java - detailed introduction to object-oriented (1)
1. What is object-oriented?
Object-Oriented (OO) is a common program structure design method.
The basis of object-oriented thinking is to put related data and methods together, combine them into a new composite data type, and then use the newly created composite data type as the basis of the project.
Object-oriented is a very abstract concept, which is relative to process-oriented.
Processes and objects are both ideas for solving problems.
Process-oriented: Emphasizes functional behavior, a process, what to do first, and then what to do;
Object-oriented: Encapsulates functions into objects, emphasizes having a certain function Object;
According to object-oriented thinking, anything can be regarded as an object!
Three characteristics of object-oriented:
Encapsulation (Encapsulation);
Inheritance (Inheritance);
Polymorphism ( Polymorphism).
My summary:
Process-oriented: emphasizing the specific function implementation; (executor)
Object-oriented: emphasizing the ability to Functional object. (Manager)
2. Class
Class (class) is the smallest programming unit of the Java language and the basis for designing and implementing Java programs. This part will go into depth. Introduce relevant knowledge of the class.
The concept of class
A class is a description of the common characteristics and functions of a group of things. A class is an overall description of a group of things. It is the smallest unit when designing according to object-oriented technology, and it is also the most basic module that makes up a project. The concept of class is abstract, similar to drawings in architectural design, and is an abstraction of the specific content that needs to be represented in reality. Classes only contain skeletal structures, not specific data. Therefore, the class represents the whole, not a specific individual.
My summary: Classes are abstract, objects are concrete, real!
Definition of class:
[modifier] class class name {
1~n construction methods;
0~n fields;
0~n methods
}
Define a class, which is actually to define the objects in the class
Objects include:
State; (Attribute)
Function, behavior; (Method)
Describe the object through the class;
State--------Member variable;
Function, behavior - method;
Eg:
class Person{
//属性
private String name;
private int age;
private int sal;
//方法
public void show(){
System.out.println("个人情况:"+name+age+sal);
}
}3. Construction method
Construction method: use To construct an instance of a class (each class has a parameterless constructor by default, which must be called with new)
Field: the data contained in the class or object, a description of the class state;
Method: Characteristics or behaviors of a class or object
Function:
Initialize the fields in the class and can be used to create objects.
Features:
The method name is the same as the class name
No need to define the return value type
No need to write a return statement
Note:
Characteristics of the default construction method.
Multiple constructors exist in the form of overloading.
Overloading of the constructor method: (Adapt whichever one is needed and call whichever one is needed)
this([actual parameter]); Call the constructor method of the current class
Note: this([actual parameter]); must be placed in the first line of the constructor;
Object generation format:
Class Name Object name = new Class name ();
Because there is (), it is a method. In fact, it is a constructor, and it is a non-private constructor.
For example:
CellPhone cp = new CellPhone();
Eg:
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
private int sal;
public void show(){
System.out.println("个人情况:"+name+age+sal);
}
public Person(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name, int age, int sal) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sal = sal;
}
}4. static keyword
Features:
Loaded as the class is loaded
Priority to object existence
Been owned by all objects Sharing
can be called directly by the class name
Usage Note:
Static methods can only access static members
But non-static member methods can access static members;
This cannot be used in static methods, and the super keyword
The main method (main) is static (you can use the class name to It is normal to call the static main method! But it will fall into an infinite loop, causing memory overflow and the jvm to stop automatically!)
public static void main(String[] agrs){}
Can modify fields and methods.
Members modified with static indicate that they belong to this class, rather than to a single instance of the class.
# STATIC modified field == class field
STATIC modified method == class method
illegal field modified fields and methods, members belong to a single instance of the class, Does not belong to class.
No static modified field == Example field
There is no static modifier method == instance method
#####Q and method syntax: ######Access class members: Class.Field Class.Method######Access instance members: Instance.Field Instance.Method#########My summary# ##: ######Fields and methods modified by static can be called by classes or instances; ######Fields and methods without static modification can only be called by instances (recommended Use: class name to call; In fact, at the bottom level, when an object calls a class member, the class name call will also be converted) ###### The static keyword cannot be used with this and super at the same time! ##################5. Anonymous object#########An object without a name is created and is not assigned to a variable;# ############## Features: ######When a method or field is called only once; ###### can be passed as an actual parameter; ##### #Only open a storage area in the heap, ######### can only be used once, and will be destroyed after use; #########When should it be used? Only use it once! ! ######new Person(); represents an anonymous object, an object without a name###
new Person().age = 17;//使用一次之后就被销毁了
6、this关键字
特点:this表示当前对象。
当前对象 ←→ 当前正在调用实例成员的对象
换言之:谁调用了方法,谁就是当前对象。
什么时候使用this关键字呢?
