What are the stages of the Servlet life cycle?
The four stages of the Servlet life cycle are: loading stage, initialization stage, request processing and destruction stage. The methods to control the Servlet object life cycle are: init(), service() and destroy ()
The entire life cycle of Servlet is managed by the Servlet container, which uses the javax.servlet.Servlet interface to understand and manage Servlet objects. The life cycle of Servlet can be divided into four stages. They are: loading phase, initialization phase, request processing and destruction phase, so in the following article, I will introduce each stage of the Servlet object life cycle in detail
[Recommended course:Java Course】
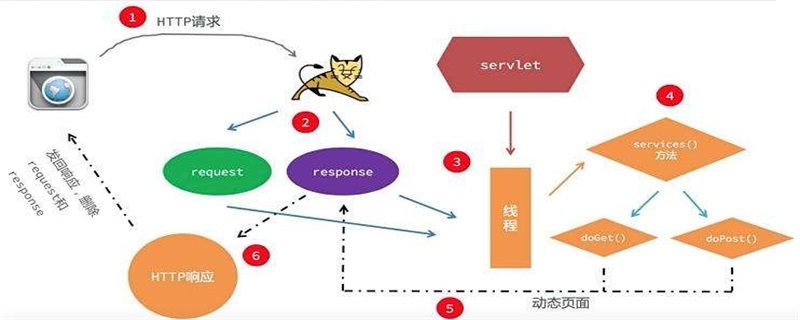
Life cycle of Servlet
1. Load Servlet
The first stage of the Servlet life cycle is to load and initialize through the Servlet container
The Servlet container loads everything Actions performed:
(1) Load Servlet class
(2) Create Servlet and instantiate
Note: If the Servlet is not in the previous stage, it may be lazy loaded process, because you need to know that the web container determines that a Servlet is needed to request services.
2. Initialization phase
After the Servlet is instantiated successfully, the Servlet container begins to initialize the Servlet object and immediately calls the Servlet.init() method to initialize resources
Servlet.init(ServletConfig)
If the Servlet cannot be initialized during this process, it will notify the Servlet container through ServletException or UnavailableException that it cannot be initialized
3. Process the request
After initialization, the Servlet instance is ready to serve client requests. When the Servlet instance is in the service request, the Servlet container will perform the following operations
(1) It will create ServletRequest and ServletResponse objects. If an HTTP request is sent, the Web container will create HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse objects
(2) After creating the request and response objects, it will call the Servlet.service() method.
Servlet.service(ServletRequest,ServletResponse)
The service() method when processing the request may throw ServletException or UnavailableException
4. Destroy the Servlet
When the Servlet container destroys the Servlet , it performs the following operations,
(1) It allows all threads currently running in the Servlet instance to be released after completing their jobs.
(2) After the currently running thread completes its job, the Servlet container releases all references to the entire servlet object instantiated by calling the destroy() method
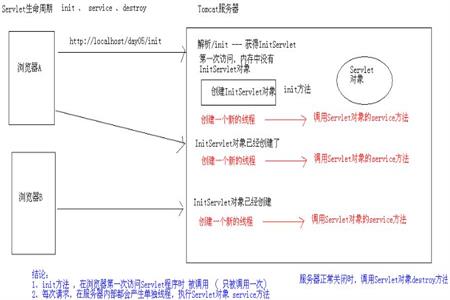
Servlet life cycle method
Method used to control the servlet life cycle, it has three life cycle methods:
init() method
Whether the Servlet object has been successfully initialized, it is called by the Servlet container. This method only accepts one parameter, the ServletConfig object
public void init(ServletConfig con)throws ServletException{ }service() method
Used to notify the Servlet object of the information requested by the client. It is the most important execution method and provides a connection between the client and the server. The web server handles the client's request and sends the response back to the client by calling the service() method.
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException { }This method accepts two parameters:
ServletRequest: Indicates collecting the data requested by the client.
ServletResponse: Indicates the generated output content.
destroy() method
This method only runs once in the servlet's life cycle and is called at the end of the servlet's life cycle. Indicates the end of Servlet object instantiation. Once this method is activated,
means that all Servlet instances will be released
public void destroy()
Summary: That’s it for this article The entire content of the article is here, I hope it will be helpful for everyone to learn the Servlet cycle
The above is the detailed content of What are the stages of the Servlet life cycle?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1421
1421
 52
52
 1315
1315
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 The servlet life cycle is divided into several stages
Feb 23, 2023 pm 01:46 PM
The servlet life cycle is divided into several stages
Feb 23, 2023 pm 01:46 PM
The Servlet life cycle refers to the entire process from creation to destruction of a servlet, which can be divided into three stages: 1. Initialization stage, calling the init() method to initialize the Servlet; 2. Running stage (processing requests), the container will Request to create a ServletRequest object representing an HTTP request and a ServletResponse object representing an HTTP response, and then pass them as parameters to the service() method of the Servlet; 3. Destruction phase.
