 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Build Apache, PHP, MySQL5.6.22, phpMyAdmin development environment on MAC OSX10.10
Build Apache, PHP, MySQL5.6.22, phpMyAdmin development environment on MAC OSX10.10
Build Apache, PHP, MySQL5.6.22, phpMyAdmin development environment on MAC OSX10.10
I am used to using an appserv or phpStudy compressed package on Windows, but I am not used to creating a PHP development environment on MAC. But there is still something to gain from setting up the environment yourself. As we all know, OSX comes with apache and php, so these two are relatively smooth. Installing the latest version of MySQL, version 5.6.22, is quite difficult, and this article records it in detail.
apache configuration
apache already comes with it, you only need the following three commands.
Start the apache service sudo apachectl start
Stop the apache service sudo apachectl stop
Restart the service httpd -v
After manually opening the apache service, enter localhost in the browser and you will see Go to the following:
The root directory of the program is under /Library/WebServer/Documents/. This It works is printed out by the info.php inside. The following describes how to change the default directory of apache to the user directory. 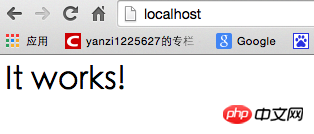 1. Create a new Sites folder in your own user directory. My user directory is yanzi
1. Create a new Sites folder in your own user directory. My user directory is yanzi
2. Go to the cd /etc/apache2/users/ directory and sudo vim username.conf. The content is:
<Directory "/Users/yanzi/Sites/"> AllowOverride AllOptions Indexes MultiViews FollowSymLinks Require all granted </Directory>
sudo chmod 644 username.conf
3, go to the /etc/apache2/ directory, sudo vim httpd.conf and remove the comments of the following three sentences:
LoadModule authz_core_module libexec/apache2/ mod_authz_core.so
LoadModule userdir_module libexec/apache2/mod_userdir.so