方法间的相互调用;
this.字段;
构造器中相互调用,但是此时this([参数])必须写在构造方法第一行。
this不能用在static修饰的方法里和static修饰的代码块里;
Eg:构造方法中的this.name = name;
7、面向对象之封装
封装的两个含义:
1.把对象的状态和行为看成一个统一的整体,将二者存放在一个独立的模块中(类);
2."信息隐藏", 把不需要让外界知道的信息隐藏起来,尽可能隐藏对象功能实现细节,字段;
封装机制在程序中的体现是:
把描述对象的状态用字段表示,描述对象的行为用方法表示,把字段和方法定义在一个类中,并保证外界不能任意更改其内部的字段值,也不允许任意调动其内部的功能方法。
程序中的一种体现:
通常将类中的成员变量私有化(private),通过对外提供方法(setXxx,getXxx),可对该变量(xxx)进行访问。
boolean 类型的变量没有getXX,只有 isXX;
Eg:
class Person1{
private String name;
private int age;
private int sal;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
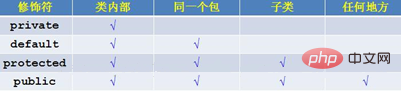
}8、访问修饰符
private 类访问权限:本类内部可以访问,不能继承到子类;
default 什么都不写,包访问权限:本类内部可以访问,同包其他类也可以访问,同包可继承;
protected 子类访问权限:本类内部可以访问,不同包的子类也可以访问,同包其他类也可以访问,能继承到子类;
public 公共访问权限:任何地方都可以访问,能继承到子类;
总结:
9. Class design analysis
Analysis ideas:
Write the class according to the requirements Contained fields;
All fields must be privatized;
The encapsulated fields can be set and obtained through setters and getters;
Several fields can be added as needed Constructor method;
Corresponding methods can be added according to requirements;
All methods in the class should not be processed directly (output and print), but should be left to the caller for processing.
10. Object-oriented inheritance
First there are classes that reflect the characteristics of general things, and then on this basis, classes that reflect special things ;
That is to say: inheritance is a relationship from general to special;
Features:
1. Improved code reusability.
2. Create a relationship between classes. Only with this inheritance relationship can we have the characteristics of polymorphism.
3. Java language only supports single inheritance (different from C language).
Because multiple inheritance can easily bring security risks (if there are too many parent classes and the functions are the same, will there be uncertainty in the call? Overwriting a method, who is overriding it?).
ps: The interface can realize multiple inheritance
4. Java supports multi-layer inheritance. Object is the super class of each class and implements a tree structure.
My summary:
Inheritance is the prerequisite for polymorphism.
For classes, only single inheritance is supported.
Format:
[Modifier] class SubClass extends SuperClass
According to this relationship, we The SuperClass class is called the parent class or base class, and the SubClass is called the subclass or derived class or extended class;
My summary:
java.lang.Object It is the parent class of all classes.
Object is either a direct parent class or an indirect parent class.
Eg:
Students belong to a special situation of human beings. At this time, I write the common characteristics of people in the Person class, in order to let students have these common characteristics (others such as teachers can also have These commonalities), then I ask students to expand the Person category.
My summary:
The relationship between the subclass and the parent class:
The subclass extends the parent class (the subclass is a special case of the parent class)
Mainly based on the parent class, and then add its own fields and methods.
The private members of the parent class cannot be inherited by subclasses;
The construction method of the parent class cannot be inherited;
Java only supports single inheritance, not multiple inheritance;/ /Otherwise, for example, if the show method inherits multiple methods, I don’t know which one to call.
A class has one and only one direct parent class;
When a class does not explicitly inherit another class, the default direct parent class is the Object class;
The direct parent class of Student is Person, and the Object class is also the parent class of Student class, but it is an indirect parent class;
Once a class explicitly inherits another class, the default direct parent class is Object will be cancelled;
A class in Java can only have one direct parent class;
java.lang.Object is the parent class of all classes, Object is either a direct parent class or an indirect parent class.
Subclass object instantiation process
In the inheritance operation, for the instantiation of subclass objects:
The subclass object must first call the parent class before instantiation 's constructor and then calls its own constructor.
The above is part of the content of this article. We will continue to organize object-oriented knowledge for everyone in the future. Please point out anything wrong, thank you!
For more related questions, please visit the PHP Chinese website: JAVA Video Tutorial
The above is the detailed content of java - detailed introduction to object-oriented (1). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1673
1673
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1333
1333
 25
25
 1277
1277
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 How to implement object-oriented event-driven programming using Go language
Jul 20, 2023 pm 10:36 PM
How to implement object-oriented event-driven programming using Go language
Jul 20, 2023 pm 10:36 PM
How to use Go language to implement object-oriented event-driven programming Introduction: The object-oriented programming paradigm is widely used in software development, and event-driven programming is a common programming model that realizes the program flow through the triggering and processing of events. control. This article will introduce how to implement object-oriented event-driven programming using Go language and provide code examples. 1. The concept of event-driven programming Event-driven programming is a programming model based on events and messages, which transfers the flow control of the program to the triggering and processing of events. in event driven
 What is the importance of @JsonIdentityInfo annotation using Jackson in Java?
Sep 23, 2023 am 09:37 AM
What is the importance of @JsonIdentityInfo annotation using Jackson in Java?
Sep 23, 2023 am 09:37 AM
The @JsonIdentityInfo annotation is used when an object has a parent-child relationship in the Jackson library. The @JsonIdentityInfo annotation is used to indicate object identity during serialization and deserialization. ObjectIdGenerators.PropertyGenerator is an abstract placeholder class used to represent situations where the object identifier to be used comes from a POJO property. Syntax@Target(value={ANNOTATION_TYPE,TYPE,FIELD,METHOD,PARAMETER})@Retention(value=RUNTIME)public
 PHP Advanced Features: Best Practices in Object-Oriented Programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
PHP Advanced Features: Best Practices in Object-Oriented Programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
OOP best practices in PHP include naming conventions, interfaces and abstract classes, inheritance and polymorphism, and dependency injection. Practical cases include: using warehouse mode to manage data and using strategy mode to implement sorting.
 Explore object-oriented programming in Go
Apr 04, 2024 am 10:39 AM
Explore object-oriented programming in Go
Apr 04, 2024 am 10:39 AM
Go language supports object-oriented programming through type definition and method association. It does not support traditional inheritance, but is implemented through composition. Interfaces provide consistency between types and allow abstract methods to be defined. Practical cases show how to use OOP to manage customer information, including creating, obtaining, updating and deleting customer operations.
 Are there any class-like object-oriented features in Golang?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:51 PM
Are there any class-like object-oriented features in Golang?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:51 PM
There is no concept of a class in the traditional sense in Golang (Go language), but it provides a data type called a structure, through which object-oriented features similar to classes can be achieved. In this article, we'll explain how to use structures to implement object-oriented features and provide concrete code examples. Definition and use of structures First, let's take a look at the definition and use of structures. In Golang, structures can be defined through the type keyword and then used where needed. Structures can contain attributes
 Analyzing the Flyweight Pattern in PHP Object-Oriented Programming
Aug 14, 2023 pm 05:25 PM
Analyzing the Flyweight Pattern in PHP Object-Oriented Programming
Aug 14, 2023 pm 05:25 PM
Analyzing the Flyweight Pattern in PHP Object-Oriented Programming In object-oriented programming, design pattern is a commonly used software design method, which can improve the readability, maintainability and scalability of the code. Flyweight pattern is one of the design patterns that reduces memory overhead by sharing objects. This article will explore how to use flyweight mode in PHP to improve program performance. What is flyweight mode? Flyweight pattern is a structural design pattern whose purpose is to share the same object between different objects.
 Analysis of object-oriented features of Go language
Apr 04, 2024 am 11:18 AM
Analysis of object-oriented features of Go language
Apr 04, 2024 am 11:18 AM
The Go language supports object-oriented programming, defining objects through structs, defining methods using pointer receivers, and implementing polymorphism through interfaces. The object-oriented features provide code reuse, maintainability and encapsulation in the Go language, but there are also limitations such as the lack of traditional concepts of classes and inheritance and method signature casts.
 In-depth understanding of PHP object-oriented programming: Debugging techniques for object-oriented programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:50 PM
In-depth understanding of PHP object-oriented programming: Debugging techniques for object-oriented programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:50 PM
By mastering tracking object status, setting breakpoints, tracking exceptions and utilizing the xdebug extension, you can effectively debug PHP object-oriented programming code. 1. Track object status: Use var_dump() and print_r() to view object attributes and method values. 2. Set a breakpoint: Set a breakpoint in the development environment, and the debugger will pause when execution reaches the breakpoint, making it easier to check the object status. 3. Trace exceptions: Use try-catch blocks and getTraceAsString() to get the stack trace and message when the exception occurs. 4. Use the debugger: The xdebug_var_dump() function can inspect the contents of variables during code execution.




