理解并写出外边距的三个特征: 同级塌陷,嵌套传递,自动挤压的案例;
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style2.css"> <title>外边距 margin</title> </head> <body> <!-- 1.同级上下塌陷、左右叠加 2.嵌套传递 3.自动挤压 --> <!--1、同级上下塌陷--> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <br> <!--1、同级左右叠加--> <div class="div1"></div> <div class="div2"></div> <br> <hr> <!--2.嵌套传递--> <div class="box3"> <div class="box4"></div> </div> <hr> <div class="box5"></div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
/********** 同级上下塌陷 **********/
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: palegreen;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.box1{
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.box2{
margin-top:50px;
}
/* 从而得出一个结论: 当二个盒子上下排列时,外边距会出现塌陷现象,小的会陷到大的里面去,简称:"同级塌陷" */
/********** 同级左右叠加 **********/
.div1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: darkblue;
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 30px;
}
.div2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightskyblue;
display: inline-block;
margin-left: 50px;
}
/* 下面演示当二个盒子相互潜逃,为父子关系时,设置了margin会出现哪些问题? */
/********** 嵌套传递 **********/
.box3 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
.box4 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
/* 我们的任务是:使box4离box3顶部之间有50px的间距,通过margin-top来实现 */
.box4 {
margin-top: 50px;
}
/* 结果发现不对, 外边距跑到了外部盒子box3上面去了,这就是外边距的"嵌套传递"现象 */
/* 当给一个子盒子添加margin时,这个margin会自动传递到父级盒子上 */
/* 所以,正确的做法是,给父级盒子添加内边距来实现 */
/* 先复位 */
.box4 {
margin-top: 0;
}
.box3 {
padding-top: 50px;
/* 修改盒子高度,将撑开的50px的高度去掉 */
height: 150px;
}
/* 下面演示margin的自动挤压,这是布局中使用非常广泛 */
/********** 自动挤压 **********/
.box5 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
/*左侧添加auto,会尽可能将左侧空间分配给盒子左外边距,盒子被挤到最右边*/
/*margin-left: auto;*/
/*右侧添加auto,会尽可能将右侧空间分配给盒子右外边距,盒子被挤到最左边*/
/*margin-right: auto;*/
/*两行等价于,最终盒子居中 */
/*margin: auto;*/
/*距离顶部50,左右居中*/
margin: 50px auto;
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
运行结果:
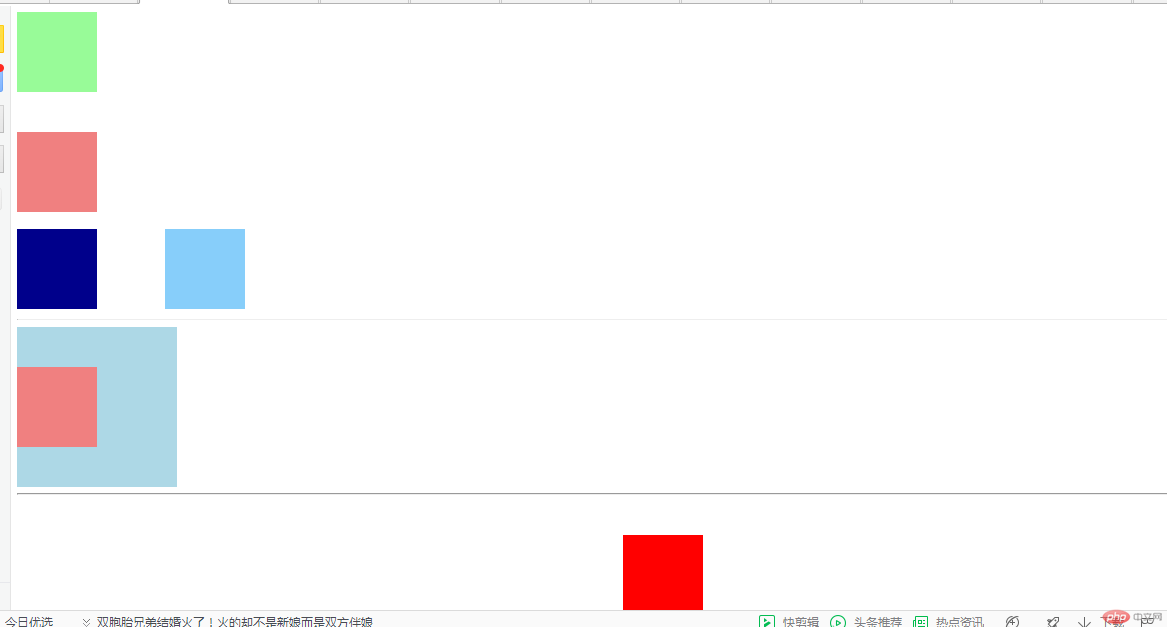
外边距三种特点:1.同级上下塌陷、左右叠加 2.嵌套传递 3.自动挤压
写案例,并分析内边距对盒中内容的影响,以及解决的三种方案是什么?
