php artisan config:cache
php artisan route:cache
php artisan optimize --force
Laravel framework performance tuning methods
This is a summary afterwards. After going through many pitfalls in the tuning process, we finally perfected and implemented a preliminary performance testing plan, and summarized some practical skills in the Laravel development process through real test data.
0x00 Origin
Recently, a colleague reported that the response of the application written in Laravel is a bit slow, and more than 20 concurrency runs the CPU full... In order to solve the slow problem, even some interfaces use nodejs Come and write.
And my first reaction was how could a popular framework be so bad? There must be something wrong with the use. In order to find out, I started this Laravel application performance tuning journey.
0x01 Tuning Tips
The optimization techniques used in this performance test plan are mainly based on the Laravel framework itself and the tools it provides.
Turn off application debug
app.debug=falseCache configuration information
php artisan config:cacheCache routing information
php artisan router:cache- ##Class map loading optimization
php artisan optimize
- Automatic loading optimization
composer dumpautoload
- Only load necessary middleware as needed
- Use a just-in-time compiler (JIT), such as: HHVM, OPcache
- Use PHP 7.x
APP_DEBUG=false
php artisan config:cache
Copy after login
Run the above command to merge all the configuration information in the config folder into a php artisan config:cache
bootstrap/cache/config.php file. Reduce the number of files loaded at runtime.
php artisan config:clear
bootstrap/cache/config.php file
php artisan route:cache
Copy after login
Running the above command will generate the file php artisan route:cache
bootstrap/cache/routes.php. Route caching can effectively improve the router's registration efficiency, and the effect is more obvious in large applications.
php artisan route:clear
bootstrap/cache/routes.php file.
php artisan optimize --force
Copy after login
Running the above command can merge commonly loaded classes into one file, improving operating efficiency by reducing the loading of files. This command will generate two files php artisan optimize --force
bootstrap/cache/compiled.php and bootstrap/cache/services.json.
config/compile.php file.
--force The parameter file can also be automatically generated.
php artisan clear-compiled
bootstrap/cache/compiled.php and bootstrap/cache/services.json .
composer dumpautoload -o
Copy after loginLaravel applications are built using composer. This command will convert PSR-0 and PSR-4 into a class mapping table to improve class loading speed.
composer dumpautoload -o
Note: This operation has already been done in the6. Load only necessary middleware as neededThe Laravel application has a lot of middleware built in and enabled. Every Laravel request loads related middleware and generates various data. Commenting out unnecessary middleware (such as session support) inphp artisan optimize --force
command.
app/Http/Kernel.php can greatly improve performance.
Well, limited to your real enterprise environment, this may not change for a long time, so I didn’t mention it.0x02 Test PlanWe use a simple Apache ab command to test only the application entry file, and record and analyze the data.
- Only test the application’s entry file index.php, and access “/” or “/index.php” to return to the welcome page of the framework. More comprehensive performance testing requires testing of more interfaces of the application.
- Use the Apache ab command.
ab -t 10 -c 10 {url}
. This command means to initiate 10 requests to the url at the same time and last for 10 seconds. The specific parameter settings in the command need to be selected based on the server performance to be tested. - In order to avoid data errors caused by machine fluctuations, each test condition will execute the ab command multiple times and record the command execution results, focusing on the number of requests processed per second and the request response time. , analyze and eliminate outliers.
Every time the test conditions are adjusted, you need to access the welcome page on the browser to ensure that there are no access errors due to the modification of the test conditions. If page access errors occur, the test results will be incorrect.
Server environment description
All test data divorced from the specific environment is meaningless, and comparisons can only be made under similar conditions.
This environment runs on a Mac with 8G memory, 2.8GHz processor, and SSD hard drive.
The test server is built using Homestead. The virtual machine is configured with a single-core CPU and 2G memory.
The server PHP version is 7.1. If not specified, OPcache is turned on.
The Laravel application tested was written in version 5.2. There are 85 routes defined in
app\Http\routes.php.During the test process, except for the virtual machine, terminal and fixed browser window, there are no programs that will affect the operation of the machine.
The above data can be referred to when you conduct your own testing.
0x03 Test process and data
1. No optimization has been done
1.1 Operation
Perform the corresponding check items according to the following operate.
Run
ab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php
Basic check items
APP_DEBUG=truedoes not exist in the .env file
bootstrap/cache/config.phpdoes not exist
bootstrap/cache/routes.phpNo There are
bootstrap/cache/compiled.phpandbootstrap/cache/services.json##app/Http/Kernel.php
Most of the middleware is enabled in- Browser access the Laravel application welcome page to ensure normal access
- Based on step 1 Modify
APP_DEBUG=false
in the .env file. - Visit the Laravel application welcome page with your browser to ensure normal access.
- Run
ab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php
.
