Complete login verification by using node.js+captchapng+jsonwebtoken
This article mainly introduces the example of node.js+captchapng+jsonwebtoken to implement login verification. It has certain reference value. Those who are interested can learn about it.
When it comes to login verification, everyone can definitely think of it. The verification code is 12306. 12306 has taken great pains to prevent ticket fraud, and the verification code has become increasingly difficult to identify, and eventually even humans may not be able to identify it.
Today, the editor will tell you how to implement image verification code in node and use token to verify login. After studying this article, you will learn:
1. Use captchapng to generate image verification code
2. Use jsonwebtoken to implement login verification
一, Image verification code generation (all codes at the end)
First, let’s go over the process. The first step is for the server to randomly generate a set of four digits.
The second step is to draw these four digits on canvas to generate a picture.
The third step is to save these four digits for comparison when the user returns the data.
So where to save it? Obviously, in order to distinguish users, it is safest to save them in session.
The first step is to have a login page. Here we still use react,
login.tsx
import * as React from 'react'
import * as ReactDom from 'react-dom'
import {Link, browserHistory} from 'react-router';
import * as axios from 'axios';
export default class Login extends React.Component<any,any>{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = {
userName : '',
password : '',
yzNoId : '',
hash : Math.random()
}
}
handleUserName(e) : any {
this.setState({
userName : e.target.value
})
}
handlePassword(e) : any {
this.setState({
password : e.target.value
})
}
handleYzId(e) : any {
this.setState({
yzNoId : e.target.value
})
}
render(){
const { userName, password, yzNoId } = this.state;
return(
<p>
<p className="nav-wrap">
<ul className="nav">
<li><Link to="/home">首页</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/imgLoad">上传</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/login">登陆</Link></li>
</ul>
</p>
<p className="content">
<p className="login-warp">
<p>
<input type="text" className="username" value={userName} onChange={this.handleUserName.bind(this)} placeholder="用户名"/>
</p>
<p>
<input type="text" className="password" value={password} onChange={this.handlePassword.bind(this)} placeholder="密码"/>
</p>
<p>
<input type="text" className="yz" value={yzNoId} onChange={this.handleYzId.bind(this)} placeholder="验证码"/>
<img src={"http://localhost:3000/captcha"} className="yz-img" />
</p>
<p>
<input type="button" className="submit" value="登陆" onClick={this.sbumit.bind(this,{userName:userName,password:password,captcha:yzNoId})} />
</p>
</p>
</p>
</p>
)
}
}The page looks like this

We need to give a verification picture through the server.
router/index.js Add the following code
var Login = require('./controller/login');
var login = new Login;
router.get('/captcha', login.captcha);
router.post('/login',login.loginer);
login是定义在控制器的一个类的实例,captcha,loginer是它的方法。分别是返回验证图片、登录验证。
controller/login.js
var rf = require('fs');
var captchapng = require('captchapng');
class Login {
constructor(){}
captcha(req, res, next) {
var str = parseInt(Math.random()*9000+1000); //随机生成数字
req.session.captcha = str; // 存入session
var p = new captchapng(80, 30, str); //生成图片
p.color(0, 0, 0, 0);
p.color(80, 80, 80, 255);
var img = p.getBase64();
var imgbase64 = new Buffer(img, 'base64');
res.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'image/png'
});
res.end(imgbase64);
}
loginer(req, res, next) {
let captcha = req.body.captcha;
let userName = req.body.userName;
let password = req.body.password;
if (captcha != req.session.captcha) {
res.status(400).send({
message: '验证码错误'
});
}else if(userName == "chenxuehui" && password == "123321"){
res.json({"code":100,"verson":true,"msg":"登陆成功","token":token});
}else{
res.json({"code":0,"verson":false,"msg":"密码错误"});
}
}
}
module.exports = LoginThe captcha method is to generate a picture containing four digits and then save the picture to the session.
Reference this method in router/index.js
router.get('/captcha', login.captcha);
That is to say, when we access localhost:3000/captcha, it will return picture.

