 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Analysis of the main features and differences of different versions of HTTP
Analysis of the main features and differences of different versions of HTTP
Analysis of the main features and differences of different versions of HTTP
HTTP has many versions, and each version also has its own differences. This article is an overview and summary of the main features of HTTP different versions. I hope it can help everyone.
HTTP1.0
The earlier HTTP version of 1.0 is a stateless, connectionless application layer protocol.
HTTP1.0 stipulates that the browser and the server maintain a short-lived connection. Each request of the browser needs to establish a TCP connection with the server. After the server completes processing The TCP connection is immediately disconnected (no connection) and the server does not track each client nor log past requests (stateless).
This statelessness can be done with the help of the cookie/session mechanism for identity authentication and status recording. The following two questions are more troublesome.
First of all, the biggest performance flaw caused by the connectionless feature is the inability to reuse connections. Every time a request is sent, a TCP connection is required, and the TCP connection release process is more troublesome. This connectionless feature makes network utilization very low.
The second is head of line blocking (head of line blocking). Because HTTP1.0 stipulates that the next request must be sent before the response to the previous request arrives. Assuming that the response to the previous request never arrives, the next request will not be sent, and the same subsequent requests will also be blocked.
In order to solve these problems, HTTP1.1 appeared.
HTTP1.1
For HTTP1.1, it not only inherits the simple features of HTTP1.0, but also overcomes many HTTP1 .0Performance issues.
First is long connection, HTTP1.1 adds a Connection field, which can be set by setting Keep-Alive Keep the HTTP connection from being disconnected, avoiding the need to repeatedly establish, release and establish the TCP connection every time the client and server request, improving network utilization. If the client wants to close the HTTP connection, it can carry Connection: false in the request header to tell the server to close the request.
Secondly, HTTP1.1 supports request pipelining (pipelining). Long connections based on HTTP1.1 make request pipelines possible. Pipelining allows requests to be transmitted in parallel. For example, if the main body of the response is a html page, and the page contains a lot of img, then keep-alive will play a big role. The function is to be able to send multiple requests in parallel. (The client establishes a connection to the server based on the domain name. Generally, PC browsers will establish 6~8 connections to the server of a single domain name at the same time. Mobile terminals generally control 4~6 connections. . This is why many large websites set up different static resource CDN domain names to load resources)
It should be noted that the server must send back the corresponding results in the order requested by the client to ensure that. The client can distinguish the response content of each request.
In other words, HTTPPipeline allows us to migrate the first-in-first-out queue from the client (request queue) to the server (response queue).
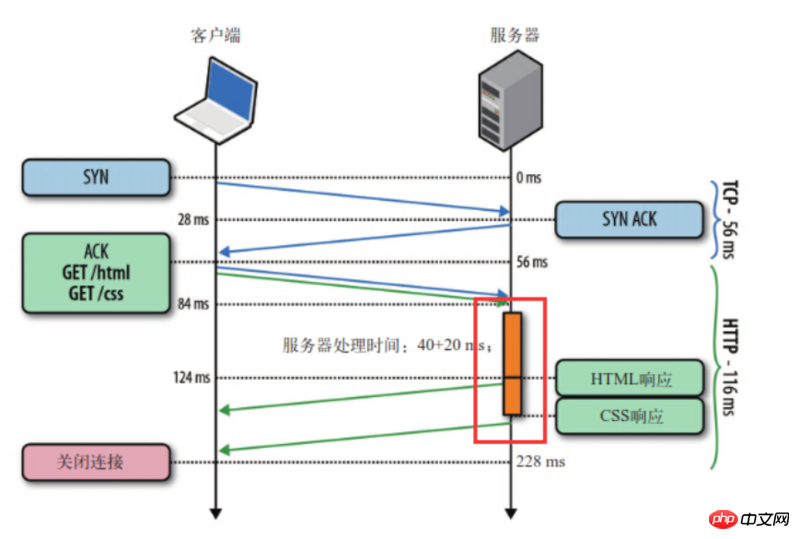
As shown in the figure, the client sent two requests at the same time to obtain html and css, if the server's css resource is ready first, the server will also send html first and then css.