The first two sentences should be uncommented. Uncomment the third sentence.
Then find the Include /private/etc/apache2/extra/httpd-userdir.conf comment and release it.
PS: Just switch to command mode under vim and enter /"words you need find" to quickly find the words you need to find.
4. Go to the /etc/apache2/extra/ directory,
sudo vim httpd-userdir.conf
Then enter in the terminal: sudo apachectl restart to restart apache, enter in the browser: loacal/~yanzi/ and you will see the effect. (yanzi is the name of my user directory,
No need to add /Sites after it
After the above steps, apache is ready. PHP configuration
Install MySQL5.6.22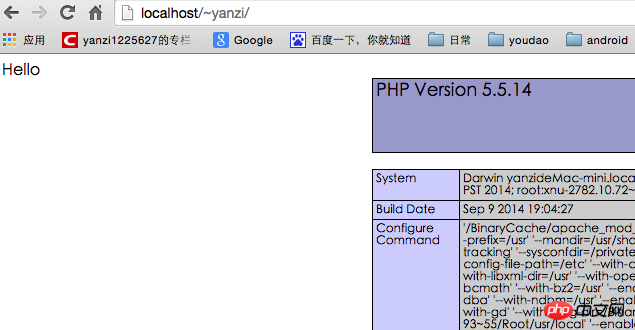
1. When double-clicking to install, do not check the StartUp Item:
After the installation is completed, in the settings - --MySQL Manually start the MySQL service. 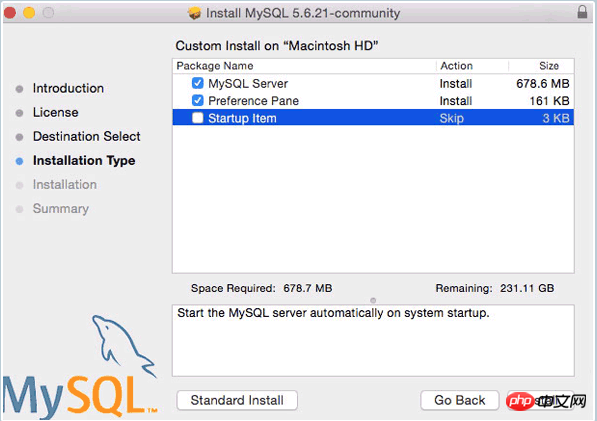
I have opened the MySQL service here. Next, set it to start automatically at boot. 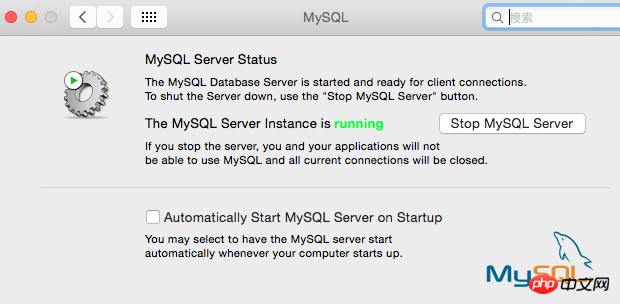 2. By default, we must enter the full path every time we use the mysql command, such as sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start to start the mysql service, /usr/local/mysql/bin /mysql -v To view the mysql version, you must first add the bin directory to the environment variable. Switch to the user root directory, vim .bash_profile, enter:
2. By default, we must enter the full path every time we use the mysql command, such as sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start to start the mysql service, /usr/local/mysql/bin /mysql -v To view the mysql version, you must first add the bin directory to the environment variable. Switch to the user root directory, vim .bash_profile, enter:
export PATH="/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH"
Finally, set the password for the mysql root user through mysqladmin -u root password ‘yourpasswordhere’. The content in single quotes is the password to be set.
