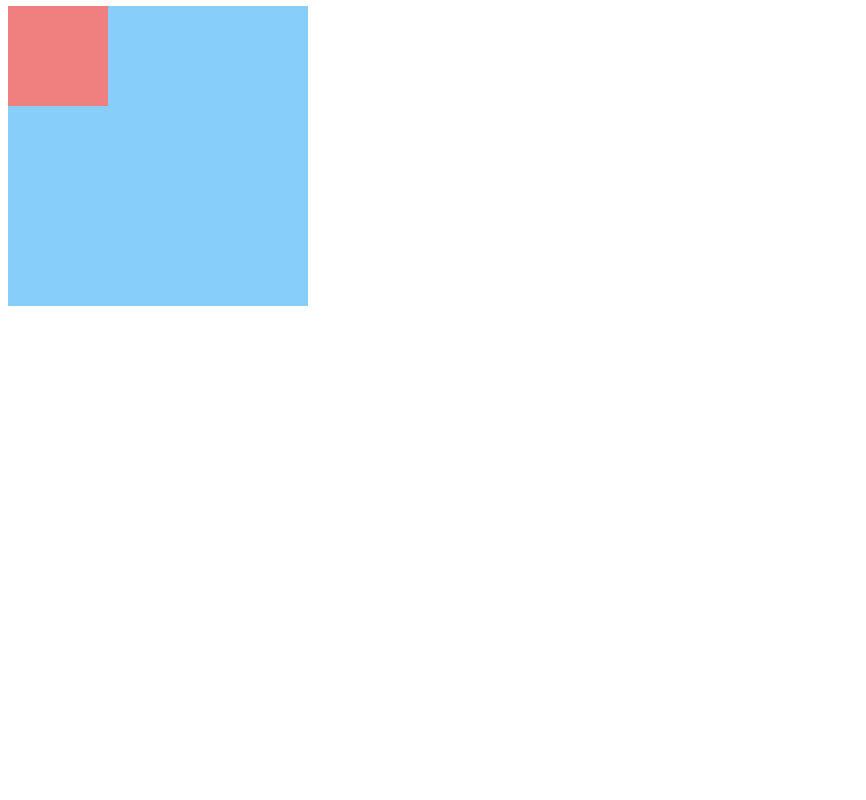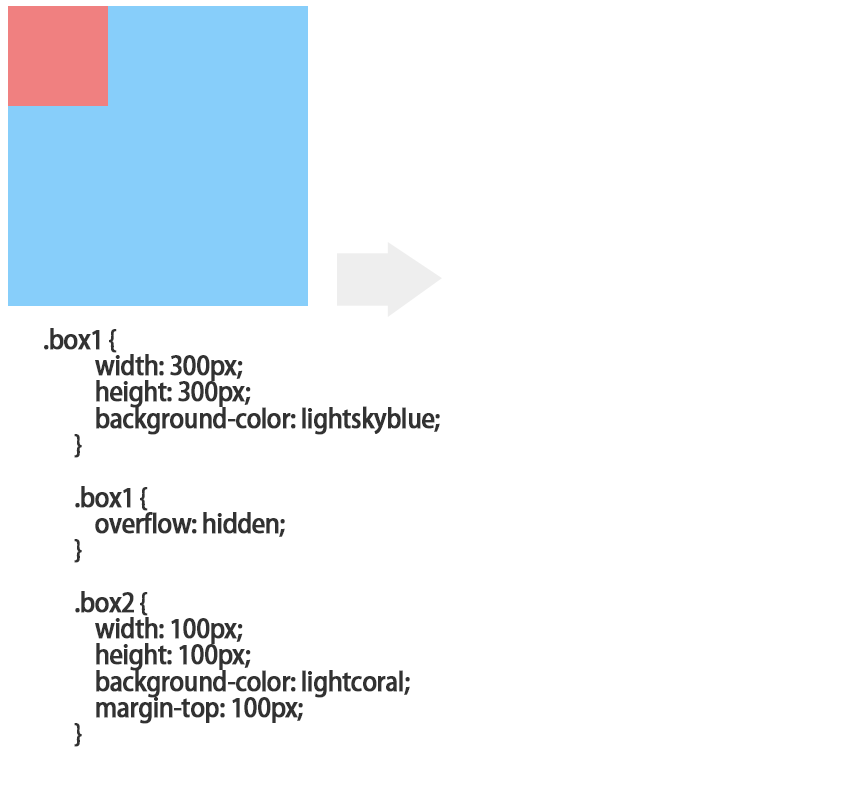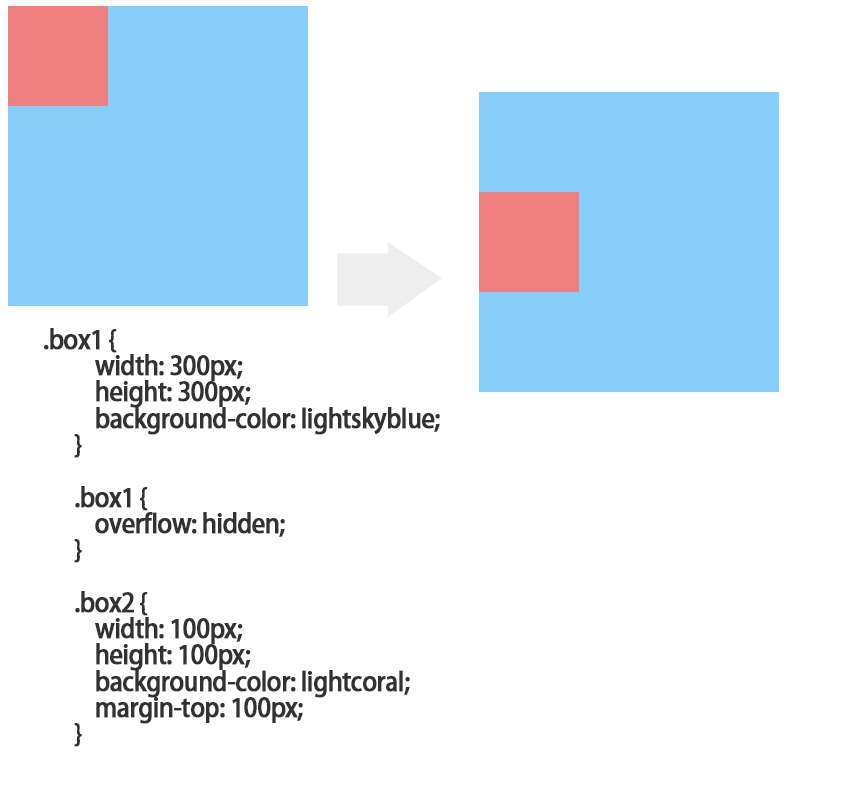
4、float:left/right;
