Java integrates crud and paging plug-in to operate mysql
This article mainly introduces the detailed steps of Spring mvc integrating mybatis (crud + paging plug-in) to operate mysql. Friends in need can refer to the following
1. Web.xml configuration
We all know that the first thing to do when starting a Java ee project is to read web.xml. I also explained the web.xml of spring mvc in detail in the previous article. No. If you understand, you can look back. I will also put the source code of the project I explained on github. You can also go there to have a look. I will not introduce it here.
web.xml configuration
<context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:/context.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!-- 监听器:启动服务器时,启动 spring --> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- spring 核心控制器 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:external-servlet.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <!-- 编码过滤器 --> <filter> <filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>forceEncoding</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
2. spring (context.xml) context configuration
This configuration File can be said to be the second one to be read by the server container. Here, the basic package path scanned during spring startup, the import of the attribute file of the external configuration, and the configuration of the database that needs to be connected are configured. , the integration of mybatis and spring, the mybatis date plug-in and paging plug-in we mentioned at the beginning are also configured here, and the location of the entity package and its mapper file scanned by mybatis.
context.xml configuration
<!-- spring 扫描的基础包路径 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.qbian" />
<!-- jdbc properties -->
<bean id="propertyConfigurer"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"
p:location="classpath:jdbc.properties" />
<!-- define the datasource (这里用的是c3p0的数据看连接池,性能不是很好,可以唤其它更好的连接池[jdbc pool等])-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<!-- define the SqlSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.qbian.**.dto" />
<property name="plugins">
<list>
<!-- 配置自己实现的日期插件 -->
<bean class="com.qbian.common.plugin.DatePlugin" />
<!-- 分页插件 -->
<bean class="com.qbian.common.plugin.PagePlugin" />
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- scan for mappers and let them be autowired -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.qbian.**.dao" />
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>
<!-- 将多个配置文件读取到容器中,交给Spring管理 -->
<bean id="configProperties" class="com.qbian.common.plugin.PropertiesConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<!--<value>classpath:redis.properties</value>-->
</list>
</property>
</bean>3. spring controller configuration
The location of the controller is configured here , and its supported request types and encodings.
external-servlet.xml configuration
<!-- 控制器扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.qbian.common.controller" /> <mvc:annotation-driven> <mvc:message-converters> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter"> <property name="supportedMediaTypes"> <list> <value>text/html;charset=UTF-8</value> </list> </property> <property name="writeAcceptCharset" value="false" /> </bean> </mvc:message-converters> </mvc:annotation-driven>
The configuration information is the above three, let’s take a look at the specific code,
##four , Code explanation
1. Java code explanation, the following is not sorted, just arranged in the order displayed inEditor. (The following contents are all under the java.com.qbian package)
common | annotation | @interface Now : 插入|更新数据的日期注解。 @interface UUID :插入数据的uuid注解。 controller | ExternalController.class :核心控制器,拦截所有请求,异常处理,跨域设置等功能。 dao | interface StudentDao :使用例子,crud 共通方法。 dto | PageInfoDto.class :分页使用的基础dto对象。 ResponseDto.class :响应数据的基本模型。 entity | Student.class :使用例子,自定义注解的使用。 enums | enum MessageEnum :统一的返回状态码及描述信息。 exception | ExternalServiceException.class :自定义异常,业务相关都抛出该异常对象。 factory | BeanFactoryUtil.class :根据bean name获取spring管理的bean实例。 hadle | ExceptionHandle.class :spring自带的统一异常捕获处理。 plugin | DatePlugin.class :自定义mybatis日期插件。 PagePlugin.class :自定义mybatis分页插件。 PropertiesConfigurer.class :将外部配置的属性文件读取到 spring 容器中统一管理。 service | interface IbaseServie :基础的service接口。 BaseService.class :基础的service抽象类。 TokenService.class :鉴权token服务类。 util | CheckUtil.class :请求信息校验相关工具类。 DateUtil.class :日期相关工具类。 ResponseUtil.class :响应信息工具类。 SecondsFormatSerializer.class :java.util.Date类型转时间戳工具类。 TimestampSecondsFormatSerializer.class :java.sql.Timestamp类型转时间戳工具类。 StringUtil.class :字符串相关工具类。 other | dao | interface StudentExtDao :使用例子,业务相关crud操作。 dto | QueryStudentSexPageDto.class :根据学生性别分页查询返回对象dto。 StudentPageDto.class :根据学生性别分页查询封装的对象。 service | AddStudentService.class :插入学生数据接口。 DeleteStudentService.class :删除学生数据接口。 FindStudentService.class :查询学生数据接口。 UpdateStudentService.class :更新学生数据接口。 QueryStudentBySexService.class :根据学生性别分页查询接口。
common | dao | StudentDao.xml :对应common.dao.StudentDao接口。 other | dao | StudentExtDao.xml :对应other.dao.StudentExtDao接口。
5. Function demonstration
1. Token verification
I have written the token here in the code, 123456 Indicates that the verification is successful. Let’s test it first using the insert data interface and pass an incorrect token, as shown below: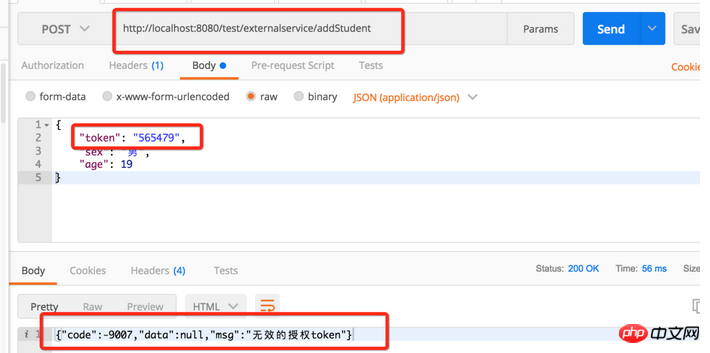
2, Request parametersVerification
Let’s take a look at what values need to be verified when inserting the data interface.// 校验请求参数
CheckUtil.checkEmpty(params, "token", "sex", "age");
// 校验 token
tokenService.checkUserLogin(params.getString("token"));
Student student = JSONObject.parseObject(params.toJSONString(), Student.class);
studentDao.insert(student);
return ResponseUtil.success();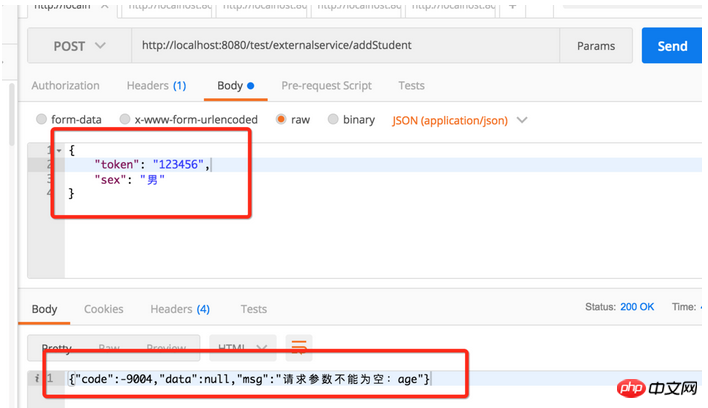
3. Insert data
Before inserting data, let’s first take a look at what data is in the database: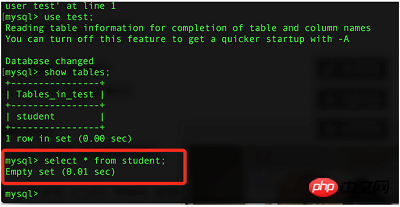
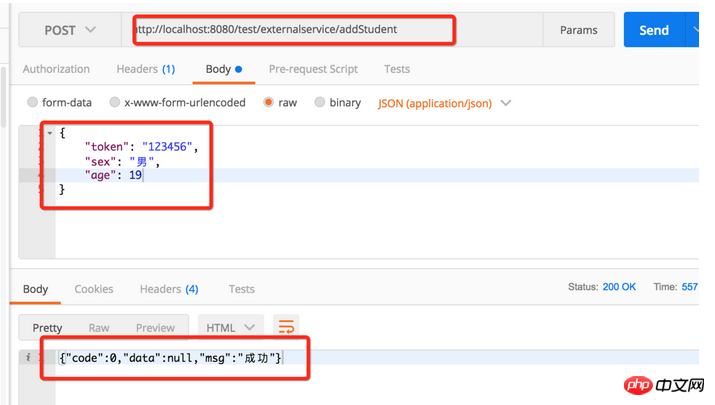
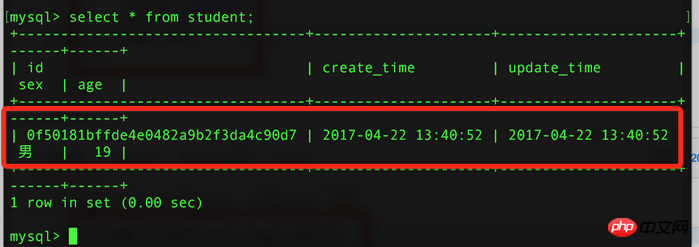
4. Query data
Query based on the ID of the previous data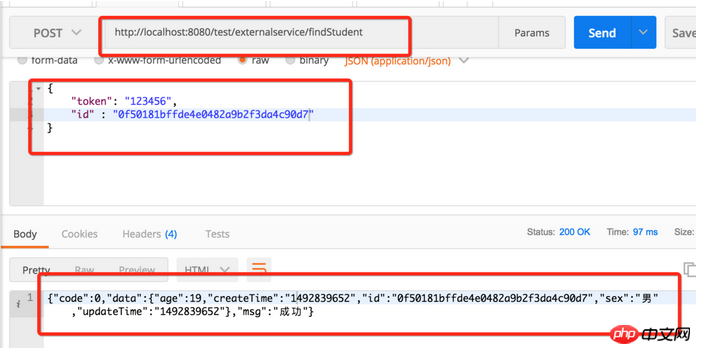
We have also queried the data we just inserted.