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style1.css"> <title>padding 图片居中显示</title> </head> <body> <!-- 将图片在容器中居中显示 --> <!-- 方法1: 重新设置原盒子的宽度--> <div class="box1"> <img src="images/girl.jpg" alt="小姐姐" width="200"> </div> <hr> <!-- 方法2: 宽度分离,利用父级div设置宽度,子级div继承的方法--> <div class="warp"> <div class="box2"> <img src="images/girl.jpg" alt="小姐姐" width="200"> </div> </div> <hr> <!-- 方法3: box-sizing :以特定的方式定义匹配某个区域的特定元素。content-box|border-box|inherit;--> <div class="box3"> <img src="images/girl.jpg" alt="小姐姐" width="200"> </div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
.box1{
/*默认情况下,width是直接使用到盒子中的内容级content*/
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color:lightblue;
border:3px solid black;
}
.box1{
padding:50px;
/* 会发现,内边距会增加盒子填充厚度,将盒子撑大 */
/*如果想保持原来盒子大小,只能手工修改box1的宽高*/
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}
/*********************** 方案2: 宽度分离 *********************/
/* 给box2认一个干爹,添加一个父级盒子wrap, 这时box2就是儿子了, width就有效了*/
/*这是利用于嵌套盒子之间,只有宽度可以继承的特征*/
.warp{
width: 300px;
border:3px solid black;
}
.box2{
padding :50px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
/*********************** 方案3: box-sizing 盒尺寸 *********************/
/*经过前面学习, 知道了在默认情况下, 宽度是作用到盒中的内容上的*/
/*而一个盒子有content,padding,border,margin四部分组成,所以改变宽度会造成盒子大小不确定*/
/*方案2: 是将width宽度直接作用到了外部盒子上, 而box2此时就自动变成了warp的内容,所以会应用到width*/
.box3{
width: 300px;
background-color: palegreen;
border: 3px solid black;
/*让宽度width作用到边框级,作用到内容级仍会撑开盒子的*/
/*box-sizing: content-box;*/
box-sizing:border-box;
/*内边距不会撑开盒子, 因为宽度作用到了边框级, 与内容无关*/
padding: 50px;
}
/* 总结:
* 第一种方案DOM结构简单,但是要修改原盒子大小
* 第二种方案不需要修改原盒子大小,但需要增加一个容器盒子
* 第三种无疑是首选, 但是不同级别的盒元素,理解起来有困难
*/点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
运行结果
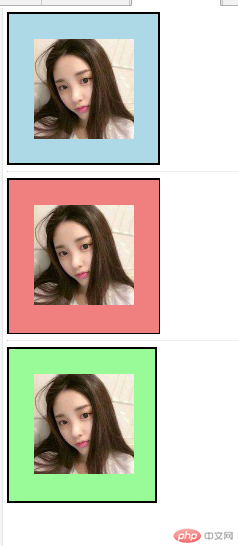
让图片居中的三种方法:
方法1: 重新设置原盒子的宽度
方法2: 宽度分离,利用父级div设置宽度,子级div继承width属性的方法