With this connection, we can get the image through the src attribute of the image, but when the image is clicked, it needs to be refreshed, so we need to add a Click refresh event. Insert the following code into login.tsx
setHash() {
this.setState({
hash : Math.random()
})
} The img tag also becomes
Copy code The code is as follows :
All codes of login.tsx at this time:
import * as React from 'react'
import * as ReactDom from 'react-dom'
import {Link, browserHistory} from 'react-router';
import * as axios from 'axios';
export default class Login extends React.Component<any,any>{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = {
userName : '',
password : '',
yzNoId : '',
hash : Math.random()
}
}
public async sbumit(params : any) : Promise<any>{
let res = await axios.post('http://localhost:3000/login',params);
}
handleUserName(e) : any {
this.setState({
userName : e.target.value
})
}
handlePassword(e) : any {
this.setState({
password : e.target.value
})
}
handleYzId(e) : any {
this.setState({
yzNoId : e.target.value
})
}
setHash() {
this.setState({
hash : Math.random()
})
}
render(){
const { userName, password, yzNoId } = this.state;
return(
<p>
<p className="nav-wrap">
<ul className="nav">
<li><Link to="/home">首页</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/imgLoad">上传</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/login">登陆</Link></li>
</ul>
</p>
<p className="content">
<p className="login-warp">
<p>
<input type="text" className="username" value={userName} onChange={this.handleUserName.bind(this)} placeholder="用户名"/>
</p>
<p>
<input type="text" className="password" value={password} onChange={this.handlePassword.bind(this)} placeholder="密码"/>
</p>
<p>
<input type="text" className="yz" value={yzNoId} onChange={this.handleYzId.bind(this)} placeholder="验证码"/>
<img src={"http://localhost:3000/captcha?aaa="+this.state.hash} className="yz-img" onClick={this.setHash.bind(this)} />
</p>
<p>
<input type="button" className="submit" value="登陆" onClick={this.sbumit.bind(this,{userName:userName,password:password,captcha:yzNoId})} />
</p>
</p>
</p>
</p>
)
}
}In this way, as long as you click img, a hash will be randomly generated, and then the new image will be called.
Then we proceed with login verification.
The loginer method is used for login verification.
Get the user's username information, password and verification code, compare them, and finally return data on whether the login is successful.
When the user logs in successfully, he does not need to log in again next time. In the past, you can choose session or cookie. Here we use token. Because we have now implemented separate development of front-end and back-end, we are more inclined to build a single page and use Ajax to build applications. Token is the most suitable for this development model.
Token login verification
Token is an encrypted string. After successful login, it is returned to the user for storage. Then the user will bring this token when requesting the interface. . So we need to encrypt the token.
Json Web Token is specifically designed to solve this problem. The principle will not be explained in detail. In fact, it is to obtain a string in a certain way and then unravel it in a certain way.
The first step we need to do is
When the user logs in successfully, create a token and return it to the user.
Step 2: After the user gets the token, he should save the token locally.
The third step: We need to write an intermediate layer. Every time the user requests, we verify whether the token carried by the user is correct. Data is returned correctly, warning is returned incorrectly.
Every time the user requests data, he or she must bring the token in the header.
The first step: Still controller/login.js
var rf = require('fs');
var jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
var captchapng = require('captchapng');
var Tokens = require('../middleware/token')
var t = new Tokens;
class Login {
constructor(){}
captcha(req, res, next) {
var str = parseInt(Math.random()*9000+1000); //随机生成数字
req.session.captcha = str; // 存入session
var p = new captchapng(80, 30, str); //生成图片
p.color(0, 0, 0, 0);
p.color(80, 80, 80, 255);
var img = p.getBase64();
var imgbase64 = new Buffer(img, 'base64');
res.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'image/png'
});
res.end(imgbase64);
}
loginer(req, res, next) {
let captcha = req.body.captcha;
let userName = req.body.userName;
let password = req.body.password;
if (captcha != req.session.captcha) {
res.status(400).send({
message: '验证码错误'
});
}else if(userName == "chenxuehui" && password == "123321"){
// 设置token
var datas = {userName:"chenxuehui"}
//调用../middleware/token 下方法设置
var token = t.setToken('cxh',300,datas)
res.json({"code":100,"verson":true,"msg":"登陆成功","token":token});
}else{
res.json({"code":0,"verson":false,"msg":"密码错误"});
}
}
}
module.exports = LoginThis time we add the setting token in the login method and return it to the user . The setToken method is a method for setting token.
Step 2: Save after the user gets it.