 What is a servlet
Jan 28, 2023 am 09:51 AM
What is a servlet
Jan 28, 2023 am 09:51 AM
The full name of Servlet is "Java Servlet", which means small service program or service connector in Chinese. It is a program running on a Web server or application server. It serves as a request from a Web browser or other HTTP client and a database on the HTTP server or The middle layer between applications. Servlet has the characteristics of being independent of platform and protocol. Its main function is to browse and generate data interactively and generate dynamic Web content.
 How does Java Servlet implement distributed session management?
Apr 16, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
How does Java Servlet implement distributed session management?
Apr 16, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
There are two ways to implement distributed session management in JavaServlet: 1. Session replication: Copy session data to each server. 2. Session distribution: Use a centralized storage service to store session data and access it from multiple servers. The specific implementation methods are: session replication configures true in the web. session data.
 What are the application scenarios of Java Servlet?
Apr 17, 2024 am 08:21 AM
What are the application scenarios of Java Servlet?
Apr 17, 2024 am 08:21 AM
JavaServlet can be used for: 1. Dynamic content generation; 2. Data access and processing; 3. Form processing; 4. File upload; 5. Session management; 6. Filter. Example: Create a FormSubmitServlet to handle form submission, taking name and email as parameters, and redirecting to success.jsp.
 Java technology stack for web development: Understand Java EE, Servlet, JSP, Spring and other technologies commonly used in web development
Dec 26, 2023 pm 02:29 PM
Java technology stack for web development: Understand Java EE, Servlet, JSP, Spring and other technologies commonly used in web development
Dec 26, 2023 pm 02:29 PM
JavaWeb development technology stack: Master JavaEE, Servlet, JSP, Spring and other technologies used for Web development. With the rapid development of the Internet, in today's software development field, the development of Web applications has become a very important technical requirement. As a widely used programming language, Java also plays an important role in the field of Web development. The JavaWeb development technology stack involves multiple technologies, such as JavaEE, Servlet, JSP, Spr
 Servlet Container Revealed: A Deeper Understanding of the Servlet Runtime Environment
Feb 19, 2024 pm 01:00 PM
Servlet Container Revealed: A Deeper Understanding of the Servlet Runtime Environment
Feb 19, 2024 pm 01:00 PM
The Servlet container is an application that provides the Servlet running environment. It is responsible for managing the life cycle of the Servlet and providing necessary WEB services, such as security, transactions, etc. There are many types of Servlet containers, the most common of which are Tomcat and Jetty. The main functions of the Servlet container are life cycle management: The Servlet container is responsible for managing the life cycle of the Servlet, including startup, initialization, service and destruction. Web services: The Servlet container provides web services, such as security, transactions, etc. Resource management: Servlet container manages resources, such as Servlet, jsP, html pages, etc. Class loading: The Servlet container is responsible for adding
 Java Errors: Servlet Errors, How to Fix and Avoid
Jun 25, 2023 pm 06:34 PM
Java Errors: Servlet Errors, How to Fix and Avoid
Jun 25, 2023 pm 06:34 PM
Servlet is a very commonly used technology in Java Web application development. However, some Servlet errors will inevitably occur during the development process. How to solve and avoid Servlet errors has become a top issue for many Java developers. This article will introduce some common Servlet errors and their solutions based on personal experience and related information. ClassNotFoundException When we try to load a class, if the class does not exist or cannot be accessed by the system,
 HttpSession interface in Servlet
Sep 02, 2023 am 10:05 AM
HttpSession interface in Servlet
Sep 02, 2023 am 10:05 AM
In the world of Java Web development, understanding the HttpSession interface is key to creating dynamic and responsive web applications. In this article, we will explore what the HttpSession interface is, how it works, and why it plays a crucial role in the Servlet specification. What is the HttpSession interface? At its core, the HttpSession interface is a fundamental component of the JavaServlet API, which enables web developers to track a user's session across multiple HTTP requests. When a user accesses a web application for the first time, a unique session is created to represent their interaction. This session allows the application to maintain state between requests and remember information about




