How to choose between Apache and Nginx
There are many WEB server products on the market, and the mainstream ones are Apache and Nginx. But how to choose between Apache and Nginx also makes many novices confused. This article compares Apache and Nginx to give everyone a clearer understanding and choice.
1. Introduction
Apache:
Apache was created in 1995 and has been developed under the Apache Software Foundation since 1999 development. Apache is flexible, efficient, has rich extension modules, and active community support, making it the most mainstream open source and free web server software in the world.
Nginx:
Nginx is a free and open source web server written by Russian software engineer Igor Sysoev. Since its launch in 2004, nginx has focused on high performance, high concurrency and low memory usage. And its features in load balancing, caching, access and bandwidth control, and efficient integration with various applications have made it gradually popular among users.
The following is the latest web server market share comparison chart updated on November 21, 2017:
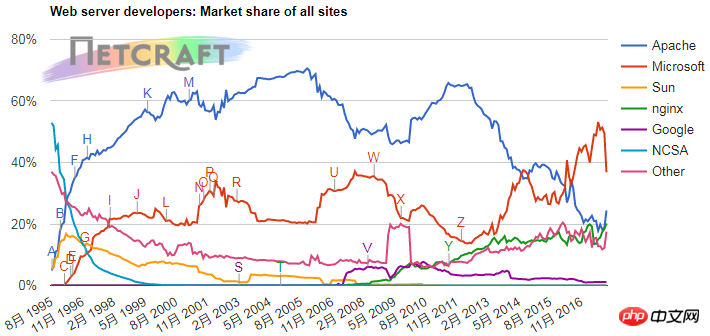
## 2. Comparison
Although Apache and Nginx have different backgrounds, their functions and purposes are the same. Simply put, they receive user requests, then process the requests, and finally return the processing results to the users. 1. Link processingThe biggest difference between Apache and Nginx is how they handle connections. Apache provides a series of multi-processing modules through which operating system resources are used, processes and thread pools are managed, and user requests are controlled and processed. Apache provides three multi-processing modules: mpm_prefork, mpm_worker, and mpm_envent. Let’s make a brief description and comparison below. mpm_prefork: The module generates many sub-processes, each sub-process is single-threaded, and each thread links a request, such a one-to-one relationship. Therefore, if the number of requests is greater than the number of processes, the performance of the server will be unsatisfactory.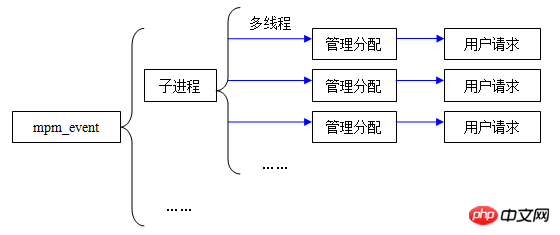

##2. Processing of static and dynamic contentWhether it is static or dynamic content, Apache can handle it. Apache has built-in capabilities to parse and execute various dynamic script languages (including PHP, Python, and Perl) without the need for external processors.
There is no doubt that dynamic content processing is probably the pain point of Nginx. Nginx is not efficient at processing dynamic content and requires the help of an external processor. So if your site has a lot of dynamic features, Apache's performance may be more to your liking. However, although Nginx has poor dynamic content processing capabilities compared to Apache, its static content processing is still very efficient.
3. SummaryApache has rich module component support, strong stability, few BUGs, and strong dynamic content processing.
Nginx is lightweight, takes up less resources, has load balancing, strong high concurrency processing, and efficient static content processing.
It makes sense to exist. Apache and Nginx have their own strengths as WEB services. I personally think that there is no such thing as one of them will completely replace the other in the future. The key is that users should carefully consider their application scenarios and decide which product to choose based on their own needs and circumstances. The one that suits them is the best.
How to configure Apache HTTP Server under Ubuntu 16.04
Detailed explanation of the installation and configuration of apache, php7 and mysql5.7 in CentOS7 Sample code for replacing Nginx server with Tengine in LNMP environment Nginx reverse proxy and load balancing practice
The above is the detailed content of How to choose between Apache and Nginx. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Nginx in Windows? Install Nginx and create a virtual host configuration. Modify the main configuration file and include the virtual host configuration. Start or reload Nginx. Test the configuration and view the website. Selectively enable SSL and configure SSL certificates. Selectively set the firewall to allow port 80 and 443 traffic.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure an Nginx domain name on a cloud server: Create an A record pointing to the public IP address of the cloud server. Add virtual host blocks in the Nginx configuration file, specifying the listening port, domain name, and website root directory. Restart Nginx to apply the changes. Access the domain name test configuration. Other notes: Install the SSL certificate to enable HTTPS, ensure that the firewall allows port 80 traffic, and wait for DNS resolution to take effect.
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]
 How to build a Zookeeper cluster in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
How to build a Zookeeper cluster in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
Deploying a ZooKeeper cluster on a CentOS system requires the following steps: The environment is ready to install the Java runtime environment: Use the following command to install the Java 8 development kit: sudoyumininstalljava-1.8.0-openjdk-devel Download ZooKeeper: Download the version for CentOS (such as ZooKeeper3.8.x) from the official ApacheZooKeeper website. Use the wget command to download and replace zookeeper-3.8.x with the actual version number: wgethttps://downloads.apache.or
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP







