PHPYaf execution process source code
Introduction
YafFramework is a # The PHP framework written in ##c language is a PHP development framework provided in the form of a PHP extension. Compared with the general PHP framework, it is faster and lighter , the memory usage is lower, that is, in the pursuit of performance, Yaf abstracts the non-variable parts of the framework, such as routing, automatic loading, bootstrap, distribution, etc., are implemented using PHP extensions to ensure performance
Yaf advantages- ##The PHP framework developed in c language is better than the native one. PHP will bring almost no additional performance overhead
- All framework classes do not need to be compiled, are loaded when PHP starts, and are resident in memory.
- Flexible automatic loading. Supports global and local loading rules, convenient
- class library yaf Disadvantages
- High maintenance cost. To maintain PHP extensions, you need to be skilled in C development and Z
- end
Api.
The target user group is small. Now many small and medium-sized websites in China use - Virtual Host Unlike other frameworks that provide a variety of feature-rich class libraries and various elegant writing methods, it only provides a basic
- MVC Yaf framework execution flow chart
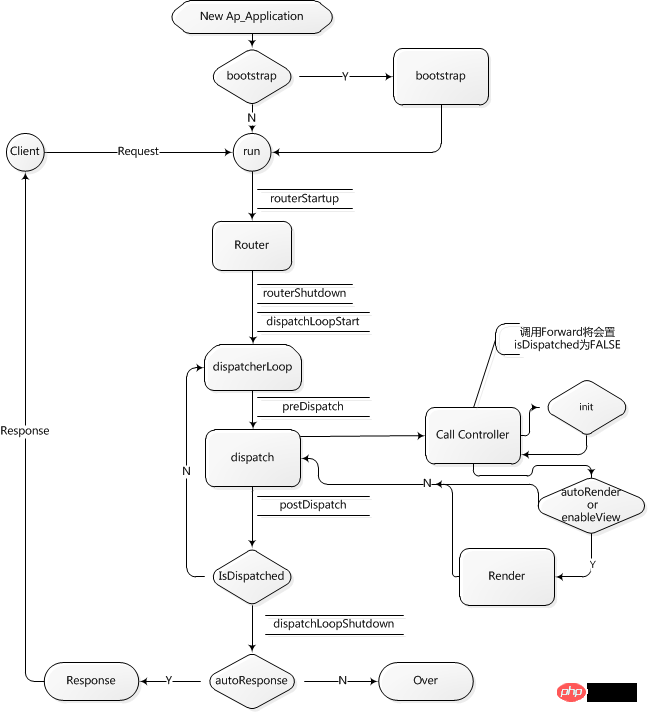
##Quote
object
, and then calls its run method. run contains all the links in the figure. Run first calls routing. The main purpose of routing is actually to find the controllers file. , and then execute the init andaction methods inside, or find the addresses of all actions and load them, and then execute the corresponding execute method. If autoRender is set, the render method will be executed when returning, which is automatic rendering of the view. , there are six links marked with double horizontal lines in the figure, which are six plug-in methods. Users can customize these methods, and then the Yaf framework will call the corresponding HOOK method at the corresponding step in the figure. Yaf frameworkDirectory structure
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
+ public
|- index.php //入口文件
|- .htaccess //重写规则
|+ css
|+ img
|+ js
+ conf
|- application.ini //配置文件
+ application
|+ actions //可将controller里面的方法单独抽出来做为一个类实现
|+ index
|- Main.php
|+ controllers
|- Index.php //默认控制器
|+ views
|+ index //控制器
|- index.phtml //默认视图
|+ modules //可以按模块来区分不同业务下的控制器层
|+ admin
|+ controllers
|- Index.php
|+ library //本地类库
|+ models //model目录
|- baseModel.php
|+ plugins //插件目录
|- testPlugin.php
Bootstrap.php 引导文件
Copy after login
Yaf configuration item description
php.ini configuration item1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
|
| 选项名称 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| yaf.environ | product | 环境名称, 当用INI作为Yaf的配置文件时, 这个指明了Yaf将要在INI配置中读取的节的名字 |
| yaf.library | NULL | 全局类库的目录路径 |
| yaf.cache_config | 0 | 是否缓存配置文件(只针对INI配置文件生效), 打开此选项可在复杂配置的情况下提高性能 |
| yaf.name_suffix | 1 | 在处理Controller, Action, Plugin, Model的时候, 类名中关键信息是否是后缀式, 比如UserModel, 而在前缀模式下则是ModelUser |
| yaf.name_separator | "" | 在处理Controller, Action, Plugin, Model的时候, 前缀和名字之间的分隔符, 默认为空, 也就是UserPlugin, 加入设置为"_", 则判断的依据就会变成:"User_Plugin", 这个主要是为了兼容ST已有的命名规范 |
| yaf.forward_limit | 5 | forward最大嵌套深度 |
| yaf.use_namespace | 0 | 开启的情况下, Yaf将会使用命名空间方式注册自己的类, 比如Yaf_Application将会变成Yaf\Application |
| yaf.use_spl_autoload | 0 | 开启的情况下, Yaf在加载不成功的情况下, 会继续让PHP的自动加载函数加载, 从性能考虑, 除非特殊情况, 否则保持这个选项关闭 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
