Detailed explanation of render cases in React
This time I will bring you a detailed explanation of the render case in React. What are the precautions for using render in React? The following is a practical case, let’s take a look.
We all know that Render will be executed during component instantiation and lifetime. Instantiation will be executed after componentWillMount is executed. There is nothing to say about this. Here we mainly analyze the execution of lifetime component updates.
Existence methods include:
- componentWillReceiveProps
- shouldComponentUpdate
- componentWillUpdate
- render
- componentDidUpdate
These methods will be in the component It is executed when the state or attribute changes. If we use Redux, it will only be executed when the attribute changes. Below we will analyze the changes in attributes from several scenarios.
First we created HelloWorldComponent, the code is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
|
The code of the AppComponent component is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
|
Here we used Redux, but the code will not be posted. , where the addNumber method will increase the count by 1 each time it is clicked.
When we click the button at this time, do you think the render method of the subgroup HelloWorldComponent will be executed?
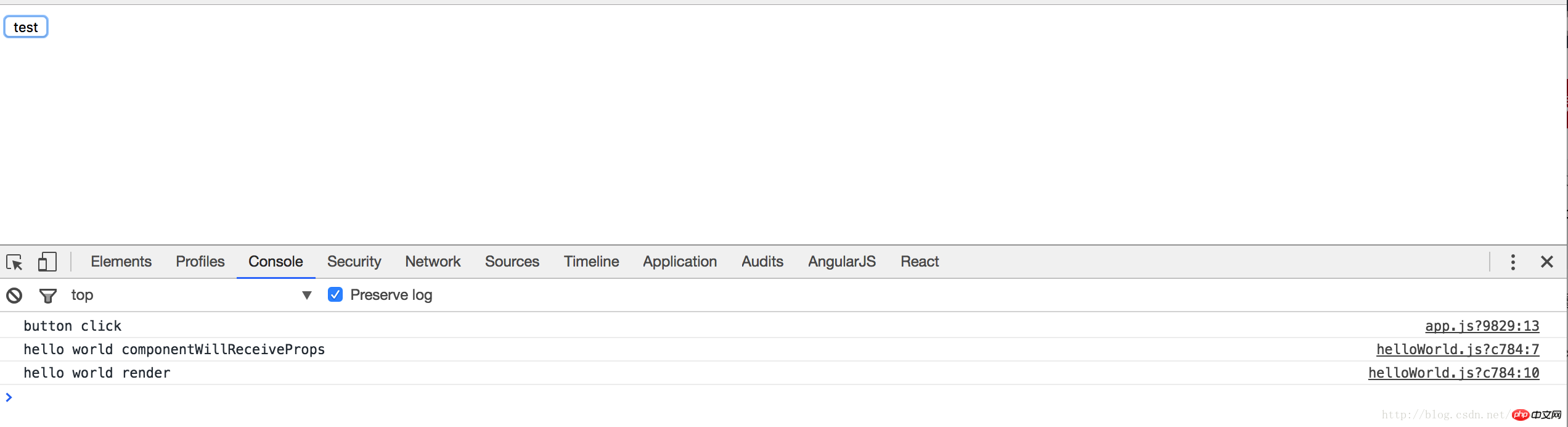
As shown in the figure, when we click the button, the render method of the subcomponent is executed. But from the code point of view, the onClick and text bound to the component have not changed. Why is the component updated?
If you add this log in componentWillReceiveProps of the subcomponent: console.log(‘isEqual’, nextProps === this.props); will the output be true or false?

Yes, you read that right, the output is false. This is why the subcomponent is updated, because the property value has changed, not the property value we bound to the component. Each time the button is clicked, the state will be triggered to change, and the entire component will be re-rendered. However, this is not what we want, because this unnecessary rendering will greatly affect the performance of our application.
In addition to inheriting Component to create components, there is also PureComponent in react. This component can avoid this situation. Let's make some modifications to the code and see the effect. Modify as follows:
1 |
|
What happened when the button was clicked this time?