In login.tsx it becomes as follows
import * as React from 'react'
import * as ReactDom from 'react-dom'
import {Link, browserHistory} from 'react-router';
import * as axios from 'axios';
export default class Login extends React.Component<any,any>{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = {
userName : '',
password : '',
yzNoId : '',
hash : Math.random()
}
}
public async sbumit(params : any) : Promise<any>{
let res = await axios.post('http://localhost:3000/login',params);
if(res.data.verson){
sessionStorage.setItem('token',res.data.token);
browserHistory.push("/home")
}
}
handleUserName(e) : any {
this.setState({
userName : e.target.value
})
}
handlePassword(e) : any {
this.setState({
password : e.target.value
})
}
handleYzId(e) : any {
this.setState({
yzNoId : e.target.value
})
}
setHash() {
this.setState({
hash : Math.random()
})
}
render(){
const { userName, password, yzNoId } = this.state;
return(
<p>
<p className="nav-wrap">
<ul className="nav">
<li><Link to="/home">首页</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/imgLoad">上传</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/login">登陆</Link></li>
</ul>
</p>
<p className="content">
<p className="login-warp">
<p>
<input type="text" className="username" value={userName} onChange={this.handleUserName.bind(this)} placeholder="用户名"/>
</p>
<p>
<input type="text" className="password" value={password} onChange={this.handlePassword.bind(this)} placeholder="密码"/>
</p>
<p>
<input type="text" className="yz" value={yzNoId} onChange={this.handleYzId.bind(this)} placeholder="验证码"/>
<img src={"http://localhost:3000/captcha?aaa="+this.state.hash} className="yz-img" onClick={this.setHash.bind(this)} />
</p>
<p>
<input type="button" className="submit" value="登陆" onClick={this.sbumit.bind(this,{userName:userName,password:password,captcha:yzNoId})} />
</p>
</p>
</p>
</p>
)
}
}In the sbumit method we put the token into sessonstorage.
Step 3: Set the middleware to verify the token every time it requests the interface. If the parsing is successful, it will be added to the request header.
./middleware/token.js
##
var jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
class Tokens {
constructor(){}
testToken(req,res,next) {
var token = req.body.token || req.query.token || req.headers['x-access-token'];
if(token) {
//存在token,解析token
jwt.verify(token, 'cxh' , function(err,decoded) {
if(err) {
// 解析失败直接返回失败警告
return res.json({success:false,msg:'token错误'})
}else {
//解析成功加入请求信息,继续调用后面方法
req.userInfo = decoded;
next()
}
})
}else {
return res.status(403).send({success:false,msg:"没有token"})
}
}
setToken(name,time,data) {
var jwtSecret = name;
var token = jwt.sign(data, jwtSecret, {
expiresIn: time
})
return token;
}
}
module.exports = Tokens
在 router/index.js
var express = require('express');
var router = express.Router();
var rf = require('fs');
var Login = require('./controller/login');
var Tokens = require('./middleware/token')
var t = new Tokens;
var login = new Login;
//主页
router.get('/', function(req, res, next) {
res.render("wap/index")
});
//获取图片验证码
router.get('/captcha', login.captcha);
//登录验证
router.post('/login',login.loginer);
//请求数据时 t.testToken 验证token
router.post('/list',t.testToken,function(req, res, next){
res.json({
//在请求信息里面拿到数据
username : req.userInfo.userName,
success : true,
result : [
{
name:'1111111'
},
{
name :'22222'
}
]
})
})
module.exports = router;我们在另一个页面调用list接口试一下
import * as axios from 'axios';
import { transToken } from '../decorator/index'
class Home extends React.Component<any,any>{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = {
data : ''
}
}
async getList(): Promise<any>{
let token = sessionStorage.getItem('token');
const config = {
// 请求头信息
headers: {'x-access-token': token}
}
let res = await axios.post('http://localhost:3000/list',{},config);
if(!res.data.success){
browserHistory.push('/login');
return;
}
this.setState({
data : res.data
})
}
render(){
const { data } = this.state;
return(
<p>
<p className="nav-wrap">
<ul className="nav">
<li><Link to="/home">首页</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/imgLoad">上传</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/login">登陆</Link></li>
</ul>
</p>
<p className="content">
Home
<span onClick={this.getList.bind(this)}>获取数据</span>
<p>{
data ? data.result.map( (val,k) => {
return <li key = {k}>{val.name}</li>
}) : null
}</p>
</p>
</p>
)
}
}
export default Home当调用getList时,如果此时没有登录res.data.success就会为false,则跳到登录页。
全部代码
node.js
app.js
var express = require('express');
