Detailed steps to compile, install and configure php8 in Centos
This article brings you relevant knowledge about PHP. It mainly introduces how to compile and install PHP in the Centos system and how to configure it correctly. The steps are very detailed! Friends who are interested can take a look below. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

PHP (full name: PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor, i.e. "PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor") is an open source general-purpose computer scripting language, especially suitable for Developed for the web and can be embedded in HTML. The syntax of PHP draws on the characteristics of popular computer languages such as C language, Java and Perl, making it easy for ordinary programmers to learn. The main goal of PHP is to allow web developers to write dynamic pages quickly.
Preparation
Download the installation file
To be safe, use php official website download: https: //www.php.net/downloads
The download speed using the official website is slower, but the security is guaranteed. If you have no requirements for security, you can also search for related mirrors on Baidu. This article chooses the latest stable version PHP 8.1.6
wget https://www.php.net/distributions/php-8.1.6.tar.gz tar -zxvf php-8.1.6.tar.gz cd php-8.1.6
yum install libxml2 libxml2-devel libsqlite3x-devel openssl bzip2 libcurl-devel libcurl libjpeg libpng freetype gmp libmcrypt libmcrypt-devel readline readline-devel libxslt libxslt-devel zlib zlib-devel glibc glib2 ncurses curl gdbm-devel db4-devel libXpm-devel libX11-devel gd-devel gmp-devel expat-devel xmlrpc-c xmlrpc-c-devel libicu-devel libmcrypt-devel libmemcached-devel -y
Note: The current Centos official image has stopped serving,
yum installInstallationdevelsoftware, if an error is reported and cannot be installed, try overwriting the file contents inCentOS-Base.repo.rpmsavein the/etc/yum.repos.d/directory. ToCentOS-Linux-BaseOS.repo,CentOS-AppStream.repo.rpmsaveis overwritten toCentOS-Linux-AppStream.repo, please make a backup before operation
Because there is no oniguruma package in the yum source, here we use the github source code to compile and install. Project address: https://github.com/kkos/oniguruma
wget https://github.com/kkos/oniguruma/releases/download/v6.9.8/onig-6.9.8.tar.gz tar -zxvf onig-6.9.8.tar.gz cd onig-6.9.8 ./configure --prefix=/usr make && make install
For security reasons, we need to create a user for running php. Generally, this user is prohibited from logging in. This article creates a user The name and user group are both www, this name can be customized
# 创建用户组 groupadd www # 创建用户 useradd -g www www -M -s /sbin/nologin
- ##-g www
Specify user group - -M
Do not create a home directory (a home directory is not required to run the program) - -s /sbin/nologin
Do not allow login , more secure
Compile and install# 生成编译文件
./configure --prefix=/www/server/php81 --with-config-file-path=/www/server/php81/etc --enable-fpm --with-fpm-group=www --enable-mysqlnd --with-mysqli=mysqlnd --with-pdo-mysql=mysqlnd --with-iconv-dir --with-freetype --with-mcrypt --with-jpeg --with-png -with-zlib --with-libxml-dir --enable-xml --disable-rpath --enable-bcmath --enable-shmop --enable-sysvsem --enable-inline-optimization --with-curl -enable-mbstring --enable-gd --with-openssl --with-mhash --enable-pcntl --with-xmlrpc --enable-zip --enable-soap --with-gettext --enable-opcache --with-xsl --enable-sockets --enable-mbregex --enable-ftp --with-webp
# 编译并安装
make && make install
# 复制配置文件
cp php.ini-production /www/server/php81/etc/php.ini
# 或者使用 development
cp php.ini-development /www/server/php81/etc/php.ini
Copy after login
# 生成编译文件 ./configure --prefix=/www/server/php81 --with-config-file-path=/www/server/php81/etc --enable-fpm --with-fpm-group=www --enable-mysqlnd --with-mysqli=mysqlnd --with-pdo-mysql=mysqlnd --with-iconv-dir --with-freetype --with-mcrypt --with-jpeg --with-png -with-zlib --with-libxml-dir --enable-xml --disable-rpath --enable-bcmath --enable-shmop --enable-sysvsem --enable-inline-optimization --with-curl -enable-mbstring --enable-gd --with-openssl --with-mhash --enable-pcntl --with-xmlrpc --enable-zip --enable-soap --with-gettext --enable-opcache --with-xsl --enable-sockets --enable-mbregex --enable-ftp --with-webp # 编译并安装 make && make install # 复制配置文件 cp php.ini-production /www/server/php81/etc/php.ini # 或者使用 development cp php.ini-development /www/server/php81/etc/php.ini
apache , you need to add --with-apxs2=/www/server/apache/bin/apxs in the compilation parameters, and the --enable-fpm parameter can be removed, where /www/server/apache is the installation directory of apache. After compilation, uncomment the php_module in the configuration file of apache. , this article will not go into details about apache configuration.
