一、网站布局之双飞翼布局练习
双飞翼布局的实现,目的是左右两栏固定宽度,中间部分自适应。这个布局的实现思路是,把三栏布局比作一只大鸟,先把最重要的身体部分放好,然后再将左右翅膀移动到适当的地方。
1.html代码中,将wrap、left、right包含在container中,wrap要放最前边,然后是left、right
2.将wrap、left、right都float:left
3.将wrap继承container的宽度,也就是width:100%
4.因为wrap占满了宽度,所以要把left拉到最左边,使用margin-left:-100%;同理right使用margin-left:-200px
5.wrap被覆盖,内层的main使用padding-left:200px;padding-right:200px。还可以考虑使用margin,margin:0 200px。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>双飞翼布局</title>
<style type="text/css">
.header .content {
/* 头部内容区居中显示,设置好宽度 */
width: 1000px;
height: 60px;
background-color: black;
/* 上下外边距为0,左右自动居中 */
margin: 0 auto;
}
/*头部内容区中的导航*/
.header .content .nav {
/* 清空UL元素的默认样式 */
margin-top: 0;
margin-bottom: 0;
padding-left: 0;
}
/*清除列表项样式*/
.header .content .nav .item {
list-style-type: none;
}
.header .content .nav .item a {
/* 将浮动设置到标签<a>上面,否则无法实现导航区的点击与高亮 */
float: left;
/* 设置最小宽度与最小高宽,以适应导航文本的变化 */
min-width: 80px;
min-height: 60px;
/* 导航文本垂直居中显示 */
line-height: 60px;
color: white;
/* 设置导航文本的左右内边距 */
padding: 0 15px;
/* 去掉下划线 */
text-decoration-line: none;
/* 文本居中显示 */
text-align: center;
}
.header .content .nav .item a:hover {
/* 当鼠标移到导航链接上时改变背景色与文本前景色,实现当前导航高亮功能 */
background-color: red;
/* 文本设置为系统根字体大小的1.1倍 */
font-size: 1.1rem;
}
/*主体容器设置总宽度,并水平居中 */
.container {
width: 1000px;
margin: 5px auto;
/*包住浮动的子元素*/
overflow: hidden;
}
/* 中间区块宽度设置在它的容器wrap中*/
.wrap {
/* 继承父级区块container宽度 width:1000px; */
width: inherit;
/*没有内容,所以设置一个最小高度*/
min-height: 800px;
background-color: cyan;
}
/* 左边栏样式 */
.left {
width: 200px;
min-height: 800px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
/* 右边栏样式 */
.right {
width: 200px;
min-height: 800px;
background-color: lightseagreen
}
.wrap, .left, .right {
float: left;
}
/* 通过设置区块的负外边距的方式,实现向反方向移动区块 */
.left {
/* 将左区块拉回到中间的起点处*/
margin-left: -100%;
}
.right {
/* 将右区块上移到中间区块右侧显示 */
margin-left: -200px;
}
.main {
/*除padding外,也可使用margin */
/*padding-left: 200px;*/
/*padding-right: 200px;*/
margin:0 200px
}
.footer .content {
width: 1000px;
height: 60px;
background-color: #444;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.footer .content p {
text-align: center;
line-height: 60px;
}
.footer .content a {
text-decoration: none;
color: lightgrey;
}
/* 鼠标移入时显示下划线并加深字体前景色 */
.footer .content a:hover {
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">
<div class="content">
<ul class="nav">
<li class="item"><a href="">首页</a></li>
<li class="item"><a href="">公司新闻</a></li>
<li class="item"><a href="">最新产品</a></li>
<li class="item"><a href="">联系我们</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 中间主体 -->
<div class="container">
<!-- 先创建中间主体区块,确保它优先被渲染出来 -->
<!-- 中间内容区需要创建一个父级容器进行包裹 -->
<div class="wrap">
<!-- 最终要展示的内容写在main区块中 -->
<div class="main">主体内容区</div>
</div>
<!-- 左侧边栏区块 -->
<div class="left">左侧</div>
<!-- 右侧边栏区块 -->
<div class="right">右侧</div>
</div>
<!-- 底部 -->
<div class="footer">
<div class="content">
<p>
<a href="">© AAAAAAAAA</a>
<a href="">3333-66666666</a>
<a href="">CN-ICP2019042901-1</a>
</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

二、清除浮动
为何要清除浮动?
在前端布局的过程中肯定会用到float(浮动)属性。浮动框脱离了文档流,当元素浮动之后,当包含框的高度小于浮动框的时候,此时就会出现“高度塌陷”,即为何我们需要清楚浮动。下面的例子即展示何为塌陷。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>清除浮动方法</title>
<style type="text/css">
.box1{
width:200px;
border:5px solid red;
}
.box2{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background-color: lawngreen;
float: right;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
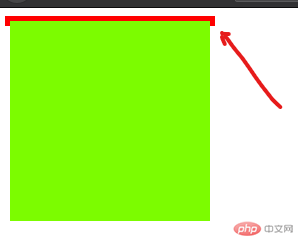
可以看到外层的边框已经处于塌陷状态
清除浮动的五种方式:
方式一:父元素设置与子元素一样的高度,以此来消除子元素浮动后带来的高度塌陷。一般情况下不使用该方法,当子元素高度变化时,需要手动修改父元素高度。
方式二:父元素跟着子元素一起浮动,该方法同样不建议使用,如果嵌套的父元素过多,需要一个个添加float。
方式三:使用额外标签法,在父级盒子内再放一个标签,在这个标签中使用clear:both,会将这个浮动盒子的父盒子高度重新撑开,来清除浮动对页面的影响.
一般情况下也不建议使用这一种方式来清除浮动。因为这种清除浮动的方式会增加页面的标签,造成结构的混乱.
方法四:在父级使用伪元素来清除浮动。
.box1:after {
content:"";//设置内容为空
height:0;//高度为0
display:table;//转为块级元素
clear:both//清除浮动
}
方式五:给父级元素添加overflow属性来清除浮动。
.box1 {
overflow:hidden或者auto
}
五种方式各有利弊,一、二两种方法最直接,简单、粗暴,但是缺点同样粗暴。第三种方式会增加许多不必要的标签。一般推荐使用方法四、五,方法五最为方便。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号