Briefly describe session usage and detailed records in java
The following editor will bring you a brief discussion of session usage and detailed records in SpringMVC. The editor thinks it’s pretty good, so I’ll share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor and take a look.
Preface
I am new to SpringMVC. Recently, I need to use it to log in to the system I built for the company. session.
I found a lot of information on the Internet and roughly mentioned two ways to save sessions:
1. HttpSession## that is common to javaWeb projects.
#2. SpringMVC-specific @SessionAttributesI personally pay more attention to the usage of @SessionAttributes. After all, I am using SpringMVC now. But when I read the articles on the Internet, they basically only explained the basic usage, and there were basically no detailed usage and details. I thought this was not enough, so I did some tests myself, and then compiled the code and made a demo. Record and share it. If you have any shortcomings, you are welcome to discuss them. Okay, enough of the nonsense, now the real show begins!Conclusion
Well, in order to save some customers who don’t like to read code the trouble of reading the conclusion, I will first summarize my conclusion here. Let’s list the conclusions after the test first.1. You can automatically save data to the session through SpringMVC's unique ModelMap and Model in the Controller, or you can save session data through traditional HttpSession and other parameters
2. The @SessionAttributes annotation must be used to save session data. This annotation has two parameter declaration methods (value and type), and the annotation declaration must be written on the class, not on the method.
3. The saved session data must correspond to the parameter list in the @SessionAttributes annotation. Undeclared parameters cannot be saved in the session.
4. Use SessionStatus to clear the session saves. Note that all the data is cleared, and the specified session data cannot be deleted individually. At the same time, the effective permissions during clearing follow the above rules 2 and 3 (this rule can be used to artificially achieve the effect of deleting the specified session data)
5. Read the data in the session through ModelMap, etc. , there are also the above parameter permission restrictions
6. When using ModelMap or Model to save session data, ModelMap must be passed in as a method parameter, and the newly defined one in the method is invalid. At the same time, as long as the ModelMap is passed in as a parameter, it will work even if it is called by other methods
#7. When using the @ResponseBody annotation (usually used with ajax), the session cannot be saved Data
8. The @SessionAttributes annotation can use two parameter lists: value and type
9. The traditional method of using HttpSession does not have the above annotations. And permissions and other restrictions, there is a simple test below, but no detailed explanation
There are a few common knowledge points below
10. The operation of session data can be across classes, and it has nothing to do with the package or URL path.
11. If the same session value is operated, the later value will overwrite the previous value
Test code and brief description
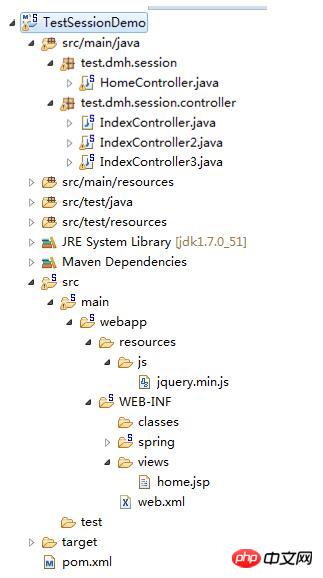
Development tools: Spring Tool Suite. spring is an IDE development tool based onFirst let’s take a screenshot of the project structure
<!-- 使用@ResponseBody注解所需的2个包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.codehaus.jackson</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-core-asl</artifactId> <version>1.9.13</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.codehaus.jackson</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-mapper-asl</artifactId> <version>1.9.13</version> </dependency>
package test.dmh.session;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.SessionAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.bind.support.SessionStatus;
/**
* @SessionAttributes 只声明了参数test1
*/
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(value={"test1"})
public class HomeController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HomeController.class);
@RequestMapping(value = "/show1")
public String show(ModelMap modelMap, HttpSession session) {
logger.info("show session");
for (Object key : modelMap.keySet()) {
Object value = modelMap.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("***********************************");
Enumeration<String> e = session.getAttributeNames();
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
String s = e.nextElement();
System.out.println(s + " == " + session.getAttribute(s));
}
System.out.println("***********************************");
return "home";
}
@RequestMapping("/set1")
public String setSession(ModelMap modelMap) {
logger.info("set session 1");
modelMap.addAttribute("test1", "value 1"); //设置一个在@SessionAttributes中声明过的参数
modelMap.addAttribute("test2", "value 2"); //设置一个未在@SessionAttributes中声明过的参数
return "home";
}
@RequestMapping("/setM")
public String setSessionM(Model model) {
logger.info("set session 1");
model.addAttribute("test1", "value 1"); //设置一个在@SessionAttributes中声明过的参数
model.addAttribute("test2", "value 2"); //设置一个未在@SessionAttributes中声明过的参数
return "home";
}
@RequestMapping("/clear1")
public String clear(SessionStatus status) {
logger.info("clear session 1");
status.setComplete();
return "home";
}
}package test.dmh.session.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* 没有使用@SessionAttributes注解
*/
@Controller
public class IndexController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(IndexController.class);
@RequestMapping("/set2")
public String setSession(ModelMap modelMap, HttpSession session) {