Note: Sometimes the above command cannot modify the root password, and you need to use phpmyadmin to modify it. In fact, the default root password for this version of mysql is root.
3, fix the socket error problem. There is a socket file responsible for communication between the mysql server and client. This version of mysql places it in the /tmp directory, but OSX looks for the /var/mysql directory by default, so a soft link must be created. Create a new directory /var/mysql, then sudo ln -s /tmp/mysql.sock /var/mysql/mysql.sock and it will be ok.
4. Let mysql start automatically when booting.
sudo vim /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.mysql.mysql.plist, enter the content:
KeepAlive
Label
com.mysql.mysqld
ProgramArguments
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe
–user=mysql
After saving, modify permissions:
sudo chown root:wheel /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.mysql.mysql.plist
sudo chmod 644 /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.mysql.mysql.plist
sudo launchctl load -w /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.mysql.mysql.plist
This way mysql will be ok!
Installation of phpMyAdmin
Download from http://www.phpmyadmin.net/home_page/downloads.php. I downloaded the version phpMyAdmin-4.4.2-all-languages.zip and unzipped it. Then change the name of the outermost folder to phpmyadmin, go to the directory ~/Sites/phpmyadmin, create a new folder: mkdir config, modify the read and write permissions: chmod o+w config
Then enter the browser: http://localhost/~ yanzi/phpmyadmin/setup/ (Note that yanzi in the middle is replaced with your own user name) 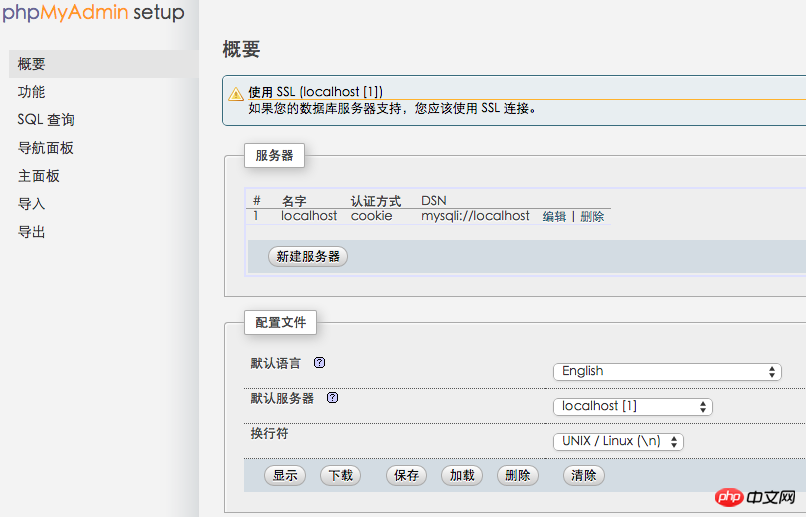
Click "New Server", I have already created it above, and then enter the mysql root user password in this interface: 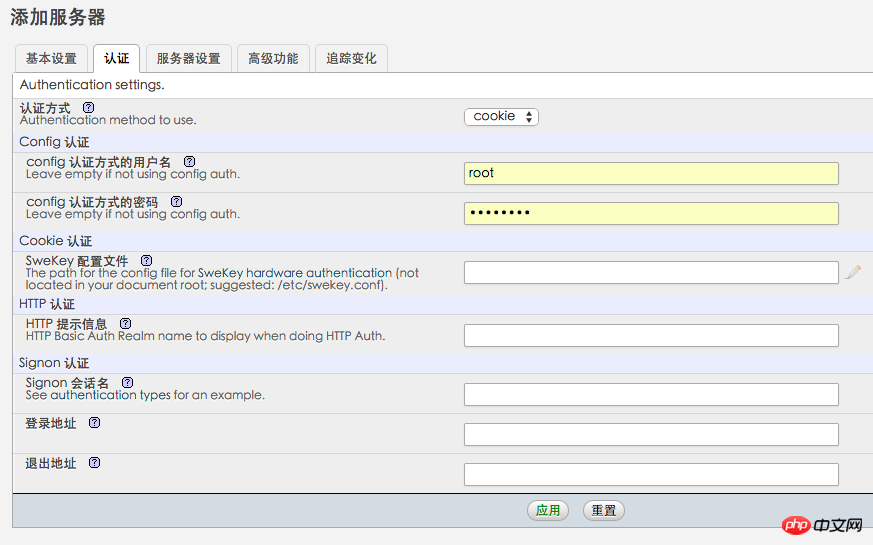
Password . Then click "Apply", remember to click the save button on the following interface so that config.inc.php is generated in the config folder, and copy the file to the root directory of phpmyadmin. 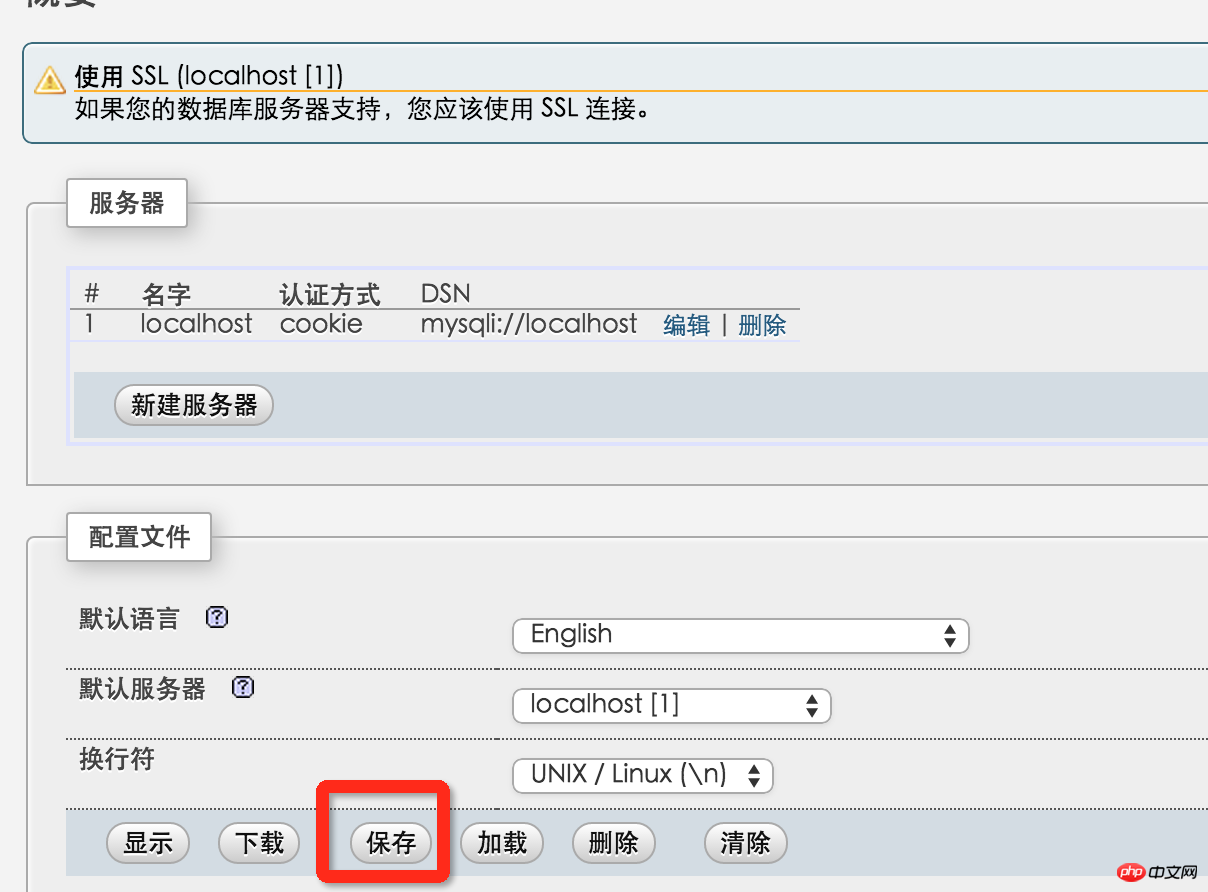