方法3: box-sizing :以特定的方式定义匹配某个区域的特定元素。content-box|border-box|inherit;
3. 浮动的实现原理与清除的技巧
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style3.css"> <title>浮动float</title> </head> <body> <!-- 1.文档流: html元素默认按照书写的顺序在浏览器中,遵循先从左到右,再从上到下进行排列 2.布局前提: 通常先将元素从文档流中脱离,这样才能随心所欲的操作 3.元素脱离文档流的手段: 浮动和绝对定位 --> <!-- 浮动的基本原理 --> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> <!-- 第四个区块不需要浮动 --> <div class="box4"></div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
.box1 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lawngreen;
}
.box2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightskyblue;
}
.box1{
float: left;/* .box1 左浮动,脱离文档流,后面的区块自动前移占据了它的空间 */
}
.box2{
float: left;
/*
第二个区块浮动后,相当于到了另一个由浮动元素组成的文档流中
所以,它碰到前一个浮动元素后就停止了向左浮动,排到了前一个浮动元素的右边
*/
}
.box3 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
/* .box3 向右浮动,直到碰到浏览器窗口右边框为止,当窗口宽度缩小到不能容纳它时会自动掉到第二排 */
.box3 {
float: right;
}
/*.box4 在文档流中,受前面浮动元素的影响,仍会自动上移并占据原浮动元素的空间*/
.box4 {
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
}
/* .box4 第四个区块,我是不希望它浮动的, */
/*所以要消除前面的浮动元素对它的影响*/
.box4 {
/* 可以通过清除浮动来解决 */
clear: left; /* 削除左边浮动元素的影响, 但会发现右浮动区块仍占据了它的一部分区别 */
clear: right; /* 消除掉右浮动元素对它的影响 */
/* 因为这个清除左右浮动经常用,所以可以简写 */
clear: both;
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
运行结果
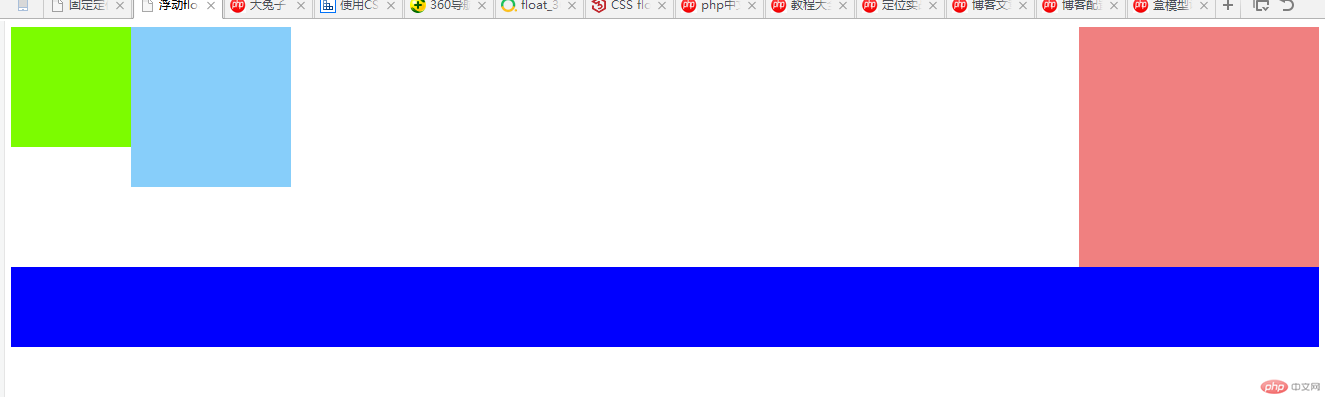
4. 相对定位与绝对定位的区别与联系,并实例演示
相对定位
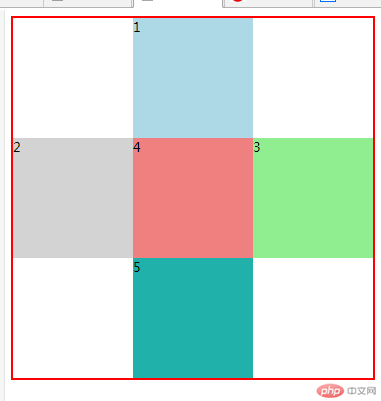
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style4.css"> <title>定位与相对定位 position:relative</title> </head> <body> <!-- 定位:将元素在页面中重新排列,分为四类 1.静态定位: 浏览器默认方式, 即文档流中的位置 2.相对定位: 元素并未脱离文档流,只是相对于它原来的位置,做相对移动 3.绝对定位: 元素脱离文档流重新排列,不论元素之前是什么类型,全部转为块元素,支持宽高 4.固定定位: 始终相对于浏览器的窗口做为定位父级,进行定位 --> <!-- 相对定位小案例: 在页面中创建一个彩色十字架--> <div class="box1">1</div> <div class="box2">2</div> <div class="box3">3</div> <div class="box4">4</div> <div class="box5">5</div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