var path = require('path');
var favicon = require('serve-favicon');
var logger = require('morgan');
var cookieParser = require('cookie-parser');
var bodyParser = require('body-parser');
var session = require("express-session");
var ejs = require('ejs');
var index = require('./routes/index');
var app = express();
// view engine setup
app.set('views', path.join(__dirname, 'views'));
// app.set('view engine', 'jade');
app.engine('html', ejs.__express);
app.set('view engine', 'html');
app.use(session({
secret:"dabao",
resave:false,
saveUninitialized:true,
cookie:{}
}));
// uncomment after placing your favicon in /public
//app.use(favicon(path.join(__dirname, 'public', 'favicon.ico')));
app.use(logger('dev'));
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(bodyParser({limit: 5000000}));
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
app.use(cookieParser());
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, '')));
app.use('/', index);
// catch 404 and forward to error handler
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
var err = new Error('Not Found');
err.status = 404;
next(err);
});
// error handler
app.use(function(err, req, res, next) {
// set locals, only providing error in development
res.locals.message = err.message;
res.locals.error = req.app.get('env') === 'development' ? err : {};
// render the error page
res.status(err.status || 500);
res.render('error');
});
module.exports = app;index.js
var express = require('express');
var router = express.Router();
var rf = require('fs');
var Login = require('./controller/login');
var Tokens = require('./middleware/token')
var t = new Tokens;
var login = new Login;
/* GET home page. */
router.get('/', function(req, res, next) {
res.render("wap/index")
});
router.post('/upLoadImg',function(req,res,next){
let imgData = req.body.imgData;
console.log(imgData)
let base64Data = imgData.replace(/^data:image\/\w+;base64,/, "");
let dataBuffer = new Buffer(base64Data, 'base64');
let timer = Number( new Date() );
console.log(timer)
rf.writeFile("views/images/artCover"+timer+".png",dataBuffer, function(err) {
if(err) {
res.json({"code":400,"verson":false,"msg":err});
}else {
res.json({"code":100,"verson":true,"url":"views/src/common/images/artCover/"+timer+".png"});
}
});
})
router.get('/captcha', login.captcha);
router.post('/login',login.loginer);
router.post('/list',t.testToken,function(req, res, next){
// 先解析token
console.log(req.userInfo)
res.json({
username : req.userInfo.userName,
success : true,
result : [
{
name:'1111111'
},
{
name :'22222'
}
]
})
})
module.exports = router;controller/login.js
var rf = require('fs');
var jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
var captchapng = require('captchapng');
var Tokens = require('../middleware/token')
var t = new Tokens;
class Login {
constructor(){}
captcha(req, res, next) {
var str = parseInt(Math.random()*9000+1000); //随机生成数字
req.session.captcha = str; // 存入session
var p = new captchapng(80, 30, str); //生成图片
p.color(0, 0, 0, 0);
p.color(80, 80, 80, 255);
var img = p.getBase64();
var imgbase64 = new Buffer(img, 'base64');
res.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'image/png'
});
res.end(imgbase64);
}
loginer(req, res, next) {
let captcha = req.body.captcha;
let userName = req.body.userName;
let password = req.body.password;
if (captcha != req.session.captcha) {
res.status(400).send({
message: '验证码错误'
});
}else if(userName == "chenxuehui" && password == "123321"){
// 设置token
var datas = {userName:"chenxuehui"}
var token = t.setToken('cxh',300,datas)
res.json({"code":100,"verson":true,"msg":"登陆成功","token":token});
}else{
res.json({"code":0,"verson":false,"msg":"密码错误"});
}
}
}
module.exports = Loginmiddleware/token.js
var jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
class Tokens {
constructor(){}
testToken(req,res,next) {
var token = req.body.token || req.query.token || req.headers['x-access-token'];
if(token) {
jwt.verify(token, 'cxh' , function(err,decoded) {
if(err) {
return res.json({success:false,msg:'token错误'})
}else {
req.userInfo = decoded;
next()
}
})
}else {
return res.status(403).send({success:false,msg:"没有token"})
}
}
setToken(name,time,data) {
var jwtSecret = name;
var token = jwt.sign(data, jwtSecret, {
expiresIn: time
})
return token;
}
}
module.exports = Tokensreact部分
login.tsx
import * as React from 'react'
import * as ReactDom from 'react-dom'
import {Link, browserHistory} from 'react-router';
import * as axios from 'axios';
