 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 Front-end Q&A
Front-end Q&A
 How does vue solve the front-end cross-domain problem in axios request (detailed example)
How does vue solve the front-end cross-domain problem in axios request (detailed example)
How does vue solve the front-end cross-domain problem in axios request (detailed example)
This article brings you relevant knowledge on how vue solves front-end cross-domain problems in axios requests. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

There are many solutions to cross-domain problems in normal development. The most common one is that the backend modifies the response header. But the front end can also be solved through reverse proxy. In order to prevent such mistakes from happening next time, record and summarize them.
So now let’s review it and solve it.
1. Why do cross-domain problems occur?
Cross-domain: When the browser requests resources from a webpage of one domain name to another domain name, if the domain name, port, or protocol are different, it is cross-domain.
In the front-end and back-end separation mode, the domain names of the front and back ends are inconsistent, and cross-domain access problems will occur. The cross-domain problem comes from JavaScript's same-origin policy, that is, only if the protocol, host name, and port number (if present) are the same, mutual access is allowed. In other words, JavaScript can only access and operate resources in its own domain, but cannot access and operate resources in other domains. Cross-domain issues are for JS and ajax. Axios is an encapsulation of ajax technology through Promise, and there are also cross-domain problems.
2. Solution
Here I will use the local machine to open two different ports for testing.
Error reported before cross-domain processing is not processed

This is how the request is not processed across domains
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/getData')
.then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
.catch(err => {
console.error(err);
})Reverse proxy
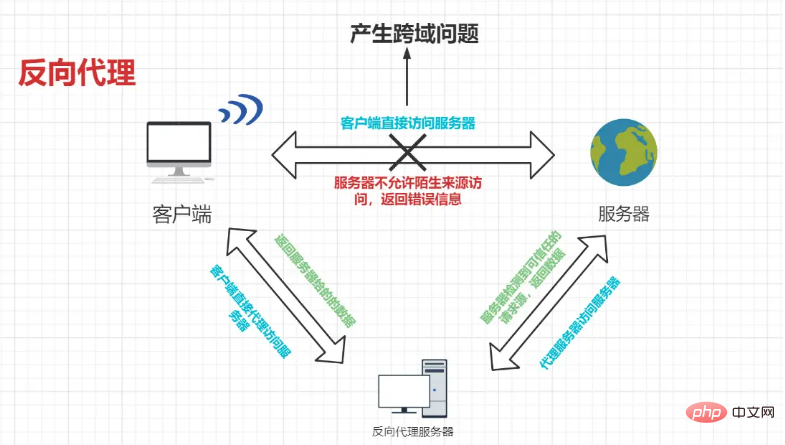
The front end performs reverse proxy to solve cross-domain problems. The schematic diagram is as follows:
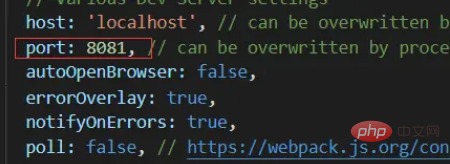
The port of the vue project is 8081
My computer has opened a port 8080, request /getData will put back the json data.
Configure proxy
1. In vue2.0
Modify the index.js file in the config folder and add the following to proxyTable Code:
proxyTable: {
'/apis': {
target: 'http://localhost:8080/', //要解决跨域的接口的域名
secure:false, //如果是https接口,需要配置这个参数
changeOrigin: true, // 如果接口跨域,需要进行这个参数配置
pathRewrite: {
'^/apis': '' // 路径重写
}
},
},Then write this in axios in the request
axios.get('apis/getData')
.then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
.catch(err => {
console.error(err);
})Analysis:
What follows the target is the public part of the URL that needs to be requested, and then use /apis to proxy This, finally rewrite some paths, and use our proxy's apis as a prefix when making requests.
We can customize this prefix. proxyTable is an object, so we can configure multiple proxies.