Then delete the entire config folder. Enter http://localhost/~yanzi/phpmyadmin/ to see the interface for logging in to phpmyadmin. So, phpMyAdmin does it.
Reading and writing permissions and grouping issues
The last remaining issue is reading and writing permissions and ownership. If you develop and test locally, this step can be ignored. If you want your mac to actually function as a server, then this needs to be set up. This step is equivalent to making everything in the public_html folder writable and belonging to www when uploading Alibaba Cloud code. Assume that there is a project of its own under the Sites folder: testsite
sudo chmod -R a+w ~/Sites/testsite Set that everyone can read and write
sudo chown -R _www ~/Sites/testsite Set that the testsite folder only belongs to _www group.
OK, this is the end of setting up PHP on MAC.
References:
1.http://coolestguidesontheplanet.com/get-apache-mysql-php-phpmyadmin-working-osx-10-10-yosemite/
2.http://blog.csdn.net/henry121212 /article/details/9210193 (Refer to this without success)
Attached is a link to set up a php virtual host:
http://coolestguidesontheplanet.com/set-virtual-hosts-apache-mac-osx-10-10-yosemite /#apacheuser
In addition, if you accidentally installed it wrong, you can refer to the following to delete mysql:
http://www.cnblogs.com/TsengYuen/archive/2011/12/06/2278574.html
I am used to using an appserv or phpStudy compressed package on Windows, but I am not used to creating a PHP development environment on MAC. But there is still something to gain from setting up the environment yourself. As we all know, OSX comes with apache and php, so these two are relatively smooth. Installing the latest version of MySQL, version 5.6.22, is quite difficult, and this article records it in detail.
apache configuration
apache already comes with it, you only need the following three commands.