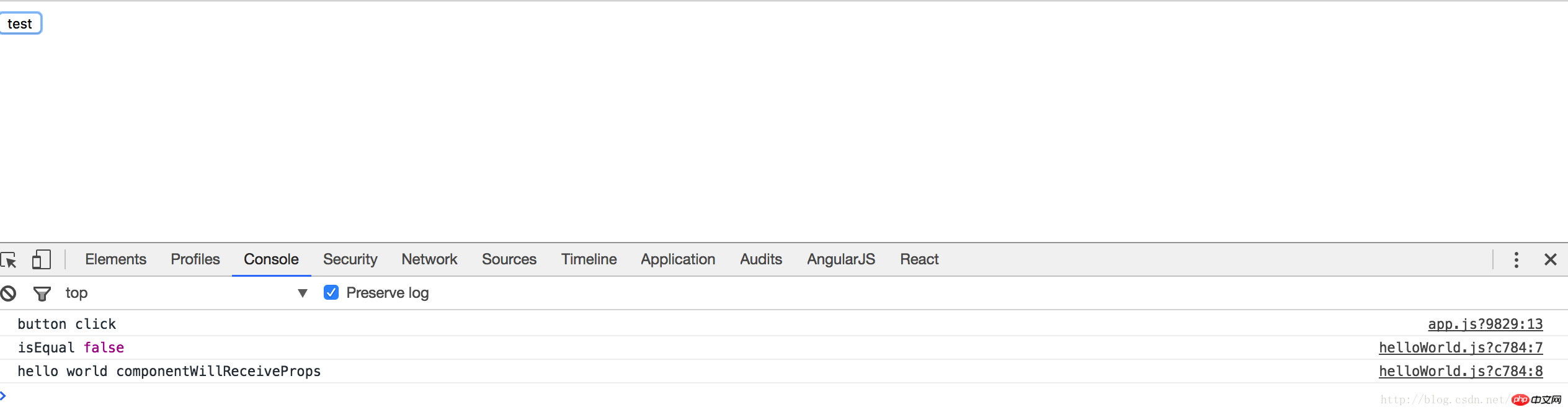
Although componentWillReceiveProps will still be executed, the component is not re-rendered this time.
So, for stateless components, we should try to use PureComponent. It should be noted that PureComponent only focuses on property values, which means that changes to objects and arrays will not trigger render.
I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the php Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
##How to dynamically bind class names in WeChat mini programs
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of render cases in React. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Integration of Java framework and front-end React framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Integration of Java framework and front-end React framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Integration of Java framework and React framework: Steps: Set up the back-end Java framework. Create project structure. Configure build tools. Create React applications. Write REST API endpoints. Configure the communication mechanism. Practical case (SpringBoot+React): Java code: Define RESTfulAPI controller. React code: Get and display the data returned by the API.
 Mpeppe (MPEPE) Coin: A New Contender in the Cryptocurrency Market Attracting Investors from Render (RNDR) and Internet Computer (ICP)
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:03 PM
Mpeppe (MPEPE) Coin: A New Contender in the Cryptocurrency Market Attracting Investors from Render (RNDR) and Internet Computer (ICP)
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:03 PM
The world of cryptocurrencies is always in flux, with new tokens capturing the attention of seasoned investors looking for the next big opportunity.
 HMD Slate Tab 5G leakes as mid-range tablet with Snapdragon 7s Gen 2, 10.6-inch display and Lumia design
Jun 18, 2024 pm 05:46 PM
HMD Slate Tab 5G leakes as mid-range tablet with Snapdragon 7s Gen 2, 10.6-inch display and Lumia design
Jun 18, 2024 pm 05:46 PM
With the Skyline, HMD Global is set to unveil a mid-range smartphone in the style of the Nokia Lumia 920 on July 10. According to the latest information from the leaker @smashx_60, the Lumia design will soon also be used for a tablet, which will be c
 Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js is suitable for small and medium-sized projects and fast iterations, while React is suitable for large and complex applications. 1) Vue.js is easy to use and is suitable for situations where the team is insufficient or the project scale is small. 2) React has a richer ecosystem and is suitable for projects with high performance and complex functional needs.
 React's Role in HTML: Enhancing User Experience
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React's Role in HTML: Enhancing User Experience
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React combines JSX and HTML to improve user experience. 1) JSX embeds HTML to make development more intuitive. 2) The virtual DOM mechanism optimizes performance and reduces DOM operations. 3) Component-based management UI to improve maintainability. 4) State management and event processing enhance interactivity.
 React and the Frontend: Building Interactive Experiences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:02 AM
React and the Frontend: Building Interactive Experiences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:02 AM
React is the preferred tool for building interactive front-end experiences. 1) React simplifies UI development through componentization and virtual DOM. 2) Components are divided into function components and class components. Function components are simpler and class components provide more life cycle methods. 3) The working principle of React relies on virtual DOM and reconciliation algorithm to improve performance. 4) State management uses useState or this.state, and life cycle methods such as componentDidMount are used for specific logic. 5) Basic usage includes creating components and managing state, and advanced usage involves custom hooks and performance optimization. 6) Common errors include improper status updates and performance issues, debugging skills include using ReactDevTools and Excellent
 React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Netflixusesacustomframeworkcalled"Gibbon"builtonReact,notReactorVuedirectly.1)TeamExperience:Choosebasedonfamiliarity.2)ProjectComplexity:Vueforsimplerprojects,Reactforcomplexones.3)CustomizationNeeds:Reactoffersmoreflexibility.4)Ecosystema
 Frontend Development with React: Advantages and Techniques
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:25 AM
Frontend Development with React: Advantages and Techniques
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:25 AM
The advantages of React are its flexibility and efficiency, which are reflected in: 1) Component-based design improves code reusability; 2) Virtual DOM technology optimizes performance, especially when handling large amounts of data updates; 3) The rich ecosystem provides a large number of third-party libraries and tools. By understanding how React works and uses examples, you can master its core concepts and best practices to build an efficient, maintainable user interface.






