Detailed explanation of PHP operating database based on ORM
This article mainly introduces PHP to operate the MySQL database based on the ORM method, and analyzes PHP's encapsulation and usage skills for common operations of the MySQL database based on specific examples. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope to be helpful.
The example in this article describes how PHP operates the MySQL database based on the ORM method. Share it with everyone for your reference, the details are as follows:
ORM----Oriented Relationship Mapper, which uses an object-oriented approach to operate the database. In the final analysis, it is still about the encapsulation of SQL statements.
First of all, our database has the following table:
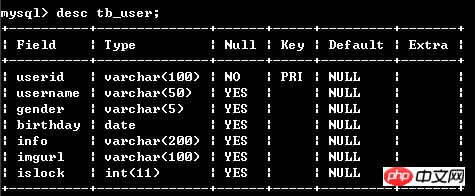
We hope to use setUserid("11111") on this table, that is, Set userid; getUserid() can get the userid of the object. Therefore, we need to create a model object corresponding to the table in the database.
Since the model corresponding to each table should have set/get operations, we use a parent class BasicModel to define it. Other models inherit from this model.
The code of BasicModel is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
|
Then, the model class TbUser corresponding to the tb_user table inherits it.
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
In this way, we can perform set/get operations on the instance of TbUser.
To use ORM to operate the database, you must be able to query with findByWhere($where), and the returned object array; save($tbUser) to save; delete($obj) to delete; update($obj) ) to perform the update operation.
Essentially, the user passes in an object, and we use code to convert the object into a SQL statement. In essence, SQL statements are still executed.
So, we use interfaces to represent a series of operations. The code of IBasicDAO is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
|
The most important thing for us is to implement this interface. Complete the conversion of objects and SQL.
BasicDAO code is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 |
|
So, when operating the tb_user table, TbUserDAO is mainly used. It sets the modelName to "TbUser", and the code knows that the table being operated is tb_user, and then You can perform a series of operations.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
|
Then, you can operate the database in an object-oriented manner.
For example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
Update the records in the database.
Related recommendations:
Detailed explanation of how to batch modify the table structure in PHP
Detailed explanation of PHP's addition, deletion and modification of xml files
Detailed explanation of how PHP implements csv file import into the database
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of PHP operating database based on ORM. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1677
1677
 14
14
 1431
1431
 52
52
 1334
1334
 25
25
 1280
1280
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 What is the significance of the session_start() function?
May 03, 2025 am 12:18 AM
What is the significance of the session_start() function?
May 03, 2025 am 12:18 AM
session_start()iscrucialinPHPformanagingusersessions.1)Itinitiatesanewsessionifnoneexists,2)resumesanexistingsession,and3)setsasessioncookieforcontinuityacrossrequests,enablingapplicationslikeuserauthenticationandpersonalizedcontent.
 How to use MySQL functions for data processing and calculation
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:21 PM
How to use MySQL functions for data processing and calculation
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:21 PM
MySQL functions can be used for data processing and calculation. 1. Basic usage includes string processing, date calculation and mathematical operations. 2. Advanced usage involves combining multiple functions to implement complex operations. 3. Performance optimization requires avoiding the use of functions in the WHERE clause and using GROUPBY and temporary tables.
 Composer: The Package Manager for PHP Developers
May 02, 2025 am 12:23 AM
Composer: The Package Manager for PHP Developers
May 02, 2025 am 12:23 AM
Composer is a dependency management tool for PHP, and manages project dependencies through composer.json file. 1) parse composer.json to obtain dependency information; 2) parse dependencies to form a dependency tree; 3) download and install dependencies from Packagist to the vendor directory; 4) generate composer.lock file to lock the dependency version to ensure team consistency and project maintainability.
 How to configure the character set and collation rules of MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:06 PM
How to configure the character set and collation rules of MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:06 PM
Methods for configuring character sets and collations in MySQL include: 1. Setting the character sets and collations at the server level: SETNAMES'utf8'; SETCHARACTERSETutf8; SETCOLLATION_CONNECTION='utf8_general_ci'; 2. Create a database that uses specific character sets and collations: CREATEDATABASEexample_dbCHARACTERSETutf8COLLATEutf8_general_ci; 3. Specify character sets and collations when creating a table: CREATETABLEexample_table(idINT
 How to rename a database in MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
How to rename a database in MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
Renaming a database in MySQL requires indirect methods. The steps are as follows: 1. Create a new database; 2. Use mysqldump to export the old database; 3. Import the data into the new database; 4. Delete the old database.
 Composer's Purpose: Managing Project Dependencies in PHP
Apr 30, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Composer's Purpose: Managing Project Dependencies in PHP
Apr 30, 2025 am 12:01 AM
We need Composer because it can effectively manage dependencies of PHP projects and avoid the hassle of version conflicts and manual library management. Composer declares dependencies through composer.json and uses composer.lock to ensure the version consistency, simplifying the dependency management process and improving project stability and development efficiency.
 MongoDB: The Document Database Explained
Apr 30, 2025 am 12:04 AM
MongoDB: The Document Database Explained
Apr 30, 2025 am 12:04 AM
MongoDB is a NoSQL database that is suitable for handling large amounts of unstructured data. 1) It uses documents and collections to store data. Documents are similar to JSON objects and collections are similar to SQL tables. 2) MongoDB realizes efficient data operations through B-tree indexing and sharding. 3) Basic operations include connecting, inserting and querying documents; advanced operations such as aggregated pipelines can perform complex data processing. 4) Common errors include improper handling of ObjectId and improper use of indexes. 5) Performance optimization includes index optimization, sharding, read-write separation and data modeling.
 How to set the rotation effect of HTML elements
Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
How to set the rotation effect of HTML elements
Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
How to set the rotation effect of an element in HTML? It can be achieved using CSS and JavaScript. 1. The transform property of CSS is used for static rotation, such as rotate(45deg). 2. JavaScript can dynamically control rotation, which is implemented by changing the transform attribute.