Start the apache service sudo apachectl start
Stop the apache service sudo apachectl stop
Restart the service httpd -v
After manually opening the apache service, enter localhost in the browser and you will see Go to the following:
The root directory of the program is under /Library/WebServer/Documents/. This It works is printed out by the info.php inside. The following describes how to change the default directory of apache to the user directory.  1. Create a new Sites folder in your own user directory. My user directory is yanzi
1. Create a new Sites folder in your own user directory. My user directory is yanzi
2. Go to the cd /etc/apache2/users/ directory and sudo vim username.conf. The content is:
<Directory "/Users/yanzi/Sites/"> AllowOverride AllOptions Indexes MultiViews FollowSymLinks Require all granted </Directory>
sudo chmod 644 username.conf
3, go to the /etc/apache2/ directory, sudo vim httpd.conf and remove the comments of the following three sentences:
LoadModule authz_core_module libexec/apache2/ mod_authz_core.so
LoadModule userdir_module libexec/apache2/mod_userdir.so
The first two sentences should be uncommented. Uncomment the third sentence.
Then find the Include /private/etc/apache2/extra/httpd-userdir.conf comment and release it.
PS: Just switch to command mode under vim and enter /"words you need find" to quickly find the words you need to find.
4. Go to the /etc/apache2/extra/ directory,
sudo vim httpd-userdir.conf
Then enter in the terminal: sudo apachectl restart to restart apache, enter in the browser: loacal/~yanzi/ and you will see the effect. (yanzi is the name of my user directory,
No need to add /Sites after it
After the above steps, apache is ready. PHP configuration
Install MySQL5.6.22
1. When double-clicking to install, do not check the StartUp Item:
After the installation is completed, in the settings - --MySQL Manually start the MySQL service. 
I have opened the MySQL service here. Next, set it to start automatically at boot.  2. By default, we must enter the full path every time we use the mysql command, such as sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start to start the mysql service, /usr/local/mysql/bin /mysql -v To view the mysql version, you must first add the bin directory to the environment variable. Switch to the user root directory, vim .bash_profile, enter:
2. By default, we must enter the full path every time we use the mysql command, such as sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start to start the mysql service, /usr/local/mysql/bin /mysql -v To view the mysql version, you must first add the bin directory to the environment variable. Switch to the user root directory, vim .bash_profile, enter:
export PATH="/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH"
Finally, set the password for the mysql root user through mysqladmin -u root password ‘yourpasswordhere’. The content in single quotes is the password to be set.
Note: Sometimes the above command cannot modify the root password, and you need to use phpmyadmin to modify it. In fact, the default root password for this version of mysql is root.
3, fix the socket error problem. There is a socket file responsible for communication between the mysql server and client. This version of mysql places it in the /tmp directory, but OSX looks for the /var/mysql directory by default, so a soft link must be created. Create a new directory /var/mysql, then sudo ln -s /tmp/mysql.sock /var/mysql/mysql.sock and it will be ok.
4. Let mysql start automatically when booting.
sudo vim /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.mysql.mysql.plist, enter the content:
KeepAlive
Label
com.mysql.mysqld
ProgramArguments
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe
–user=mysql
After saving, modify permissions:
sudo chown root:wheel /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.mysql.mysql.plist
sudo chmod 644 /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.mysql.mysql.plist
sudo launchctl load -w /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.mysql.mysql.plist
This way mysql will be ok!
Installation of phpMyAdmin
Download from http://www.phpmyadmin.net/home_page/downloads.php. I downloaded the version phpMyAdmin-4.4.2-all-languages.zip and unzipped it. Then change the name of the outermost folder to phpmyadmin, go to the directory ~/Sites/phpmyadmin, create a new folder: mkdir config, modify the read and write permissions: chmod o+w config
Then enter the browser: http://localhost/~ yanzi/phpmyadmin/setup/ (Note that yanzi in the middle is replaced with your own user name) 
Click "New Server", I have already created it above, and then enter the mysql root user password in this interface: 
Password . Then click "Apply", remember to click the save button on the following interface so that config.inc.php is generated in the config folder, and copy the file to the root directory of phpmyadmin. 