application.ini 配置项
| 选项名称 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| application.ext | php | PHP脚本的扩展名 |
| application.bootstrap | Bootstrapplication.php | Bootstrap路径(绝对路径) |
| application.library | application.directory + "/library" | 本地(自身)类库的绝对目录地址 |
| application.baseUri | NULL | 在路由中, 需要忽略的路径前缀, 一般不需要设置, Yaf会自动判断. |
| application.dispatcher.defaultModule | index | 默认的模块 |
| application.dispatcher.throwException | True | 在出错的时候, 是否抛出异常 |
| application.dispatcher.catchException | False | 是否使用默认的异常捕获Controller, 如果开启, 在有未捕获的异常的时候, 控制权会交给ErrorController的errorAction方法, 可以通过$request->getException()获得此异常对象 |
| application.dispatcher.defaultController | index | 默认的控制器 |
| application.dispatcher.defaultAction | index | 默认的动作 |
| application.view.ext | phtml | 视图模板扩展名 |
| application.modules | modules | 声明存在的模块名, 请注意, 如果你要定义这个值, 一定要定义Index Module |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
|
可以看到在application.ini配置文件里面除了配置框架本身的配置项,还可以添加一些我们自定义的配置项,同时支持继承配置功能,在框架启动的时候会根据yaf.environ设定的节点名字去读取.
配置文件解析完毕后读取到内存的状态
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
|
调用Yaf框架
1 2 3 4 |
|
Bootstrap.php 类文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
|
Plugin.php 插件类文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
Controller.php 类文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
|
Action.php 类文件
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
Model 类文件
1 2 3 4 |
|
注意: Yaf并没有实现Model层,需要自己实现或者调用现成的Model库.
扩展-核心功能模块实现
扩展 Yaf_Application 类注册
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 |
|
上面这个就是在扩展里面注册一个类的实现,Yaf其他的类文件在注册类的时候也几乎和上面方式一致,具体看下源码就可以了,下面将从实例化一个Yaf_Application类开始分析。
扩展 Yaf_Application 类构造函数 construct 实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 |
|
PHP_METHOD(Yaf_application, bootstrap) 扩展实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 |
|
PHP_METHOD(yaf_application, run) 扩展实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
|
yaf_dispatcher_dispatch() 方法里面主要分两部分,路由+分发,其中夹杂着一些插件调用,就是上图中双横线标出的环节,先看下官方对插件的说明。
| 触发顺序 | 名称 | 触发时机 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | routerStartup | 在路由之前触发 |
| 2 | routerShutdown | 路由结束之后触发 |
| 3 | dispatchLoopStartup | 分发循环开始之前被触发 |
| 4 | preDispatch | 分发之前触发 |
| 5 | postDispatch | 分发结束之后触发 |
| 6 | dispatchLoopShutdown | 分发循环结束之后触发 |
扩展中插件方法名用宏表示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
yaf_dispatcher_dispatch(yaf_dispatcher_t *dispatcher TSRMLS_DC)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 |
|
yaf_dispatcher_route() 路由入口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
|
这段代码是路由环节的入口,dispatcher初始化时会创建内置路由器,这里只涉及路由器概念,上面的自定义并不是自定义路由协议,而是你可以重新写一个路由器,我们通常在项目中自定义路由协议就可以了,没有必要自己实现一个路由器。而且框架中其实也是写死了内置路由器,没有给你set自定义路由器的接口。
yaf_router_route() 执行路由
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 |
|
内置的路由协议
Yaf_Route_Static
Yaf_Route_Simple
Yaf_Route_Supervar
Yaf_Route_Rewrite
Yaf_Route_Regex
Yaf_Route_Map
上面几种路由协议源代码列表
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
无路是哪个路由协议最后功能都是为了设置module,controller,action的名称
yaf_dispatcher_handle() 开始分发
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 |
|
yaf_dispatcher_get_controller() 获取 controller 类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 |
|
yaf_dispatcher_get_action() 获取 action 类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 |
|
上面也看到action的路径是按照你所填写的映射中地址加载,但是类名却是action的名称拼接的,所以虽然类文件不需要按照Yaf的标准路径设定,但是类名必须和action一致,在这个环节可能会因为action的特殊性出现找不到类的问题.
