Understand Python crawler in one article
This article brings you relevant knowledge about Python, which mainly introduces relevant knowledge about crawlers. Simply put, crawlers are a name for the process of using programs to obtain data on the Internet. Let’s take a look at it together. I hope it helps everyone.

What is a crawler?
A crawler is simply a name for the process of using a program to obtain data on the Internet.
Principle of crawler
If we want to obtain data on the network, we need to give the crawler a website address (usually called URL in the program), the crawler sends an HTTP request to the server of the target web page, and the server returns the data To the client (that is, our crawler), the crawler then performs a series of operations such as data parsing and saving.
Process
Crawlers can save us time. For example, if I want to get the top 250 Douban movies, if we don’t use crawlers, we must first enter the URL of Douban movies on the browser, and the client ( The browser) finds the IP address of the server of the Douban Movie web page through analysis, and then establishes a connection with it. The browser creates an HTTP request and sends it to the Douban Movie server. After the server receives the request, it extracts the Top250 list from the database. , encapsulate it into an HTTP response, and then return the response result to the browser. The browser displays the response content and we see the data. Our crawler is also based on this process, but it is changed into code form.
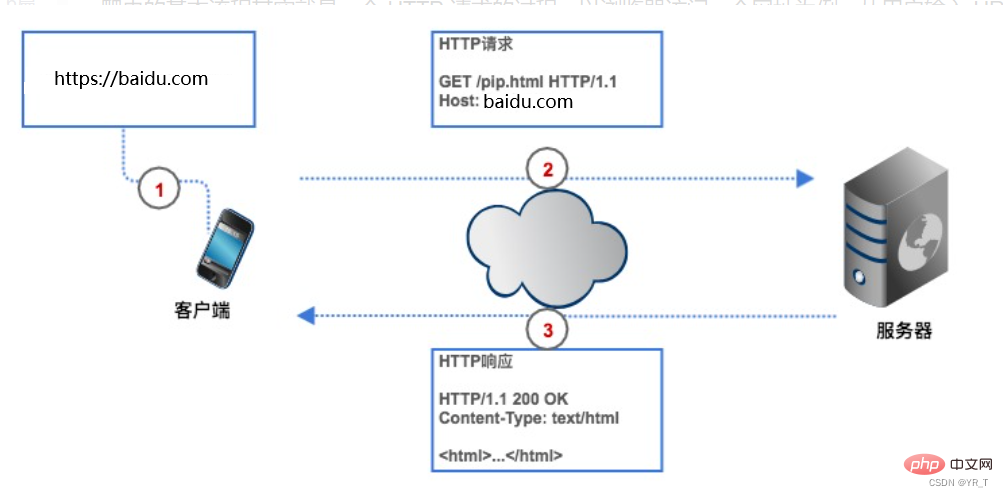
HTTP request
HTTP request consists of request line, request header, blank line, and request body.

The request line consists of three parts:
1. Request method, common request methods are GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD
2. The resource path that the client wants to obtain
3. It is the HTTP protocol version number used by the client
The request header is a supplementary description of the request sent by the client to the server, such as the identity of the visitor, which will be discussed below .
The request body is the data submitted by the client to the server, such as the account and password information that needs to be improved when the user logs in. The request header and request body are separated by blank lines. The request body is not included in all requests. For example, general GET does not have a request body.
The picture above is the HTTP POST request sent to the server when the browser logs into Douban. The username and password are specified in the request body.
HTTP response
HTTP response format is very similar to the request format, and also consists of response lines, response headers, blank lines, and response bodies.

The response line also contains three parts, namely the HTTP version number of the server, the response status code and the status description.
There is a table of status codes here, corresponding to the meaning of each status code



cmd run: pip install requests to install requests.Then enter import requests on IDLE or a compiler (personally recommend VS Code or Pycharm) to run. If no error is reported, the installation is successful. The method to install most libraries is: pip install xxx (name of library)
Methods of requests
| Construct a request and support the basic methods of each method | |
| The main method to obtain HTML web pages, corresponding to HTTP's GET | |
| requests.head() | Method to obtain HTML web page header information, corresponding to HTTP HEAD |
| To The method of submitting a POST request to an HTML web page, corresponding to HTTP's POST | |
| The method of submitting a PUT request to an HTML web page, corresponding to HTTP's PUT | |
| Submit a partial modification request to the HTML web page, corresponding to HTTP's PATCT | |
| Submit a delete request to an HTML web page, corresponding to HTTP's DELETE |
| The return status of the HTTP request, 200 indicates successful connection, 404 indicates failure | |
| The string form of the HTTP response content, that is, the page content corresponding to the url | |
| The response content encoding method guessed from the HTTP header (if the header If charset does not exist, the encoding is considered to be ISO-8859-1) | |
| The response content encoding method analyzed from the content (alternative encoding method ) | |
| The binary form of the HTTP response content |
| Network connection error exception, such as DNS query failure, connection refused, etc. | |
| HTTP error exception | |
| URL missing exception | |
| Exceeds the maximum number of redirects and generates Redirect exception | |
| Timeout exception when connecting to the remote server | |
| The request URL times out, resulting in a timeout exception |
I will first put the project structure of a small crawler project I made. The complete source code can be downloaded by private chatting with me.
import requests
def English_Chinese():
url = "https://fanyi.baidu.com/sug"
s = input("请输入要翻译的词(中/英):")
dat = {
"kw":s
}
resp = requests.post(url,data = dat)# 发送post请求
ch = resp.json() # 将服务器返回的内容直接处理成json => dict
resp.close()
dic_lenth = len(ch['data'])
for i in range(dic_lenth):
print("词:"+ch['data'][i]['k']+" "+"单词意思:"+ch['data'][i]['v'])

[ {xx:xx} , {xx:xx} , {xx:xx} , {xx:xx} ] }
The place I marked in red is information we need. Suppose there are n dictionaries in the list marked blue, we can get the value of n through the len() function, and use a for loop to traverse to get the result.dic_lenth = len(ch['data']
for i in range(dic_lenth):
print("词:"+ch['data'][i]['k']+" "+"单词意思:"+ch['data'][i]['v'])# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import requests
import bs4
def get_web(url):
header = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.114 Safari/537.36 Edg/91.0.864.59"}
res = requests.get(url, headers=header, timeout=5)
# print(res.encoding)
content = res.text.encode('ISO-8859-1')
return content
def parse_content(content):
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(content, 'lxml')
'''
存放天气情况
'''
list_weather = []
weather_list = soup.find_all('p', class_='wea')
for i in weather_list:
list_weather.append(i.text)
'''
存放日期
'''
list_day = []
i = 0
day_list = soup.find_all('h1')
for each in day_list:
if i <= 6:
list_day.append(each.text.strip())
i += 1
# print(list_day)
'''
存放温度:最高温度和最低温度
'''
tem_list = soup.find_all('p', class_='tem')
i = 0
list_tem = []
for each in tem_list:
if i == 0:
list_tem.append(each.i.text)
i += 1
elif i > 0:
list_tem.append([each.span.text, each.i.text])
i += 1
# print(list_tem)
'''
存放风力
'''
list_wind = []
wind_list = soup.find_all('p', class_='win')
for each in wind_list:
list_wind.append(each.i.text.strip())
# print(list_wind)
return list_day, list_weather, list_tem, list_wind
def get_content(url):
content = get_web(url)
day, weather, tem, wind = parse_content(content)
item = 0
for i in range(0, 7):
if item == 0:
print(day[i]+':\t')
print(weather[i]+'\t')
print("今日气温:"+tem[i]+'\t')
print("风力:"+wind[i]+'\t')
print('\n')
item += 1
elif item > 0:
print(day[i]+':\t')
print(weather[i] + '\t')
print("最高气温:"+tem[i][0]+'\t')
print("最低气温:"+tem[i][1] + '\t')
print("风力:"+wind[i]+'\t')
print('\n')Python3 video tutorial】
The above is the detailed content of Understand Python crawler in one article. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1667
1667
 14
14
 1426
1426
 52
52
 1328
1328
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1255
1255
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".