 ##2.3 Comparison results
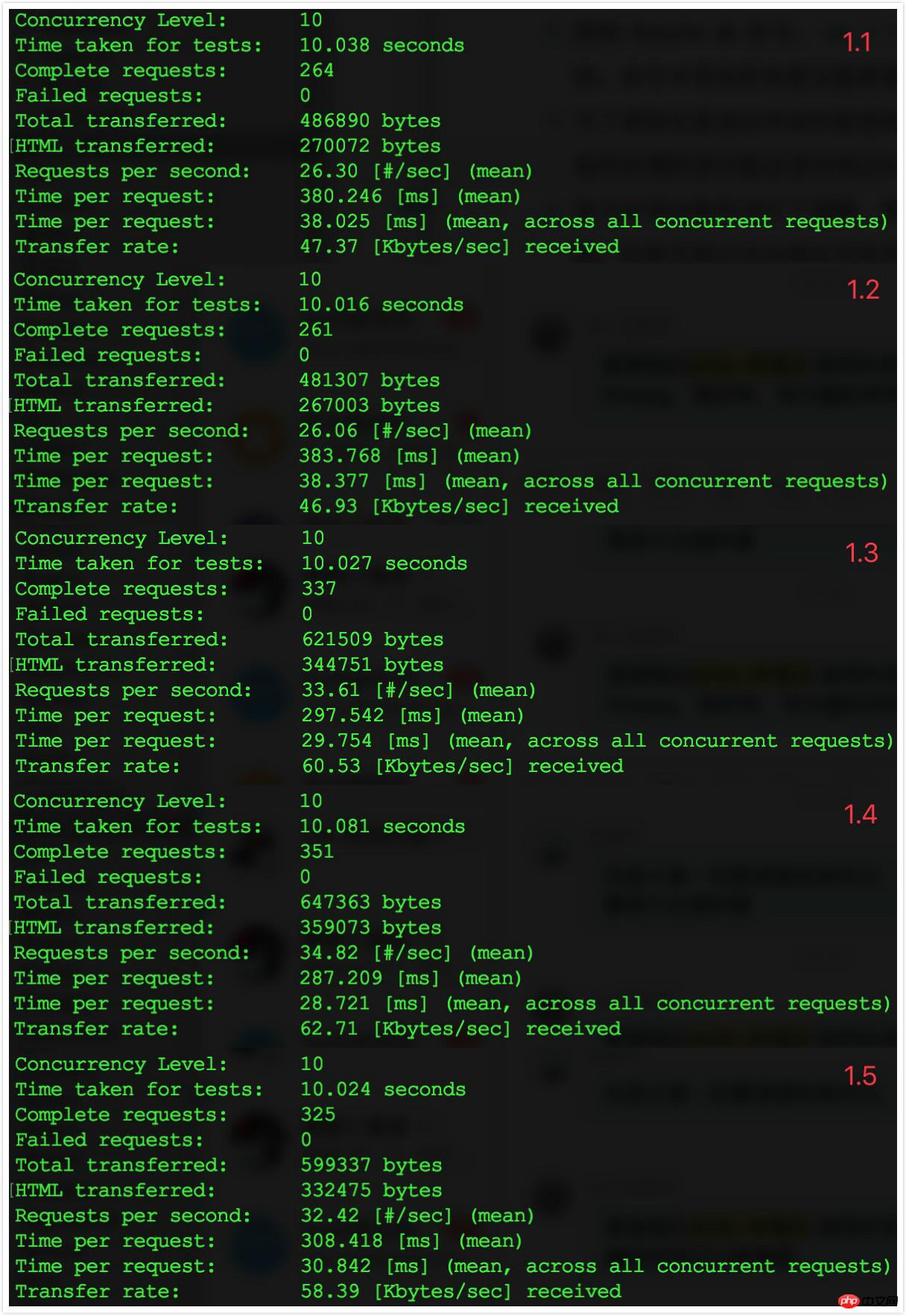
##2.3 Comparison results
Compare with the results of step 1 Discovery: After turning off application debugging, the number of requests processed per second increased from 26-34 to 33-35, and the request response time dropped from mostly more than 300ms to about 290ms.
The effect is not obvious, but there is indeed a certain improvement.Note: This part is closely related to the usage of logs in the application.
3. Enable cache configuration information
3.1 Operation
- Based on step 2, run
- php artisan config:cache
, confirm the generation of
bootstrap/cache/config.php. Visit the Laravel application welcome page with your browser to ensure normal access. - Run
- ab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php
.
3.2 Data record
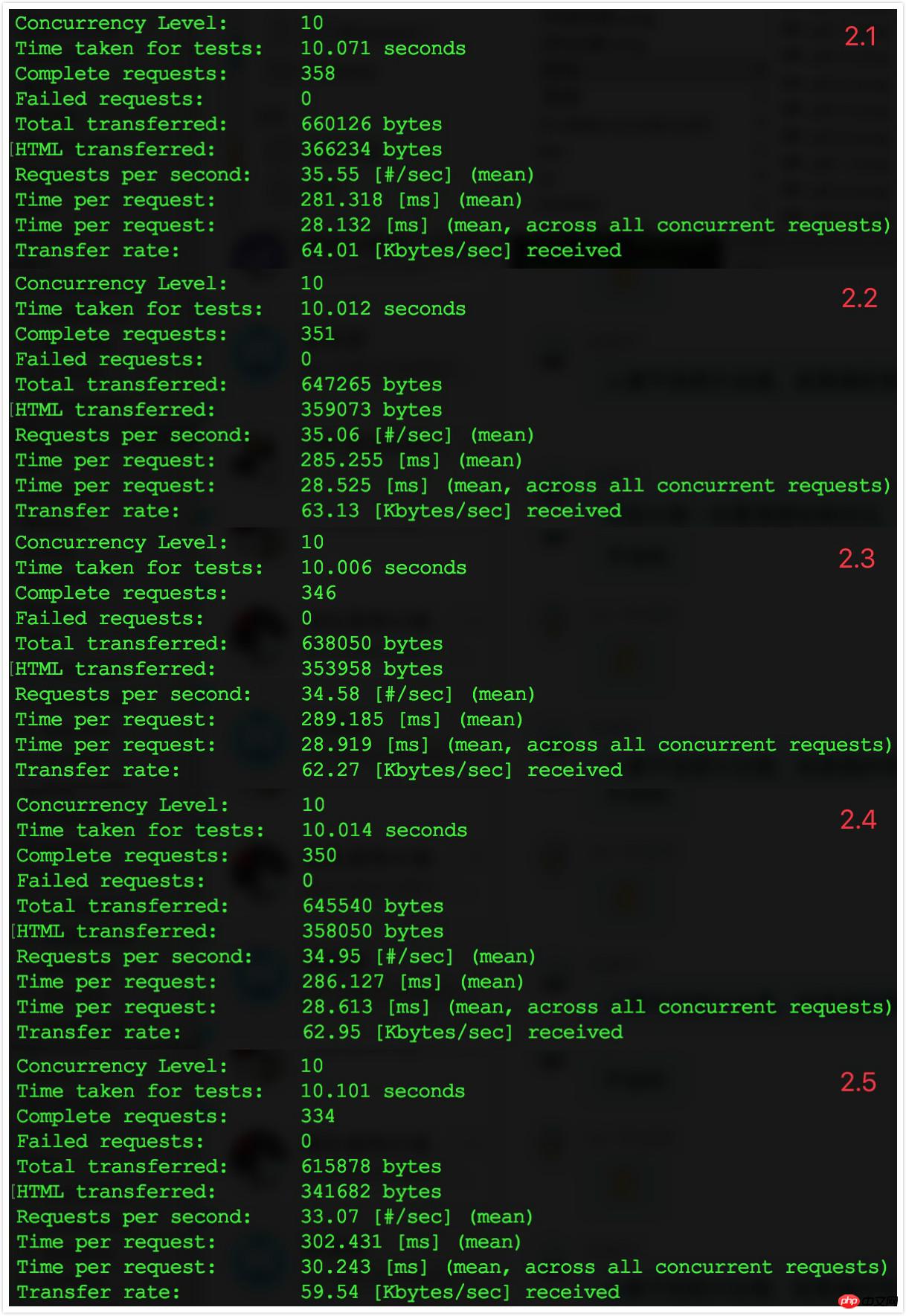
 ##3.3 Comparison results
##3.3 Comparison results
The effect is not obvious, but there is indeed a certain improvement.
4. Enable cache routing information
4.1 Operation##Based on step 3, run
php artisan route:cache- , confirm the generation of
- bootstrap/cache/routes.php
.
Visit the Laravel application welcome page with your browser to ensure normal access. -
Run
ab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php . 4.2 Data record
##4.3 Comparison results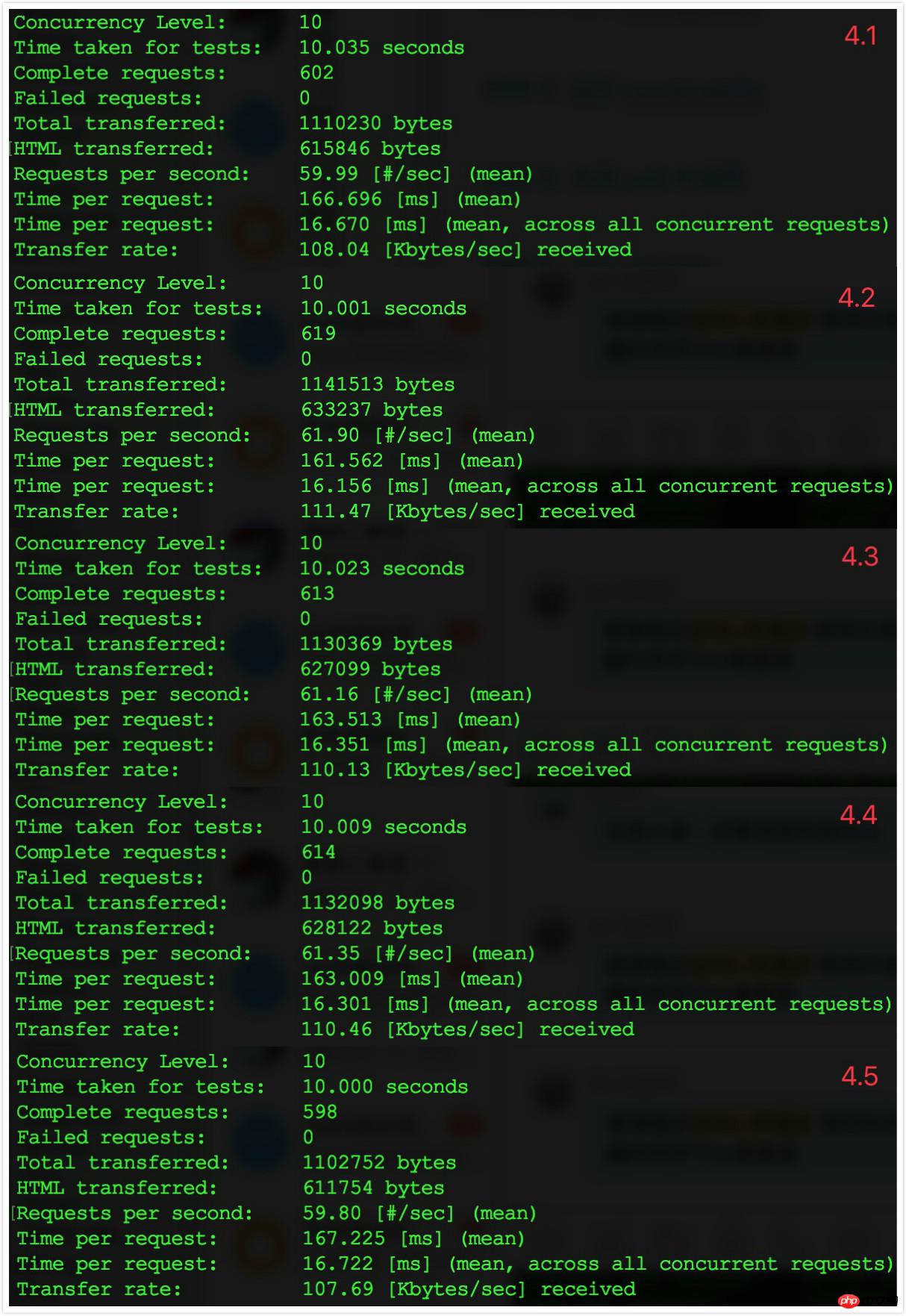 Compare with the results of step 3 Discovery: After turning on the routing information cache, the number of requests processed per second increased from 36-38 to about 60, and the request response time dropped from 260ms to about 160ms. The effect was significant. From the perspective of TPS, it increased by 70%.
Compare with the results of step 3 Discovery: After turning on the routing information cache, the number of requests processed per second increased from 36-38 to about 60, and the request response time dropped from 260ms to about 160ms. The effect was significant. From the perspective of TPS, it increased by 70%.
5.1 Operation
Based on step 4, comment out unnecessary middleware code.- Visit the Laravel application welcome page with your browser to ensure normal access.
- Run
ab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php
.
Note: I commented out all the middleware in this test. In actual situations, you should try to keep only necessary middleware.
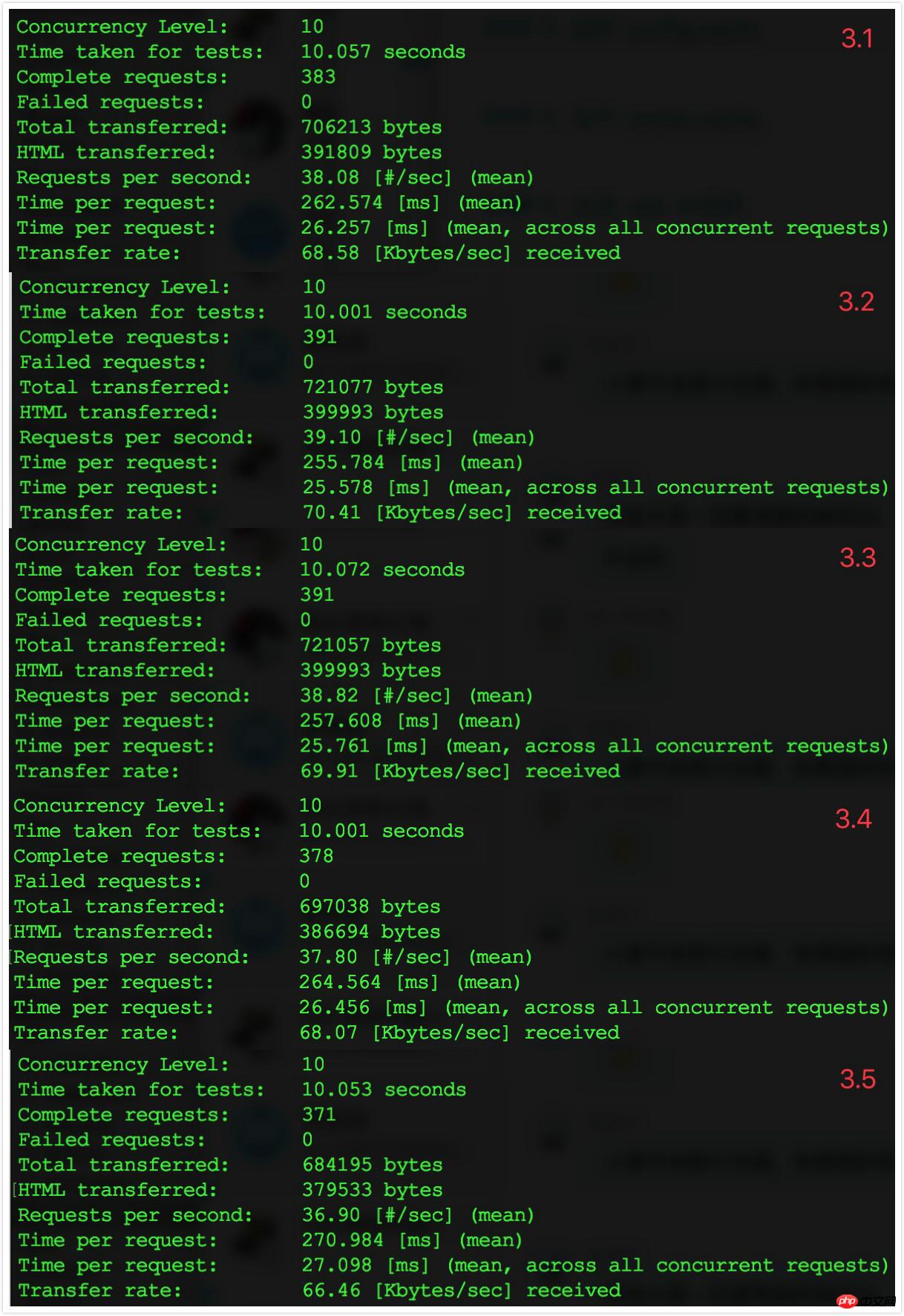
5.2 Data record
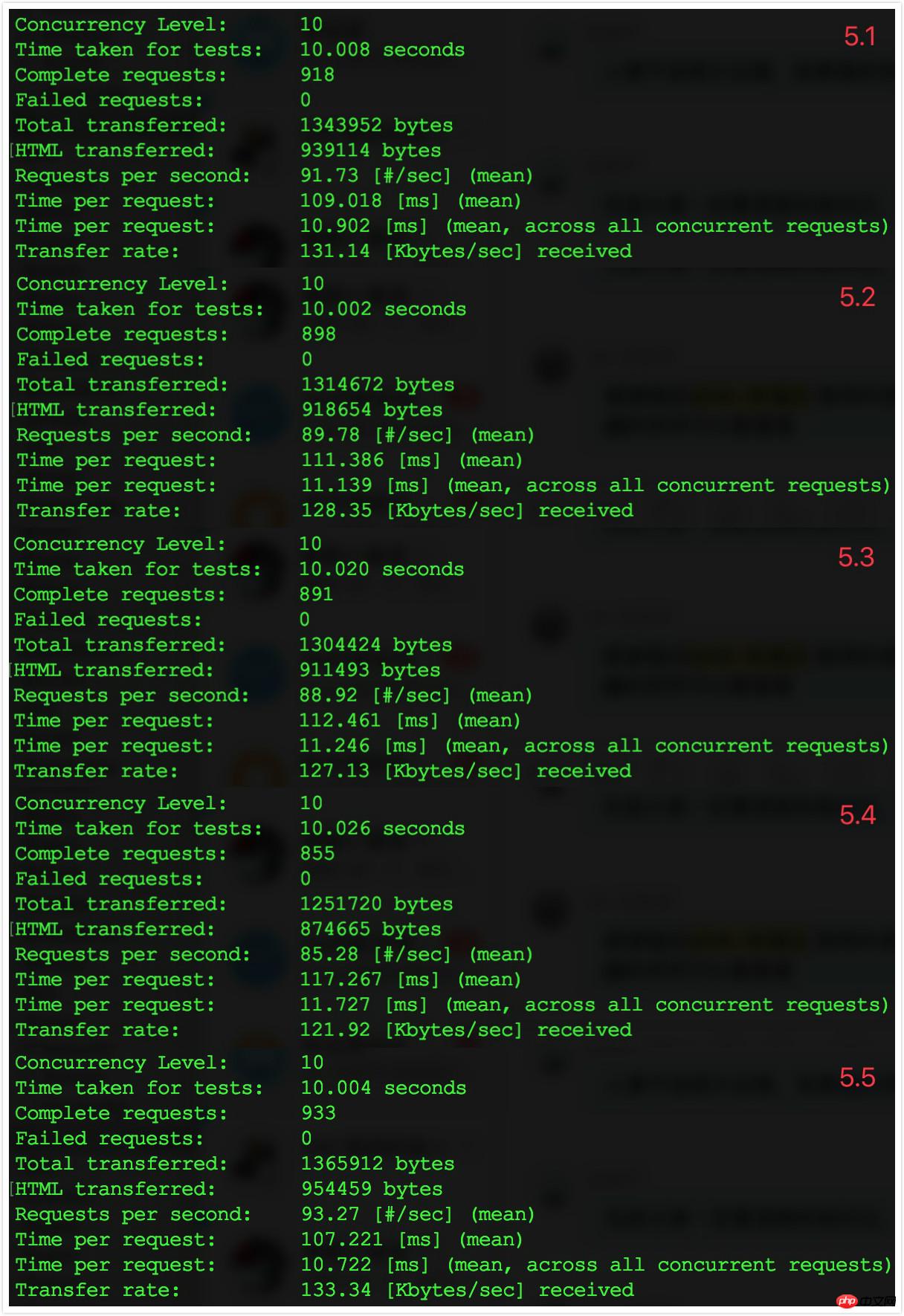
The effect is very obvious. From the perspective of TPS, it has increased by 50%.
6. Turn on class map loading optimization6.1 Operation- Based on step 5, run
php artisan optimize - -force
, confirm the generation ofbootstrap/cache/compiled.phpandbootstrap/cache/services.json. - Visit the Laravel application welcome page with your browser to ensure normal access.
- Run
ab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php
.
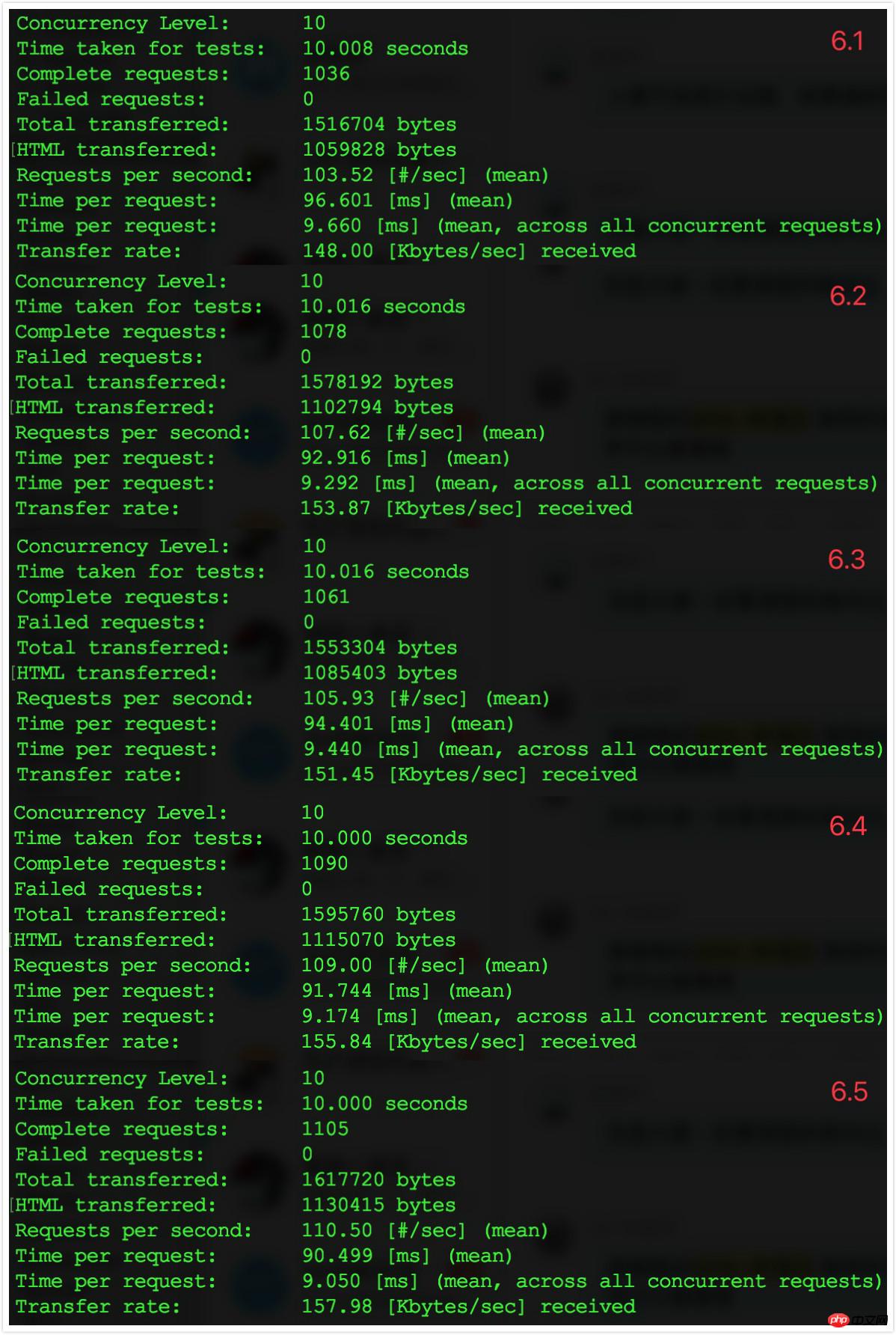 ##6.3 Comparison results
##6.3 Comparison results
Compare with the results of step 5 Discovery: After optimizing class mapping loading, the number of requests processed per second increased from 90 to 110, and the request response time dropped from 110ms to less than 100ms. The
effect is quite obvious.7. Close OPcache
7.1 Operation
- Based on step 6, close PHP’s OPcache and restart the server. Confirm that OPcache is closed via phpinfo()'s Zend OPcache.
- Visit the Laravel application welcome page with your browser to ensure normal access.
- Run
- ab -t 10 -c 10 http://myurl.com/index.php
.
7.2 Data record
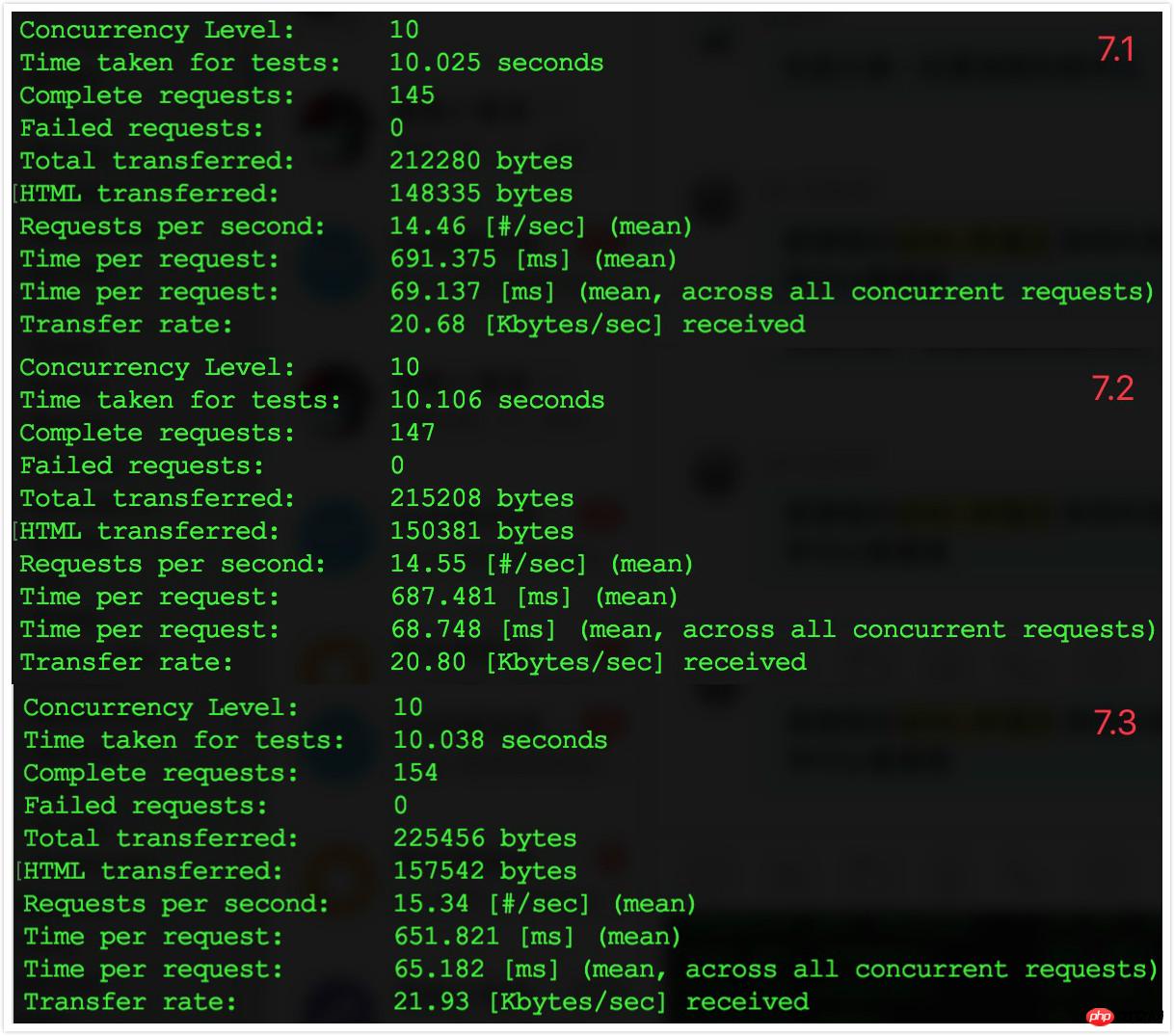 ##7.3 Comparison results
##7.3 Comparison results
Turning OPcache on and off, the data is actually several times different.
After that, I reopened PHP’s OPcache and the data was restored to the level of step 6.
1. [LogicException] Unable to prepare route [/] for serialization. Uses Closure.Running0x04 Pitfalls
php The artisan route:cache
command reports this error.Cause: Closure is used when processing "/" in the routing file. To run this command, the routing implementation must not use closures.
php artisan route:cache
command.Cause: Duplicate routes are defined in the routing file.
resource
method which is likely to result in duplication of its methods.3. [RuntimeException] Invalid filename provided.
php artisan optimize --force
naming.Cause: The corresponding file was not found when loading the class that needs to be compiled. The file path to be compiled is defined in the 5.2 version of vendor/laravel/framework/src/Illuminate/Foundation/Console/Optimize/config.php
/vendor/laravel/framework /src/Illuminate/Database/Eloquent/ActiveRecords.php was not found, so this error was reported. Modification plan: Temporarily comment out the ../ActiveRecords.php
4. InvalidArgumentException in FileViewFinder.php line 137: View [welcome] not found.
php artisan config:cache
, access the Laravel application on the browser The program welcome page reports this error.Reason: The Laravel application server is built on a virtual machine using Homestead. I ran this command outside the virtual machine, which caused the path in the generated config.php to be the local path, not the path on the virtual machine. So the view file cannot be found.
- app.debug=false
-
Cache configuration information php artisan config:cache -
Cache routing information php artisan router:cache Class map loading optimization
php artisan optimize(including automatic loading optimizationcomposer dumpautoload)As needed Only load necessary middleware
Use a just-in-time compiler (JIT), such as: HHVM, OPcache
2. Things to note when writing code
The specific implementation of routing is placed in the controller.
Do not define duplicate routes, pay special attention to the
resoucemethod.Clear the role of each middleware and delete unnecessary middleware references.
0x06 Next step
The above tuning skills and coding considerations are mainly for the framework itself. There are many specific optimization skills in real business logic coding. This is not discussed.
Following optimization will focus on specific coding practices:
Use Memcached to store session config/session.php
-
Use a professional cache driver
Database request optimization
Write caching logic for the data set
-
Front-end resource merge Elixir
![]()
The above is the detailed content of Laravel framework performance tuning methods. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement the custom table function of clicking to add data in dcat admin?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to implement the custom table function of clicking to add data in dcat admin?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to implement the table function of custom click to add data in dcatadmin (laravel-admin) When using dcat...
 How to get the return code when email sending fails in Laravel?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:45 PM
How to get the return code when email sending fails in Laravel?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:45 PM
Method for obtaining the return code when Laravel email sending fails. When using Laravel to develop applications, you often encounter situations where you need to send verification codes. And in reality...
 Laravel Redis connection sharing: Why does the select method affect other connections?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:45 AM
Laravel Redis connection sharing: Why does the select method affect other connections?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:45 AM
The impact of sharing of Redis connections in Laravel framework and select methods When using Laravel framework and Redis, developers may encounter a problem: through configuration...
 Laravel multi-tenant extension stancl/tenancy: How to customize the host address of a tenant database connection?
Apr 01, 2025 am 09:09 AM
Laravel multi-tenant extension stancl/tenancy: How to customize the host address of a tenant database connection?
Apr 01, 2025 am 09:09 AM
Custom tenant database connection in Laravel multi-tenant extension package stancl/tenancy When building multi-tenant applications using Laravel multi-tenant extension package stancl/tenancy,...
 Laravel Eloquent ORM in Bangla partial model search)
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
Laravel Eloquent ORM in Bangla partial model search)
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
LaravelEloquent Model Retrieval: Easily obtaining database data EloquentORM provides a concise and easy-to-understand way to operate the database. This article will introduce various Eloquent model search techniques in detail to help you obtain data from the database efficiently. 1. Get all records. Use the all() method to get all records in the database table: useApp\Models\Post;$posts=Post::all(); This will return a collection. You can access data using foreach loop or other collection methods: foreach($postsas$post){echo$post->
 How to effectively check the validity of Redis connections in Laravel6 project?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:00 PM
How to effectively check the validity of Redis connections in Laravel6 project?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:00 PM
How to check the validity of Redis connections in Laravel6 projects is a common problem, especially when projects rely on Redis for business processing. The following is...
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 Laravel database migration encounters duplicate class definition: How to resolve duplicate generation of migration files and class name conflicts?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Laravel database migration encounters duplicate class definition: How to resolve duplicate generation of migration files and class name conflicts?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
A problem of duplicate class definition during Laravel database migration occurs. When using the Laravel framework for database migration, developers may encounter "classes have been used...