Cross-domain solution
2. After the scaffolding of
vue-cli3 is completed in vue3.0 , there is no vue.config.js file in the project directory, you need to manually create
to create a new vue.config.js and configure the following information, which can also be solved.
module.exports = {
devServer: {
proxy: {
'^/api': {
target: 'http://localhost:8080/',//接口的前缀
ws:true,//代理websocked
changeOrigin:true,//虚拟的站点需要更管origin
pathRewrite:{
'^/api':''//重写路径
}
}
}
}
}Summary:
changeOrigin: true: Turn on the proxy: A fake server will be created locally, then send the requested data and receive the requested data at the same time, so The server and the server can interact with data.
apis is the prefix of the actual request of the interface, which proxies the public part of our actual interface prefix, which is the protocol host name and port number
For example, the request interface is localhost:8080/getData We Just pass in: getData
Then the public domain name is localhost:8080/, we are changing the public domain name localhost:8080/ of the request interface to api/!
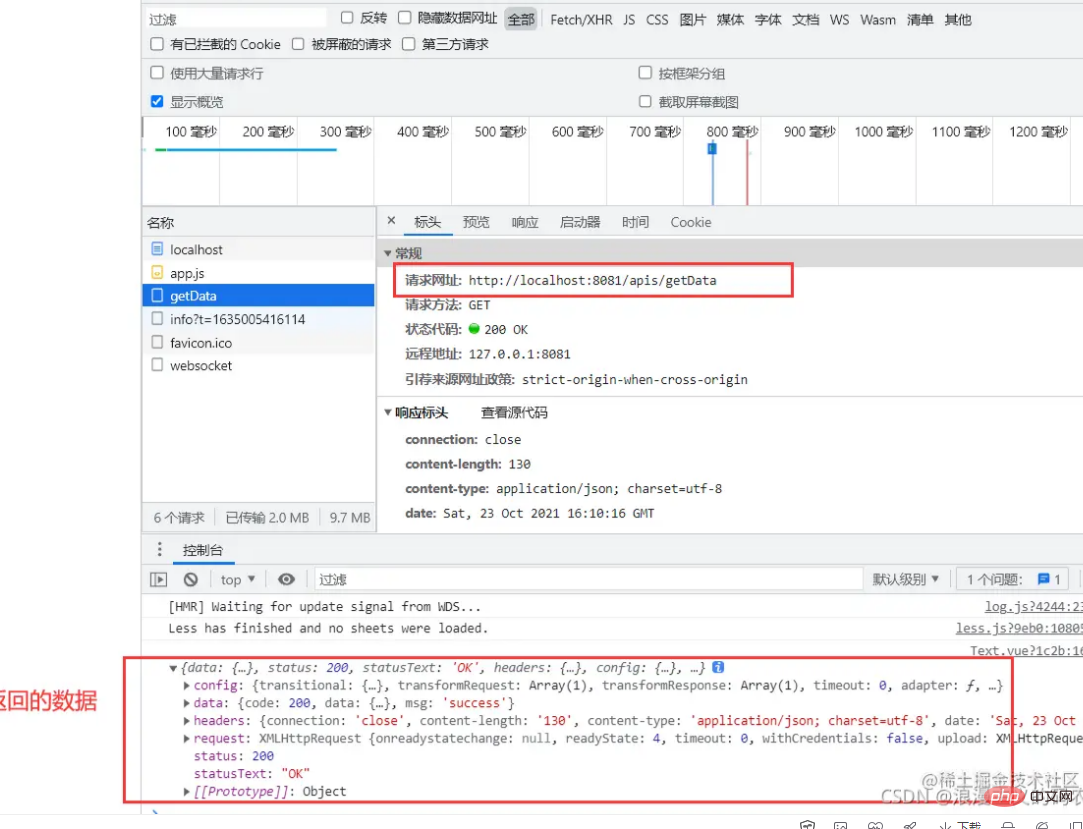
Run the project When you look up, you can see that the path of the interface request is: localhost:8081/apis/getData
. After entering the proxy, the actual request path is: localhost:8080/getData
[Related recommendations: "vue.js tutorial"】
The above is the detailed content of How does vue solve the front-end cross-domain problem in axios request (detailed example). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1668
1668
 14
14
 1427
1427
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Netflixusesacustomframeworkcalled"Gibbon"builtonReact,notReactorVuedirectly.1)TeamExperience:Choosebasedonfamiliarity.2)ProjectComplexity:Vueforsimplerprojects,Reactforcomplexones.3)CustomizationNeeds:Reactoffersmoreflexibility.4)Ecosystema
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.