Configuration
Configuration environment variables
In/etc/profile Add PATH=$PATH:/www/server/php81/bin && export PATH, and use source /etc/profile to make the configuration take effect immediately.
php-fpm Soft link:
ln -s /www/server/php81/sbin/php-fpm /www/server/php81/bin/php-fpm
nginx configuration php
Copy the configuration file. If you have copied it before, please skip this step:cp /www/server/php81/etc/php-fpm.conf.default /www/server/php81/etc/php-fpm.conf cp /www/server/php81/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf.default /www/server/php81/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
/www/server/php81/sbin/php-fpm
nginx.conf file, add the following content under the corresponding server:
location ~ [^/]\.php(/|$) {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
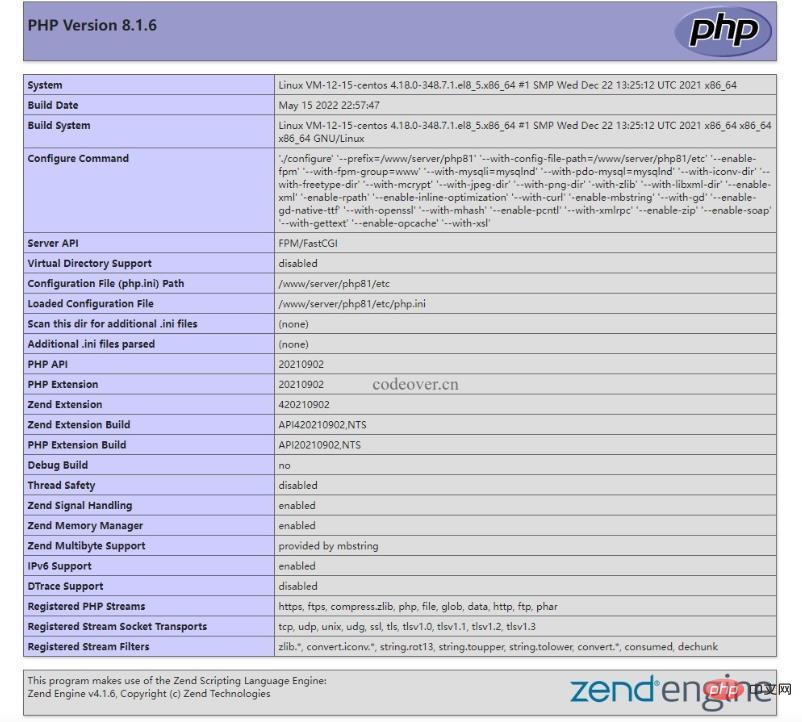
}, create a new phpinfo.php file in the root directory of the website: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'><?php
phpinfo();</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>
推荐学习:《PHP视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of Detailed steps to compile, install and configure php8 in Centos. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP is used to build dynamic websites, and its core functions include: 1. Generate dynamic content and generate web pages in real time by connecting with the database; 2. Process user interaction and form submissions, verify inputs and respond to operations; 3. Manage sessions and user authentication to provide a personalized experience; 4. Optimize performance and follow best practices to improve website efficiency and security.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP: Handling Databases and Server-Side Logic
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP: Handling Databases and Server-Side Logic
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP uses MySQLi and PDO extensions to interact in database operations and server-side logic processing, and processes server-side logic through functions such as session management. 1) Use MySQLi or PDO to connect to the database and execute SQL queries. 2) Handle HTTP requests and user status through session management and other functions. 3) Use transactions to ensure the atomicity of database operations. 4) Prevent SQL injection, use exception handling and closing connections for debugging. 5) Optimize performance through indexing and cache, write highly readable code and perform error handling.
 Why Use PHP? Advantages and Benefits Explained
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Why Use PHP? Advantages and Benefits Explained
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:16 AM
The core benefits of PHP include ease of learning, strong web development support, rich libraries and frameworks, high performance and scalability, cross-platform compatibility, and cost-effectiveness. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners; 2) Good integration with web servers and supports multiple databases; 3) Have powerful frameworks such as Laravel; 4) High performance can be achieved through optimization; 5) Support multiple operating systems; 6) Open source to reduce development costs.
 How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Improve HDFS performance on CentOS: A comprehensive optimization guide to optimize HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system) on CentOS requires comprehensive consideration of hardware, system configuration and network settings. This article provides a series of optimization strategies to help you improve HDFS performance. 1. Hardware upgrade and selection resource expansion: Increase the CPU, memory and storage capacity of the server as much as possible. High-performance hardware: adopts high-performance network cards and switches to improve network throughput. 2. System configuration fine-tuning kernel parameter adjustment: Modify /etc/sysctl.conf file to optimize kernel parameters such as TCP connection number, file handle number and memory management. For example, adjust TCP connection status and buffer size
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.