 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Three ways of infinite classification (iteration, recursion, reference)
Three ways of infinite classification (iteration, recursion, reference)
Three ways of infinite classification (iteration, recursion, reference)
There are two general classification tree structures:
One is the adjacency list, which is the form of id and parent id.
The other is nested set, which is the form of left and right values.
The left and right value formquery is more efficient and does not require recursion, etc. It is recommended to use, but it is not as simple and intuitive as the pid form, and some are old The structural design of databases similar to regions has always been in the form of pid (it seems that there are algorithms that can convert the two, but I won’t go into details), so. . .
The following are all in the form of adjacency list. The data table is similar to the format of id, pid, name.
Usually, this is achieved by reading all the data from the database and then assembling the array. Of course, you can also query the database every time you recurse, but it will cause database pressure, and It is not easy to encapsulate into a method and is not recommended.
Currently, there are three commonly used methods. Let’s implement the select drop-down menu display style:
1. The first is the most commonly used and common, and also the least efficient. The recursive method: just keep foreachlooprecursion.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
|
2. The second method is to use the recursion of pushing and popping into the stack to calculate. The efficiency is better than the previous one, but It's also quite slow. The process is to first reverse the array, then take out the top-level array and push it onto the stack, start the while loop, first pop one out of the stack to find if there is a child node under it, and if there is a child node, push this child node into the stack as well. The next while loop will check the child nodes, and so on:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
|
3. Use to quote Processing, this is really clever and the most efficient, you can refer to here:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
|
Then recursively generate the select drop-down menu required , due to the special format above, the recursion is very fast:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
The above three are suitable for small amounts of data. , it doesn’t matter which one is used, but it is very obvious for large amounts of data. Efficiency comparison of test results using 4000 regional data:
The first method (recursive) is time-consuming : About 8.9441471099854
The second method (iteration) takes about 6.7250330448151
The third method (reference) takes time: 0.028863906860352 Left and right
Let me go, this gap, the third method is really outrageous. But remind me again, this is only when reading a lot of data at one time. When the amount of data is very small, the difference is almost the same. You don’t have to use the most efficient one. It can also be achieved through other methods such as lazy loading.
Encapsulate a class by the way, you can add some padding or something. More details can be found in the following classes:
1 |
|
View Code
Record the above, if you reprint, please indicate the source address
The above is the detailed content of Three ways of infinite classification (iteration, recursion, reference). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1304
1304
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Is there a limit to recursion depth?
Apr 23, 2024 am 09:30 AM
Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Is there a limit to recursion depth?
Apr 23, 2024 am 09:30 AM
The recursion depth of C++ functions is limited, and exceeding this limit will result in a stack overflow error. The limit value varies between systems and compilers, but is usually between 1,000 and 10,000. Solutions include: 1. Tail recursion optimization; 2. Tail call; 3. Iterative implementation.
 Do C++ lambda expressions support recursion?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Do C++ lambda expressions support recursion?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Yes, C++ Lambda expressions can support recursion by using std::function: Use std::function to capture a reference to a Lambda expression. With a captured reference, a Lambda expression can call itself recursively.
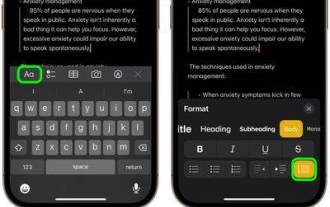 How to use block quotes in Apple Notes
Oct 12, 2023 pm 11:49 PM
How to use block quotes in Apple Notes
Oct 12, 2023 pm 11:49 PM
In iOS 17 and macOS Sonoma, Apple has added new formatting options for Apple Notes, including block quotes and a new Monostyle style. Here's how to use them. With additional formatting options in Apple Notes, you can now add block quotes to your notes. The block quote format makes it easy to visually offset sections of writing using the quote bar to the left of the text. Just tap/click the "Aa" format button and select the block quote option before typing or when you are on the line you want to convert to a block quote. This option applies to all text types, style options, and lists, including checklists. In the same Format menu you can find the new Single Style option. This is a revision of the previous "equal-width"
 Count the number of occurrences of a substring recursively in Java
Sep 17, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
Count the number of occurrences of a substring recursively in Java
Sep 17, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
Given two strings str_1 and str_2. The goal is to count the number of occurrences of substring str2 in string str1 using a recursive procedure. A recursive function is a function that calls itself within its definition. If str1 is "Iknowthatyouknowthatiknow" and str2 is "know" the number of occurrences is -3. Let us understand through examples. For example, input str1="TPisTPareTPamTP", str2="TP"; output Countofoccurrencesofasubstringrecursi
 Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Comparative analysis of recursive and non-recursive algorithms?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Comparative analysis of recursive and non-recursive algorithms?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
The recursive algorithm solves structured problems through function self-calling. The advantage is that it is simple and easy to understand, but the disadvantage is that it is less efficient and may cause stack overflow. The non-recursive algorithm avoids recursion by explicitly managing the stack data structure. The advantage is that it is more efficient and avoids the stack. Overflow, the disadvantage is that the code may be more complex. The choice of recursive or non-recursive depends on the problem and the specific constraints of the implementation.
 C++ Recursion Advanced: Understanding Tail Recursion Optimization and Its Application
Apr 30, 2024 am 10:45 AM
C++ Recursion Advanced: Understanding Tail Recursion Optimization and Its Application
Apr 30, 2024 am 10:45 AM
Tail recursion optimization (TRO) improves the efficiency of certain recursive calls. It converts tail-recursive calls into jump instructions and saves the context state in registers instead of on the stack, thereby eliminating extra calls and return operations to the stack and improving algorithm efficiency. Using TRO, we can optimize tail recursive functions (such as factorial calculations). By replacing the tail recursive call with a goto statement, the compiler will convert the goto jump into TRO and optimize the execution of the recursive algorithm.
 What are the benefits of C++ functions returning reference types?
Apr 20, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
What are the benefits of C++ functions returning reference types?
Apr 20, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
The benefits of functions returning reference types in C++ include: Performance improvements: Passing by reference avoids object copying, thus saving memory and time. Direct modification: The caller can directly modify the returned reference object without reassigning it. Code simplicity: Passing by reference simplifies the code and requires no additional assignment operations.
 Detailed explanation of C++ function recursion: application of recursion in string processing
Apr 30, 2024 am 10:30 AM
Detailed explanation of C++ function recursion: application of recursion in string processing
Apr 30, 2024 am 10:30 AM
A recursive function is a technique that calls itself repeatedly to solve a problem in string processing. It requires a termination condition to prevent infinite recursion. Recursion is widely used in operations such as string reversal and palindrome checking.