At the same time, pipeline technology only allows the client to send a set of requests to a server at the same time. If the client wants to initiate another set of requests to the same server, it must also wait for the previous set of requests. All responses completed.
It can be seen that HTTP1.1 solves the problem of head of line blocking (head of line blocking) is not yet complete. At the same time, there are various problems with "pipeline" technology, so many browsers either do not support it at all, or they simply turn it off by default, and the conditions for turning it on are very strict...
In addition, HTTP1.1 also adds caching processing (strong cache and negotiation cache [portal]), supports breakpoint transmission, and adds a Host field(Enables one server to be used to create multiple Web sites).
HTTP2.0
The new features of HTTP2.0 are roughly as follows:
Binary Framing
HTTP2.0By adding a binary framing layer between the application layer and the transport layer, it breaks through the performance limitations of HTTP1.1 and improves transmission performance.
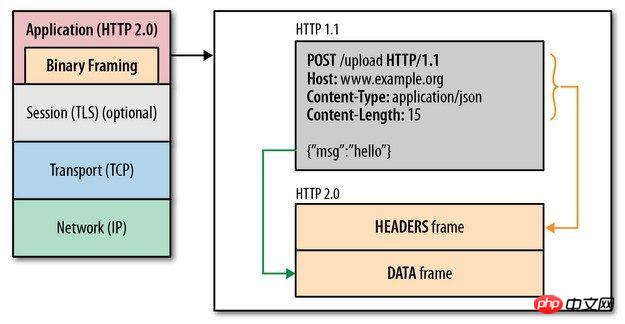
It can be seen that although the specifications between the HTTP2.0 protocol and the HTTP1.x protocol are completely different, in fact HTTP2.0 has not changed The semantics of HTTP1.x.
Simply put, HTTP2.0 just replaces the header and body parts of the original HTTP1.x with frameJust re-encapsulated one layer.
Multiplexing (connection sharing)
The following are several concepts:
Stream (
stream): Bidirectional byte stream on an established connection.Message: A complete series of data frames corresponding to the logical message.
Frame (
frame):HTTP2.0The smallest unit of communication. Each frame contains a frame header, which at least identifies the current The stream to which the frame belongs (stream id).
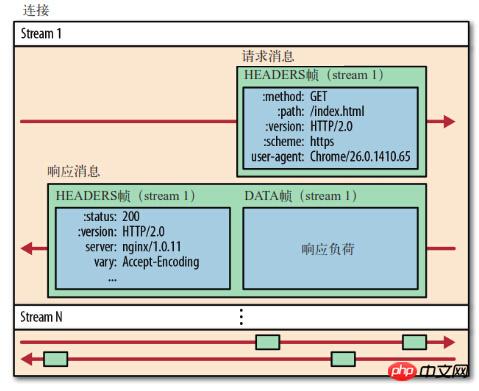
HTTP2.0 communications are completed on one connection , this connection can carry any number of bidirectional data streams.
stream id) in the header of each frame.
stream id for identification. Frames belonging to different data streams can be randomly mixed together in the connection. The receiver can re-attribute the frames to different requests based on stream id.
HTTP2.0 can set priority and dependencies. Data flows with high priority will be processed by the server first and returned to the client. Data flows can also depend on other sub-data flows.
Header compression
InHTTP1.x, header metadata is sent in plain text and is usually added to each request 500~800 bytes of payload.
cookie, by default, the browser will attach cookie to header and send it to server. (Since cookie is relatively large and is sent repeatedly every time, information is generally not stored and is only used for status recording and identity authentication)
HTTP2.0Useencoder To reduce the size of header that needs to be transmitted, both communicating parties cache each have a header fields table, which avoids duplication of header 's transmission also reduces the size that needs to be transmitted. An efficient compression algorithm can greatly compress header, reduce the number of packets sent and thereby reduce latency.
Server Push
In addition to responding to the initial request, the server can push additional resources to the client without explicit request from the client. SummaryHTTP1.0
- ##Stateless, no connection
- Persistent Connection
- Request Pipelining
- Add caching processing
- Add
- Host
field, support breakpoint transmission, etc.
- Binary Framing
- Multiplexing (or connection sharing)
- Header Compression
- Server Push
- Related recommendations:
The above is the detailed content of Analysis of the main features and differences of different versions of HTTP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand the meaning of HTTP 301 status code: common application scenarios of web page redirection. With the rapid development of the Internet, people's requirements for web page interaction are becoming higher and higher. In the field of web design, web page redirection is a common and important technology, implemented through the HTTP 301 status code. This article will explore the meaning of HTTP 301 status code and common application scenarios in web page redirection. HTTP301 status code refers to permanent redirect (PermanentRedirect). When the server receives the client's
 How to implement HTTP streaming using C++?
May 31, 2024 am 11:06 AM
How to implement HTTP streaming using C++?
May 31, 2024 am 11:06 AM
How to implement HTTP streaming in C++? Create an SSL stream socket using Boost.Asio and the asiohttps client library. Connect to the server and send an HTTP request. Receive HTTP response headers and print them. Receives the HTTP response body and prints it.
 Are there any class-like object-oriented features in Golang?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:51 PM
Are there any class-like object-oriented features in Golang?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:51 PM
There is no concept of a class in the traditional sense in Golang (Go language), but it provides a data type called a structure, through which object-oriented features similar to classes can be achieved. In this article, we'll explain how to use structures to implement object-oriented features and provide concrete code examples. Definition and use of structures First, let's take a look at the definition and use of structures. In Golang, structures can be defined through the type keyword and then used where needed. Structures can contain attributes
 What status code is returned for an HTTP request timeout?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
What status code is returned for an HTTP request timeout?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
The HTTP request times out, and the server often returns the 504GatewayTimeout status code. This status code indicates that when the server executes a request, it still fails to obtain the resources required for the request or complete the processing of the request after a period of time. It is a status code of the 5xx series, which indicates that the server has encountered a temporary problem or overload, resulting in the inability to correctly handle the client's request. In the HTTP protocol, various status codes have specific meanings and uses, and the 504 status code is used to indicate request timeout issues. in customer
 Choose the applicable Go version, based on needs and features
Jan 20, 2024 am 09:28 AM
Choose the applicable Go version, based on needs and features
Jan 20, 2024 am 09:28 AM
With the rapid development of the Internet, programming languages are constantly evolving and updating. Among them, Go language, as an open source programming language, has attracted much attention in recent years. The Go language is designed to be simple, efficient, safe, and easy to develop and deploy. It has the characteristics of high concurrency, fast compilation and memory safety, making it widely used in fields such as web development, cloud computing and big data. However, there are currently different versions of the Go language available. When choosing a suitable Go language version, we need to consider both requirements and features. head
 How to solve HTTP 503 error
Mar 12, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
How to solve HTTP 503 error
Mar 12, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
Solution: 1. Retry: You can wait for a period of time and try again, or refresh the page; 2. Check the server load: Check the server's CPU, memory and disk usage. If the capacity limit is exceeded, you can try to optimize the server configuration or increase the capacity. Server resources; 3. Check server maintenance and upgrades: You can only wait until the server returns to normal; 4. Check network connection: Make sure the network connection is stable, check whether the network device, firewall or proxy settings are correct; 5. Ensure cache or CDN configuration Correct; 6. Contact the server administrator, etc.
 How to implement HTTP file upload security using Golang?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:45 PM
How to implement HTTP file upload security using Golang?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:45 PM
Implementing HTTP file upload security in Golang requires following these steps: Verify file type. Limit file size. Detect viruses and malware. Store files securely.
 C++ function types and characteristics
Apr 11, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
C++ function types and characteristics
Apr 11, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
C++ functions have the following types: simple functions, const functions, static functions, and virtual functions; features include: inline functions, default parameters, reference returns, and overloaded functions. For example, the calculateArea function uses π to calculate the area of a circle of a given radius and returns it as output.