5、display:inline-block;
6、父级加决对定位position:absolute;
自动挤压:常用在布局中,设置margin:0 atuto;左右两边的外边距自动挤压,如果设置了宽度那就会根据宽度变化;
如果想在整个页面居中 就要设置上下的高度的具体值,因为块级元素的高度默认是内容高度,与父级元素没有直接关系,
垂直方向的auto被重置为0;
![]()
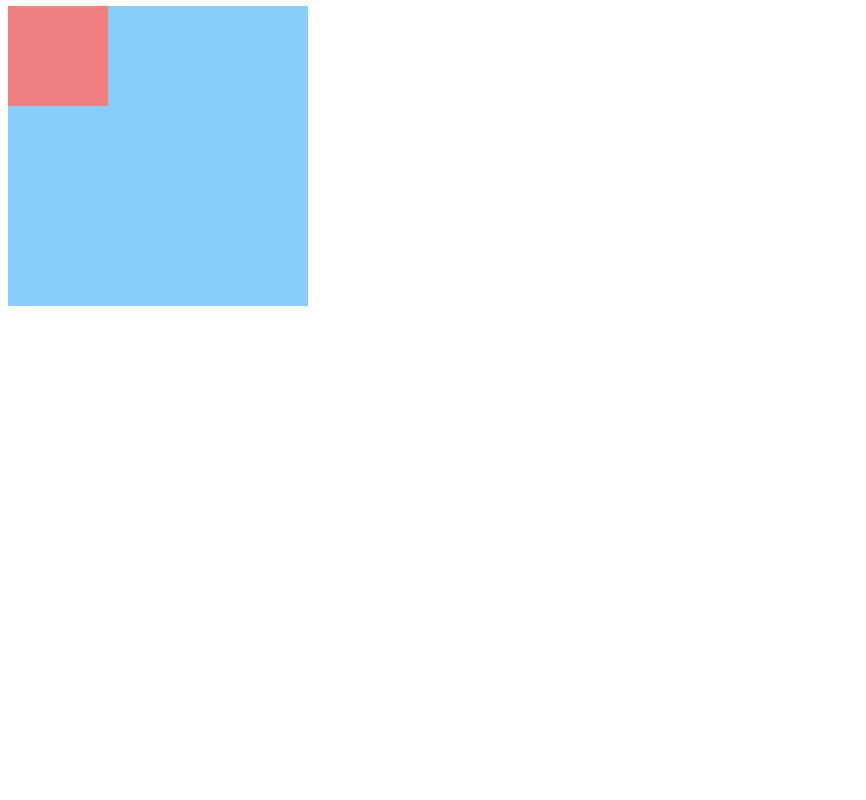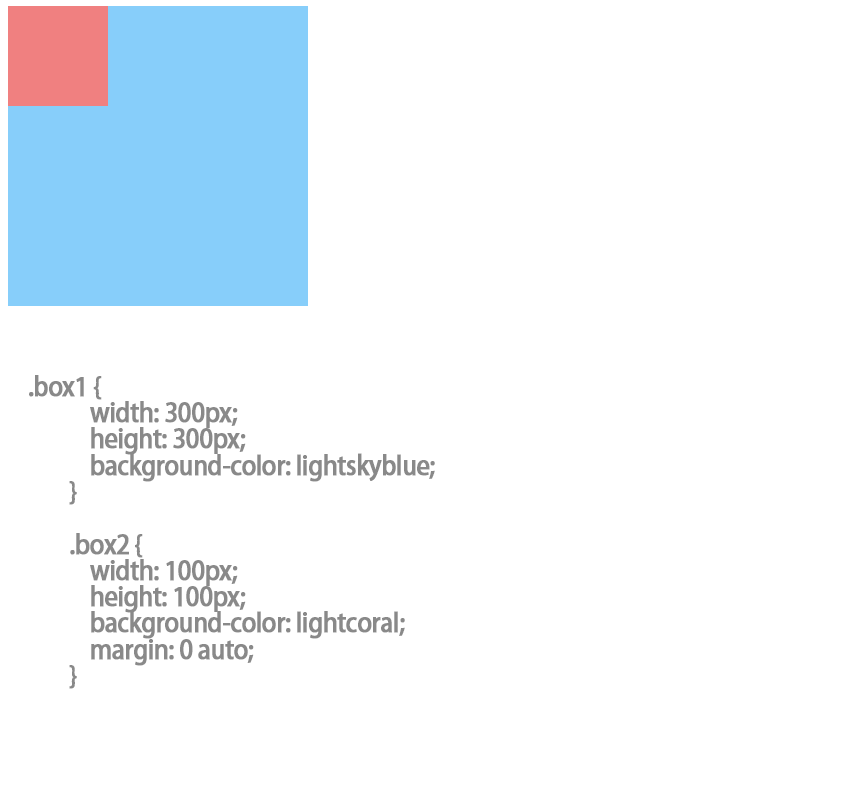