.box1 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
.box2 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightgray;
}
.box3 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
.box4 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.box5 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
/* 相对定位 */
.box1{
position: relative;
left: 150px;
}
.box3{
position: relative;
left: 300px;
top: -150px;/* 注: 这里必须使用负数才可以向反方向移动 */
}
.box4{
position:relative;
left: 150px;
top:-300px;
}
.box5{
position:relative;
left: 150px;
top:-300px;
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
相对定位运行结果
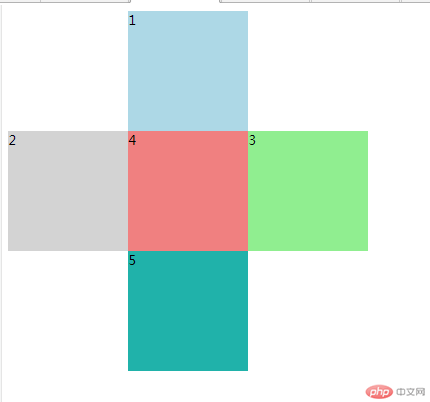
绝对定位
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style5.css"> <title>绝对定位 position:absolute</title> </head> <body> <!-- 定位参照物: 1. 相对定位, 是以元素在文档流中的原始位置为参照物进行定位的 2. 绝对定位, 它是脱离了文档流的, 所有必须要有一个定位父级做为参照物 position: absolute; 默认以整个窗口进行绝对定位, 定位父级是<body> --> <div class="parent"> <div class="box1">1</div> <div class="box2">2</div> <div class="box3">3</div> <div class="box4">4</div> <div class="box5">5</div> </div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
.parent{
position:relative;
border:2px solid red;
width: 450px;
height: 450px;
}
.box1 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
.box2 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightgray;
}
.box3 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
.box4 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.box5 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
/*绝对定位*/
.box1{
position: absolute;
left: 150px;
}
.box2{
position: absolute;
top:150px;
}
.box3{
position: absolute;
left: 300px;
top:150px;
}
.box4{
position: absolute;
left: 150px;
top:150px;
}
.box5{
position: absolute;
left: 150px;
top: 300px;