5. Update data
Update the queried data: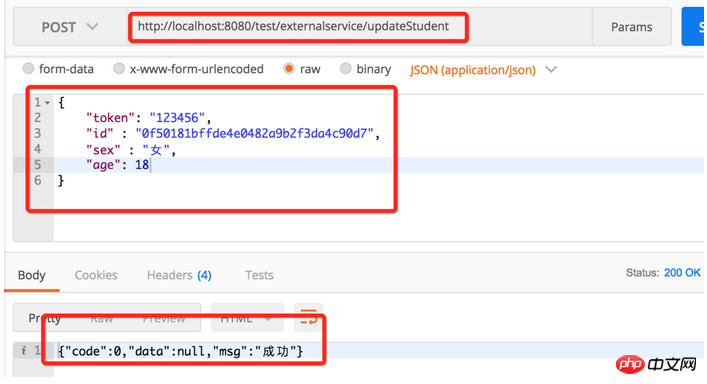
Then we query the data again
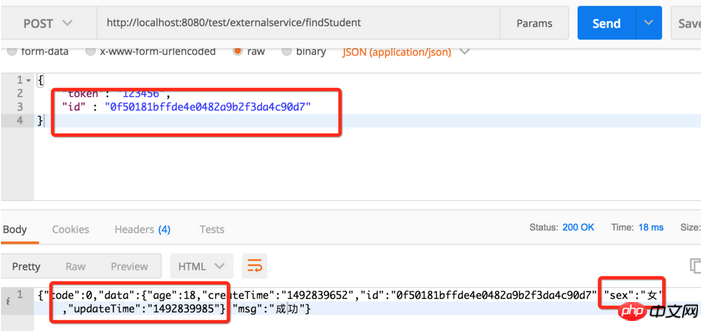
6. Paging query
Let’s take a look at the code first:// 校验请求参数
CheckUtil.checkEmpty(params, "token", "sex", "pageNo", "pageSize");
// 校验 token
tokenService.checkUserLogin(params.getString("token"));
// 根据性别分页查询 Student,查询总数会自动封装到pageDto对象上
QueryStudentSexPageDto pageDto = JSONObject.parseObject(params.toJSONString(), QueryStudentSexPageDto.class);
List<Student> students = studentExtDao.queryBySexWithPage(pageDto);
StudentPageDto studentPageDto = new StudentPageDto();
// 查询总数会自动封装到pageDto对象上
studentPageDto.setTotalSize(pageDto.getTotalSize());
studentPageDto.setStudents(students);
return ResponseUtil.success(studentPageDto);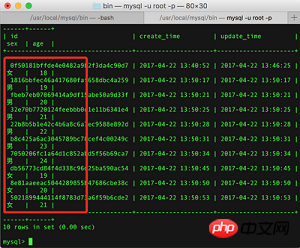