export default class Login extends React.Component<any,any>{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = {
userName : '',
password : '',
yzNoId : '',
hash : Math.random()
}
}
public async sbumit(params : any) : Promise<any>{
let res = await axios.post('http://localhost:3000/login',params);
if(res.data.verson){
sessionStorage.setItem('token',res.data.token);
browserHistory.push("/home")
}
}
handleUserName(e) : any {
this.setState({
userName : e.target.value
})
}
handlePassword(e) : any {
this.setState({
password : e.target.value
})
}
handleYzId(e) : any {
this.setState({
yzNoId : e.target.value
})
}
setHash() {
this.setState({
hash : Math.random()
})
}
render(){
const { userName, password, yzNoId } = this.state;
return(
<p>
<p className="nav-wrap">
<ul className="nav">
<li><Link to="/home">首页</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/imgLoad">上传</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/login">登陆</Link></li>
</ul>
</p>
<p className="content">
<p className="login-warp">
<p>
<input type="text" className="username" value={userName} onChange={this.handleUserName.bind(this)} placeholder="用户名"/>
</p>
<p>
<input type="text" className="password" value={password} onChange={this.handlePassword.bind(this)} placeholder="密码"/>
</p>
<p>
<input type="text" className="yz" value={yzNoId} onChange={this.handleYzId.bind(this)} placeholder="验证码"/>
<img src={"http://localhost:3000/captcha?aaa="+this.state.hash} className="yz-img" onClick={this.setHash.bind(this)} />
</p>
<p>
<input type="button" className="submit" value="登陆" onClick={this.sbumit.bind(this,{userName:userName,password:password,captcha:yzNoId})} />
</p>
</p>
</p>
</p>
)
}
}home.js 获取列表信息
import * as React from 'react'
import * as ReactDom from 'react-dom'
import {Link, browserHistory} from 'react-router';
import * as axios from 'axios';
class Home extends React.Component<any,any>{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = {
data : ''
}
}
async getList(): Promise<any>{
let token = sessionStorage.getItem('token');
const config = {
// 请求头信息
headers: {'x-access-token': token}
}
let res = await axios.post('http://localhost:3000/list',{},config);
if(!res.data.success){
browserHistory.push('/login');
return;
}
this.setState({
data : res.data
})
}
render(){
const { data } = this.state;
return(
<p>
<p className="nav-wrap">
<ul className="nav">
<li><Link to="/home">首页</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/imgLoad">上传</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/login">登陆</Link></li>
</ul>
</p>
<p className="content">
Home
<span onClick={this.getList.bind(this)}>获取数据</span>
<p>{
data ? data.result.map( (val,k) => {
return <li key = {k}>{val.name}</li>
}) : null
}</p>
</p>
</p>
)
}
}
export default HomeThe above is the detailed content of Complete login verification by using node.js+captchapng+jsonwebtoken. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
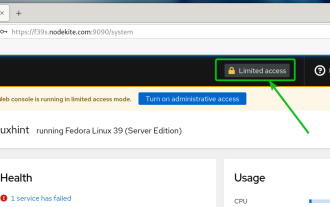 How to enable administrative access from the cockpit web UI
Mar 20, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
How to enable administrative access from the cockpit web UI
Mar 20, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
Cockpit is a web-based graphical interface for Linux servers. It is mainly intended to make managing Linux servers easier for new/expert users. In this article, we will discuss Cockpit access modes and how to switch administrative access to Cockpit from CockpitWebUI. Content Topics: Cockpit Entry Modes Finding the Current Cockpit Access Mode Enable Administrative Access for Cockpit from CockpitWebUI Disabling Administrative Access for Cockpit from CockpitWebUI Conclusion Cockpit Entry Modes The cockpit has two access modes: Restricted Access: This is the default for the cockpit access mode. In this access mode you cannot access the web user from the cockpit
 what does web mean
Jan 09, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
what does web mean
Jan 09, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
The web is a global wide area network, also known as the World Wide Web, which is an application form of the Internet. The Web is an information system based on hypertext and hypermedia, which allows users to browse and obtain information by jumping between different web pages through hyperlinks. The basis of the Web is the Internet, which uses unified and standardized protocols and languages to enable data exchange and information sharing between different computers.