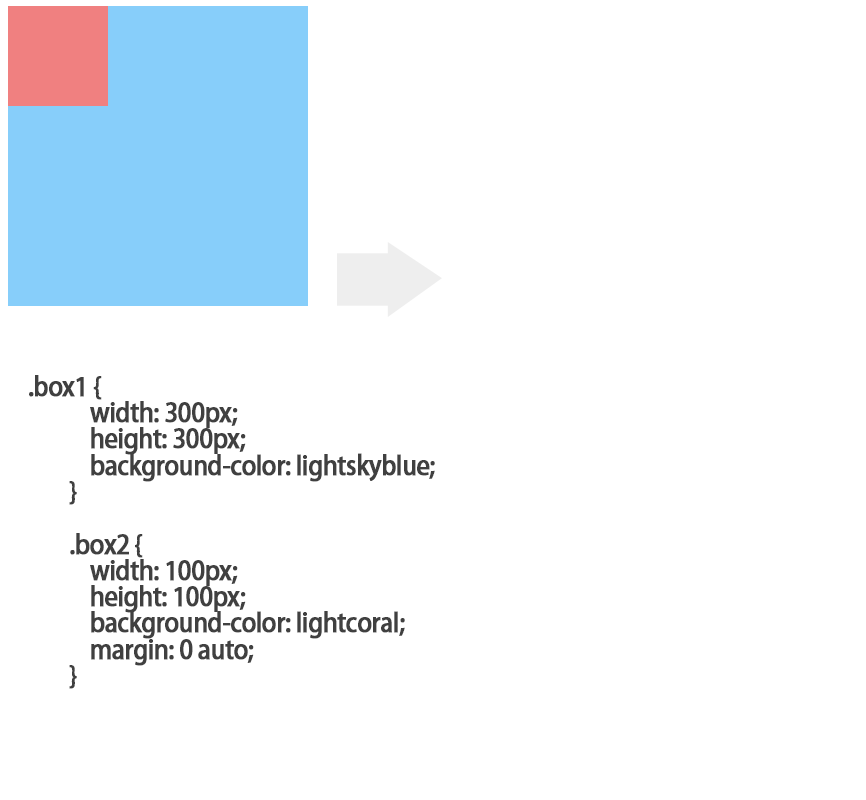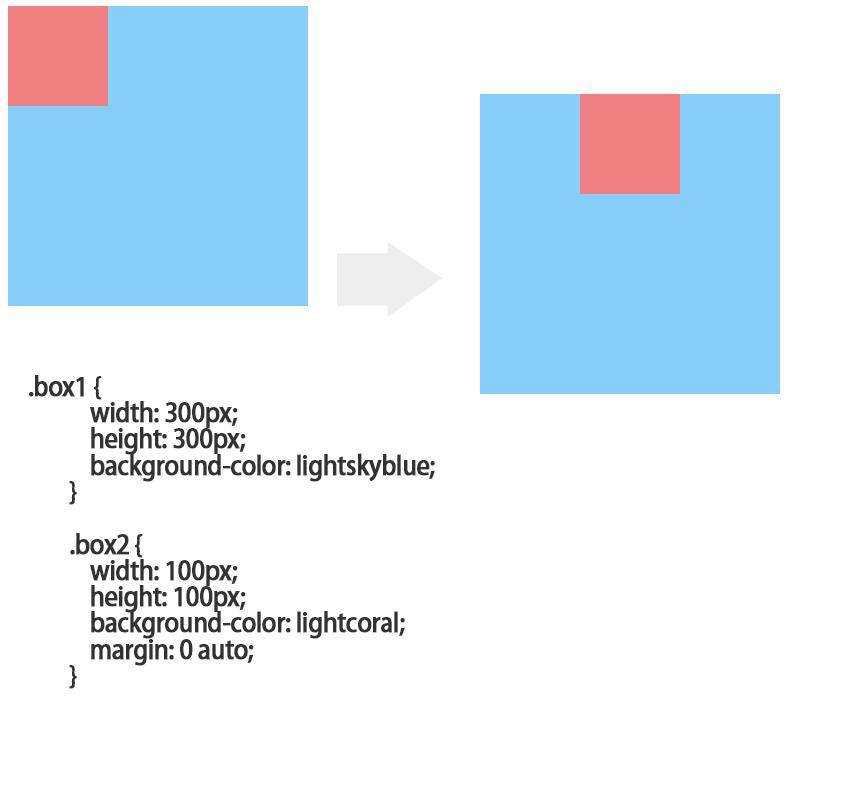

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号