Test data before pagination
You can see that the database currently has ten test data, including six for boys, ranging in age from 19 to 24. Okay, let’s start calling the paging query interface:
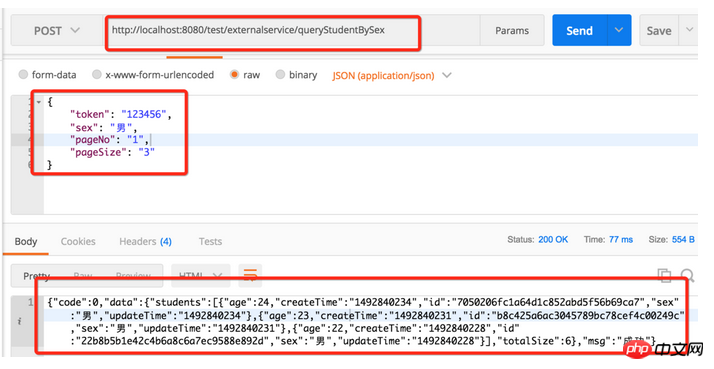
Call the paging query interface to return the results
Format the returned data:
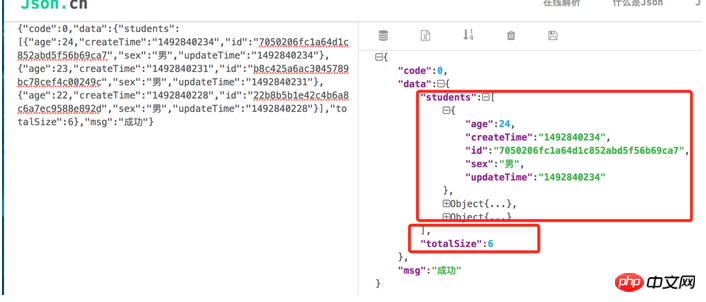
Paging query return results sorting
This is the same as what we see when directly querying the database.
7. Delete data
The last step is to delete the data interface. We will delete the first test data.
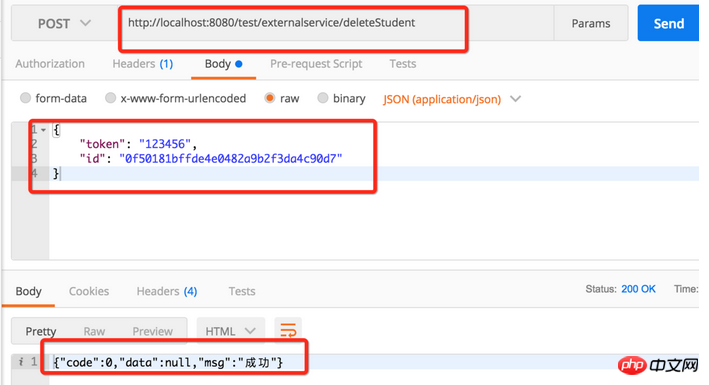
Call the delete interface to return the result
Then we check whether it is really deleted.
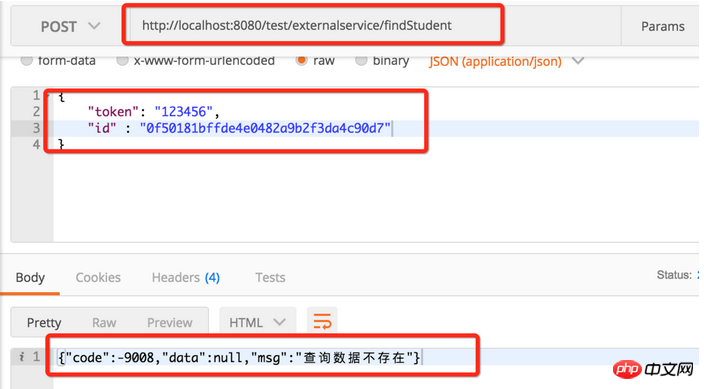
Query after deletion
The data has been deleted.