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
绝对定位运行结果
定位:将元素在页面中重新排列,分为四类
1.静态定位(static): 浏览器默认方式, 即文档流中的位置
2.相对定位(relative): 元素并未脱离文档流,只是相对于它原来的位置,做相对移动
3.绝对定(absolute): 元素脱离文档流重新排列,不论元素之前是什么类型,全部转为块元素,支持宽高
4.固定定位(fixed): 始终相对于浏览器的窗口做为定位父级,进行定位
相对定位, 是以元素在文档流中的原始位置为参照物进行定位的
绝对定位, 它是脱离了文档流的, 所有必须要有一个定位父级做为参照物
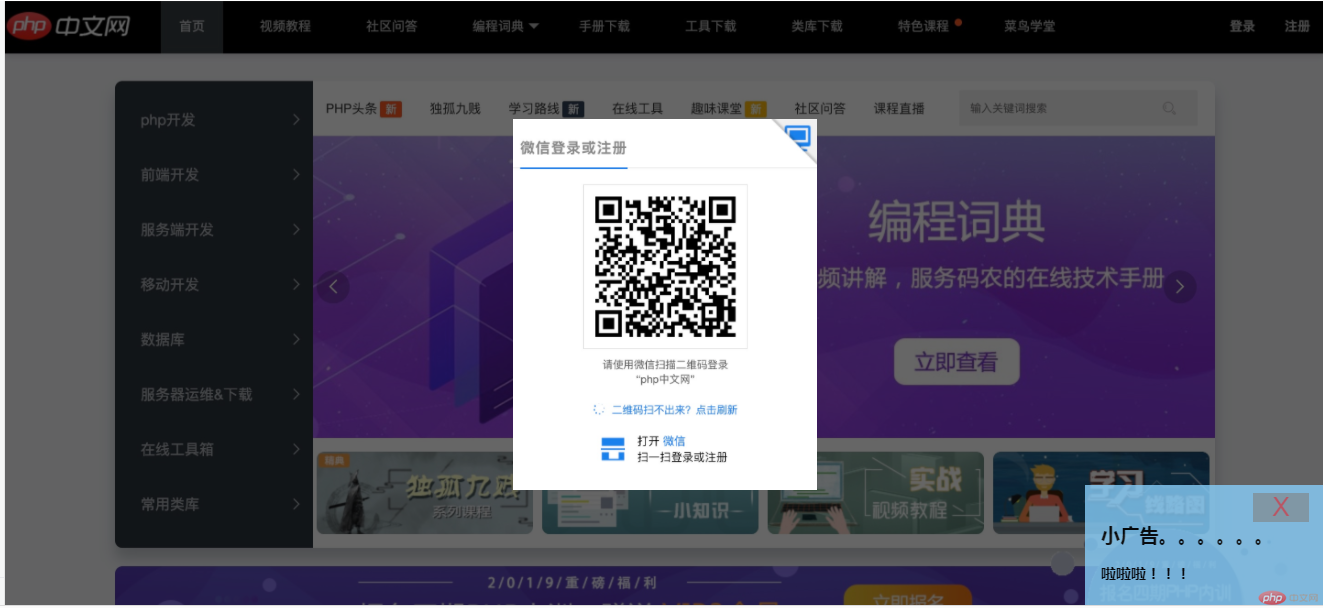
5. 模仿完成课堂上的二个定位案例:模拟php中文网登陆(遮罩+绝对定位)和固定定位广告的展示方式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style6.css"> <title>定位小案例</title> </head> <body> <div class="shade"></div> <div class="login"><img src="images/login.jpg" alt="登录"></div> <div class="ads"> <button onclick="this.parentNode.style.display='none'">X</button> <h2>小广告。。。。。。</h2> <h3>啦啦啦!!!</h3> </div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
body{
margin: 0;
background-image: url(../images/php.jpg);
background-size: cover;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
.shade{
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top:0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
/* 将背景设置为纯黑,并通过透明度使背影内容透出来 */
background-color: black;
opacity:0.6;
}
.login img{
width: 380px;
height: 460px;
}
.login{
background-color: white;
position:absolute;
left: 50%;
top:50%;
margin-left: -190px;
margin-top: -230px;
}
.ads{
width: 300px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightskyblue;
opacity: 0.8;
position: fixed;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
button{
width: 70px;
float: right;
margin-top: 10px;
margin-right: 20px;
border: none;
padding: 0;
background-color: #888888;
opacity:0.6;
color: red;
font-size:2em;
}
button:hover{
background-color: lightcoral;
color: black;
border: 1px solid red;
}
h2,h3{
padding-left: 20px;
clear: both;
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
运行结果

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号