Then delete the entire config folder. Enter http://localhost/~yanzi/phpmyadmin/ to see the interface for logging in to phpmyadmin. So, phpMyAdmin does it.
Reading and writing permissions and grouping issues
The last remaining issue is reading and writing permissions and ownership. If you develop and test locally, this step can be ignored. If you want your mac to actually function as a server, then this needs to be set up. This step is equivalent to making everything in the public_html folder writable and belonging to www when uploading Alibaba Cloud code. Assume that there is a project of its own under the Sites folder: testsite
sudo chmod -R a+w ~/Sites/testsite Set that everyone can read and write
sudo chown -R _www ~/Sites/testsite Set that the testsite folder only belongs to _www group.
OK, this is the end of setting up PHP on MAC.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Alipay PHP SDK transfer error: How to solve the problem of 'Cannot declare class SignData'?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Alipay PHP SDK transfer error: How to solve the problem of 'Cannot declare class SignData'?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Alipay PHP...
 Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JWT is an open standard based on JSON, used to securely transmit information between parties, mainly for identity authentication and information exchange. 1. JWT consists of three parts: Header, Payload and Signature. 2. The working principle of JWT includes three steps: generating JWT, verifying JWT and parsing Payload. 3. When using JWT for authentication in PHP, JWT can be generated and verified, and user role and permission information can be included in advanced usage. 4. Common errors include signature verification failure, token expiration, and payload oversized. Debugging skills include using debugging tools and logging. 5. Performance optimization and best practices include using appropriate signature algorithms, setting validity periods reasonably,
 How does session hijacking work and how can you mitigate it in PHP?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
How does session hijacking work and how can you mitigate it in PHP?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Session hijacking can be achieved through the following steps: 1. Obtain the session ID, 2. Use the session ID, 3. Keep the session active. The methods to prevent session hijacking in PHP include: 1. Use the session_regenerate_id() function to regenerate the session ID, 2. Store session data through the database, 3. Ensure that all session data is transmitted through HTTPS.
 What are Enumerations (Enums) in PHP 8.1?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:05 AM
What are Enumerations (Enums) in PHP 8.1?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The enumeration function in PHP8.1 enhances the clarity and type safety of the code by defining named constants. 1) Enumerations can be integers, strings or objects, improving code readability and type safety. 2) Enumeration is based on class and supports object-oriented features such as traversal and reflection. 3) Enumeration can be used for comparison and assignment to ensure type safety. 4) Enumeration supports adding methods to implement complex logic. 5) Strict type checking and error handling can avoid common errors. 6) Enumeration reduces magic value and improves maintainability, but pay attention to performance optimization.
 Describe the SOLID principles and how they apply to PHP development.
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Describe the SOLID principles and how they apply to PHP development.
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The application of SOLID principle in PHP development includes: 1. Single responsibility principle (SRP): Each class is responsible for only one function. 2. Open and close principle (OCP): Changes are achieved through extension rather than modification. 3. Lisch's Substitution Principle (LSP): Subclasses can replace base classes without affecting program accuracy. 4. Interface isolation principle (ISP): Use fine-grained interfaces to avoid dependencies and unused methods. 5. Dependency inversion principle (DIP): High and low-level modules rely on abstraction and are implemented through dependency injection.
 How to debug CLI mode in PHPStorm?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
How to debug CLI mode in PHPStorm?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
How to debug CLI mode in PHPStorm? When developing with PHPStorm, sometimes we need to debug PHP in command line interface (CLI) mode...
 How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set the permissions of unixsocket after the system restarts. Every time the system restarts, we need to execute the following command to modify the permissions of unixsocket: sudo...
 How to send a POST request containing JSON data using PHP's cURL library?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to send a POST request containing JSON data using PHP's cURL library?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Sending JSON data using PHP's cURL library In PHP development, it is often necessary to interact with external APIs. One of the common ways is to use cURL library to send POST�...