Finally, the project source code is attached: github.com/Qbian61/spring-mvc-mybatis
[Related recommendations]
2. Comprehensive analysis of Java annotations
3. Alibaba Java Development Manual
The above is the detailed content of Java integrates crud and paging plug-in to operate mysql. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Use Spring Boot and Spring AI to build generative artificial intelligence applications
Apr 28, 2024 am 11:46 AM
Use Spring Boot and Spring AI to build generative artificial intelligence applications
Apr 28, 2024 am 11:46 AM
As an industry leader, Spring+AI provides leading solutions for various industries through its powerful, flexible API and advanced functions. In this topic, we will delve into the application examples of Spring+AI in various fields. Each case will show how Spring+AI meets specific needs, achieves goals, and extends these LESSONSLEARNED to a wider range of applications. I hope this topic can inspire you to understand and utilize the infinite possibilities of Spring+AI more deeply. The Spring framework has a history of more than 20 years in the field of software development, and it has been 10 years since the Spring Boot 1.0 version was released. Now, no one can dispute that Spring
 Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Interpretation of MyBatis dynamic SQL tags: Detailed explanation of Set tag usage MyBatis is an excellent persistence layer framework. It provides a wealth of dynamic SQL tags and can flexibly construct database operation statements. Among them, the Set tag is used to generate the SET clause in the UPDATE statement, which is very commonly used in update operations. This article will explain in detail the usage of the Set tag in MyBatis and demonstrate its functionality through specific code examples. What is Set tag Set tag is used in MyBati
 Detailed explanation of MyBatis cache mechanism: understand the cache storage principle in one article
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:09 PM
Detailed explanation of MyBatis cache mechanism: understand the cache storage principle in one article
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:09 PM
Detailed explanation of MyBatis caching mechanism: One article to understand the principle of cache storage Introduction When using MyBatis for database access, caching is a very important mechanism, which can effectively reduce access to the database and improve system performance. This article will introduce the caching mechanism of MyBatis in detail, including cache classification, storage principles and specific code examples. 1. Cache classification MyBatis cache is mainly divided into two types: first-level cache and second-level cache. The first-level cache is a SqlSession-level cache. When
 Detailed explanation of MyBatis first-level cache: How to improve data access efficiency?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 08:13 PM
Detailed explanation of MyBatis first-level cache: How to improve data access efficiency?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 08:13 PM
Detailed explanation of MyBatis first-level cache: How to improve data access efficiency? During the development process, efficient data access has always been one of the focuses of programmers. For persistence layer frameworks like MyBatis, caching is one of the key methods to improve data access efficiency. MyBatis provides two caching mechanisms: first-level cache and second-level cache. The first-level cache is enabled by default. This article will introduce the mechanism of MyBatis first-level cache in detail and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand
 Analyze the caching mechanism of MyBatis: compare the characteristics and usage of first-level cache and second-level cache
Feb 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Analyze the caching mechanism of MyBatis: compare the characteristics and usage of first-level cache and second-level cache
Feb 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Analysis of MyBatis' caching mechanism: The difference and application of first-level cache and second-level cache In the MyBatis framework, caching is a very important feature that can effectively improve the performance of database operations. Among them, first-level cache and second-level cache are two commonly used caching mechanisms in MyBatis. This article will analyze the differences and applications of first-level cache and second-level cache in detail, and provide specific code examples to illustrate. 1. Level 1 Cache Level 1 cache is also called local cache. It is enabled by default and cannot be turned off. The first level cache is SqlSes
 MyBatis Generator configuration parameter interpretation and best practices
Feb 23, 2024 am 09:51 AM
MyBatis Generator configuration parameter interpretation and best practices
Feb 23, 2024 am 09:51 AM
MyBatisGenerator is a code generation tool officially provided by MyBatis, which can help developers quickly generate JavaBeans, Mapper interfaces and XML mapping files that conform to the database table structure. In the process of using MyBatisGenerator for code generation, the setting of configuration parameters is crucial. This article will start from the perspective of configuration parameters and deeply explore the functions of MyBatisGenerator.
 Security First: Best Practices to Prevent SQL Injection in MyBatis
Feb 22, 2024 pm 12:51 PM
Security First: Best Practices to Prevent SQL Injection in MyBatis
Feb 22, 2024 pm 12:51 PM
As network technology continues to develop, database attacks are becoming more and more common. SQL injection is one of the common attack methods. Attackers enter malicious SQL statements into the input box to perform illegal operations, causing data leakage, tampering or even deletion. In order to prevent SQL injection attacks, developers must pay special attention when writing code, and when using an ORM framework such as MyBatis, they need to follow some best practices to ensure the security of the system. 1. Parameterized query Parameterized query is the anti-
 Sharing optimization tips for batch Insert statements in MyBatis
Feb 22, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
Sharing optimization tips for batch Insert statements in MyBatis
Feb 22, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
MyBatis is a popular Java persistence layer framework that implements the mapping of SQL and Java methods through XML or annotations, and provides many convenient functions for operating databases. In actual development, sometimes a large amount of data needs to be inserted into the database in batches. Therefore, how to optimize batch Insert statements in MyBatis has become an important issue. This article will share some optimization tips and provide specific code examples. 1.Use BatchExecu