Yaf 自动加载
在实例化 application 类的时候,内部会自动实例化一个 Yaf_Loader 对象,同时往内核注册了一个自动加载器 autoload 这里注册自动加载器也是用内核提供的 spl_autoload_register
yaf_loader_register() 注册自动加载器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 |
|
PHP_METHOD(yaf_loader, autoload) 自动加载器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 |
|
yaf_internal_autoload() 加载类文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 |
|
结束
上面介绍的大致就是 Yaf 框架一个运行流程,并且把框架的主要代码都分析了一遍,可以以此作为引导,在阅读分析源码的时候可以边看源码边对照 Yaf 框架官方文档 或者在用Yaf框架搭建一个环境,运行下,在对照源码分析即可。
The above is the detailed content of PHPYaf execution process source code. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1311
1311
 25
25
 1262
1262
 29
29
 1234
1234
 24
24
 Explain different error types in PHP (Notice, Warning, Fatal Error, Parse Error).
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Explain different error types in PHP (Notice, Warning, Fatal Error, Parse Error).
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:03 AM
There are four main error types in PHP: 1.Notice: the slightest, will not interrupt the program, such as accessing undefined variables; 2. Warning: serious than Notice, will not terminate the program, such as containing no files; 3. FatalError: the most serious, will terminate the program, such as calling no function; 4. ParseError: syntax error, will prevent the program from being executed, such as forgetting to add the end tag.
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 Explain secure password hashing in PHP (e.g., password_hash, password_verify). Why not use MD5 or SHA1?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Explain secure password hashing in PHP (e.g., password_hash, password_verify). Why not use MD5 or SHA1?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:06 AM
In PHP, password_hash and password_verify functions should be used to implement secure password hashing, and MD5 or SHA1 should not be used. 1) password_hash generates a hash containing salt values to enhance security. 2) Password_verify verify password and ensure security by comparing hash values. 3) MD5 and SHA1 are vulnerable and lack salt values, and are not suitable for modern password security.
 PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is widely used in e-commerce, content management systems and API development. 1) E-commerce: used for shopping cart function and payment processing. 2) Content management system: used for dynamic content generation and user management. 3) API development: used for RESTful API development and API security. Through performance optimization and best practices, the efficiency and maintainability of PHP applications are improved.
 What are HTTP request methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) and when should each be used?
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:09 AM
What are HTTP request methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) and when should each be used?
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:09 AM
HTTP request methods include GET, POST, PUT and DELETE, which are used to obtain, submit, update and delete resources respectively. 1. The GET method is used to obtain resources and is suitable for read operations. 2. The POST method is used to submit data and is often used to create new resources. 3. The PUT method is used to update resources and is suitable for complete updates. 4. The DELETE method is used to delete resources and is suitable for deletion operations.
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 How does PHP handle file uploads securely?
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:37 AM
How does PHP handle file uploads securely?
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:37 AM
PHP handles file uploads through the $\_FILES variable. The methods to ensure security include: 1. Check upload errors, 2. Verify file type and size, 3. Prevent file overwriting, 4. Move files to a permanent storage location.
 Explain the difference between self::, parent::, and static:: in PHP OOP.
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain the difference between self::, parent::, and static:: in PHP OOP.
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
In PHPOOP, self:: refers to the current class, parent:: refers to the parent class, static:: is used for late static binding. 1.self:: is used for static method and constant calls, but does not support late static binding. 2.parent:: is used for subclasses to call parent class methods, and private methods cannot be accessed. 3.static:: supports late static binding, suitable for inheritance and polymorphism, but may affect the readability of the code.




