What are the ways to make an Observer in Vue?
This time I will bring you the methods of making an Observer in Vue, and what are the precautions for making an Observer in Vue. The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
Introduction:
This article is an in-depth introduction to the responsive principles of Vue’s official documentation (https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/reactivity.html) Understand and restore the implementation process through source code.
The responsive principle can be divided into two steps, the process of relying on collection and the process of triggering and re-rendering. There are three very important classes in the dependency collection process, namely Watcher, Dep, and Observer. This article mainly explains Observer.
This article explains the content of Observer that was not covered in the previous article. Let’s first look at this picture on the official website:
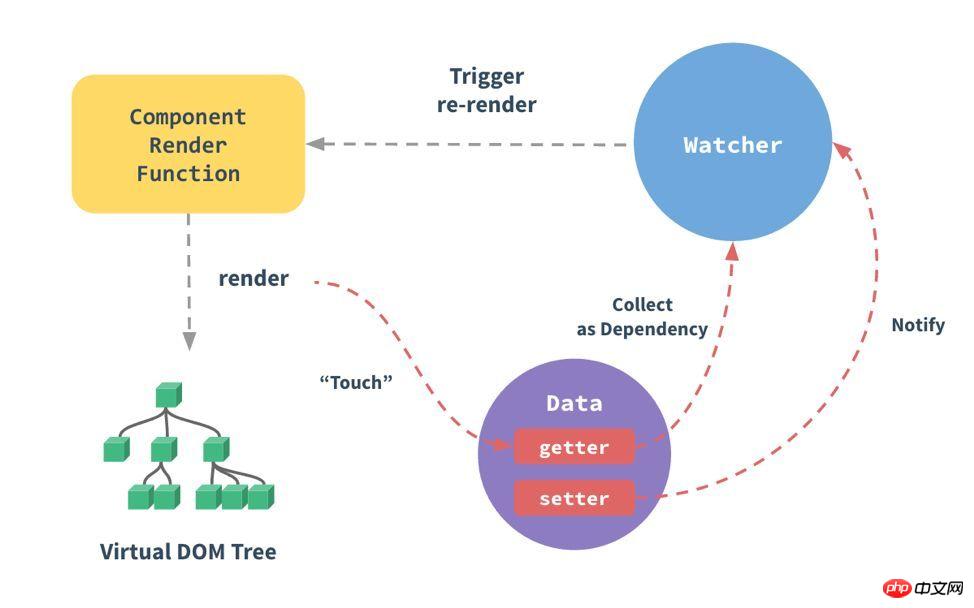
The main function of Observer It realizes the process of touch -Data(getter) - Collect as Dependency in the picture above, which is the process of dependency collection.
Let’s take the following code as an example to sort it out:
(Note: Swipe left and right to view the complete code, the same below)
varvm = newVue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
firstName: 'Hello',
fullName: ''
},
watch: {
firstName(val) {
this.fullName = val + 'TalkingData';
},
}
})In the source code, restore Vue The process of instantiation, step by step from the beginning to the source code of the Observer class, is as follows (a lot of code that is not discussed in this article is omitted):
// src/core/instance/index.js
functionVue(options) {
if(process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'&&
!(thisinstanceofVue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
// src/core/instance/init.js
Vue.prototype._init = function(options?: Object) {
constvm: Component = this
// ...
initState(vm)
// ...
}
// src/core/instance/state.js
exportfunctioninitState(vm: Component) {
// ...
constopts = vm.$options
if(opts.data) {
initData(vm)
}
// ...
}
functioninitData(vm: Component) {
letdata = vm.$options.data
data = vm._data = typeofdata === 'function'
? getData(data, vm)
: data || {}
// ...
// observe data
observe(data, true/* asRootData */)
}In the initData method, the data in the data item begins Performing "observation" will turn all data into observable. Next, look at the code of the observe method:
// src/core/observer/index.js
functionobserve(value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer| void{
// 如果不是对象,直接返回
if(!isObject(value) || value instanceofVNode) {
return
}
letob: Observer | void
if(hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceofObserver) {
// 如果有实例则返回实例
ob = value.__ob__
} elseif(
// 确保value是单纯的对象,而不是函数或者是Regexp等情况
observerState.shouldConvert &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
// 实例化一个 Observer
ob = newObserver(value)
}
if(asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++
}
returnob
}The function of the observe method is to create an Observer instance for data and return it. If data has the ob attribute, it means there is already an Observer instance, and the existing instance is returned. Vue's responsive data will have an ob attribute, which stores the Observer instance of the attribute to prevent repeated binding. Let’s look at what happens in the new Observer(value) process:
exportclassObserver{
value: any;
dep: Dep;
vmCount: number; // number of vms that has this object as root $data
constructor(value: any) {
this.value = value
this.dep = newDep()
this.vmCount = 0
def(value, '__ob__', this)
if(Array.isArray(value)) {
// ...
this.observeArray(value)
} else{
this.walk(value)
}
}
walk (obj: Object) {
constkeys = Object.keys(obj)
for(leti = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive(obj, keys[i], obj[keys[i]])
}
}
observeArray (items: Array<any>) {
for(leti = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i])
}
}
}As you can see from the source code, there are two main judgments made in the process of instantiating Observer. If it is an array, call the oberser method again for each item in the array to observe; if it is a non-array object, traverse each attribute of the object and call the defineReactive method on it. The defineReactive method here is the core! Dependency collection is completed by using the Object.defineProperty method to add get/set to each property that needs to be observed. After dependencies are collected, each property will have a Dep to save all Watcher objects. According to the example at the beginning of the article, get/set is added to firstName and fullName respectively, and each of them has a Dep instance to save all the Watcher objects that observe them. The following is the source code of defineReactive:
exportfunctiondefineReactive(
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: ?Function,
shallow?: boolean
) {
constdep = newDep()
// 获取属性的自身描述符
constproperty = Object.getOwnPropertyDeor(obj, key)
if(property && property.configurable === false) {
return
}
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
// 检查属性之前是否设置了 getter/setter
// 如果设置了,则在之后的 get/set 方法中执行设置了的 getter/setter
constgetter = property && property.get
constsetter = property && property.set
// 通过对属性再次调用 observe 方法来判断是否有子对象
// 如果有子对象,对子对象也进行依赖搜集
letchildOb = !shallow && observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: functionreactiveGetter() {
// 如果属性原本拥有getter方法则执行
constvalue = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if(Dep.target) {
// 进行依赖收集
dep.depend()
if(childOb) {
// 如果有子对象,对子对象也进行依赖搜集
childOb.dep.depend()
// 如果属性是数组,则对每一个项都进行依赖收集
// 如果某一项还是数组,则递归
if(Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
returnvalue
},
set: functionreactiveSetter(newVal) {
// 如果属性原本拥有getter方法则执行
// 通过getter方法获取当前值,与新值进行比较
// 如果新旧值一样则不需要执行下面的操作
constvalue = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if(newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if(process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'&& customSetter) {
customSetter()
}
if(setter) {
// 如果属性原本拥有setter方法则执行
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else{
// 如果原本没有setter则直接赋新值
val = newVal
}
// 判断新的值是否有子对象,有的话继续观察子对象
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
// 通知所有的观察者,更新状态
dep.notify()
}
})
}I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
How to package and optimize webpack4.0
Make json and array key value casing Convert
The above is the detailed content of What are the ways to make an Observer in Vue?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.
 How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
There are two ways to jump div elements in Vue: use Vue Router and add router-link component. Add the @click event listener and call this.$router.push() method to jump.