logger.info("set session 2 : without @SessionAttributes");
modelMap.addAttribute("test3", "value 3");
session.setAttribute("test4", "value 4");
return "home";
}
}package test.dmh.session.controller;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.SessionAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.bind.support.SessionStatus;
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(value={"test5", "index"})
public class IndexController2 {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(IndexController2.class);
@RequestMapping("/set3")
public String setSession(ModelMap modelMap, HttpSession session) {
logger.info("set session 3");
modelMap.addAttribute("test5", "value 5");
session.setAttribute("test6", "value 6");
ModelMap map = new ModelMap();
map.addAttribute("test7", "value 7");
this.setValueToSession(modelMap, session, "Hello World");
return "home";
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value="/login")
public Map<String, Object> login(ModelMap modelMap, HttpSession session) {
logger.info("login");
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("success", true);
map.put("info", "登录成功!");
modelMap.addAttribute("testAjax", "test ajax value");
session.setAttribute("httpTestAjax", "http test ajax Value");
setValueToSession(modelMap, session, "This is Ajax");
return map;
}
private void setValueToSession(ModelMap modelMap, HttpSession session, String value) {
logger.info("set session private");
modelMap.addAttribute("index", value);
session.setAttribute("httpIndex", value);
}
@RequestMapping("/clear2")
public String clear(SessionStatus status) {
logger.info("clear session 2");
status.setComplete();
return "home";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/show2")
public String show(ModelMap modelMap, HttpSession session) {
logger.info("show session");
for (Object key : modelMap.keySet()) {
Object value = modelMap.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("***********************************");
Enumeration<String> e = session.getAttributeNames();
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
String s = e.nextElement();
System.out.println(s + " == " + session.getAttribute(s));
}
System.out.println("***********************************");
return "home";
}
}<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
4 <html>
<head>
<title>Home</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>
Hello world!
</h1>
<p> The test1 is ${sessionScope.test1}. </p>
<p> The test2 is ${sessionScope.test2}. </p>
<p> The test3 is ${sessionScope.test3}. </p>
<p> The test4 is ${sessionScope.test4}. </p>
<p> The test5 is ${sessionScope.test5}. </p>
<p> The test6 is ${sessionScope.test6}. </p>
<p> The test7 is ${sessionScope.test7}. </p>
<p> The index is ${sessionScope.index}. </p>
<p> The httpIndex is ${sessionScope.httpIndex}. </p>
<br>
<input type="button" value="test" onclick="test();">
<script src="resources/js/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function test() {
$.ajax({
type : "POST",
url : "login",
dataType : "json",
success : function(data) {
console.log(data);
window.open("/session/test", "_self");
},
error : function() {
alert("出错了!");
}
});
}
</script>
</body>
</html>package test.dmh.session.controller;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.SessionAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.bind.support.SessionStatus;
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(value={"index1", "index2"}, types={String.class, Integer.class})
public class IndexController3 {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(IndexController3.class);
@RequestMapping("/setIndex")
public String setSession(ModelMap modelMap) {
logger.info("set session index");
modelMap.addAttribute("index1", "aaa");
modelMap.addAttribute("index2", "bbb");
modelMap.addAttribute("index2", "ccc");
modelMap.addAttribute("DDD");
modelMap.addAttribute("FFF");
modelMap.addAttribute(22);
return "home";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/showIndex")
public String show(ModelMap modelMap, HttpSession session) {
logger.info("show session");
for (Object key : modelMap.keySet()) {
Object value = modelMap.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("***********************************");
Enumeration<String> e = session.getAttributeNames();
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
String s = e.nextElement();
System.out.println(s + " == " + session.getAttribute(s));
}
System.out.println("***********************************");
return "home";
}
@RequestMapping("/clearIndex")
public String clear(SessionStatus status) {
logger.info("clear session index");
status.setComplete();
return "home";
}
}A brief description of the test process:
Because there are many parameters, I was too lazy to think of names, so the serialized test1, 2, and 3 passed. When testing, enter the URL on the browser: localhost:8080/session/show1Then change the suffix show1 to something else, such as set1, set2 and clear1, clear2, etc., specifically Please see the @RequestMapping configuration in my code.Every time you enter set1 and set2, you need to enter show1 and show2 to view the contents of the session through the console. Of course, you can also view the display information directly on the browser.
Here I will talk about the main conclusions:
1. To use ModelMap to automatically save data to the session, you must configure the @SessionAttributes annotation
2. The @SessionAttributes annotation can only be declared on a class. After the declaration, the methods in the class can only operate on the parameters configured in @SessionAttributes, including saving, Clear and read.
Finally, there are some conclusions drawn about the parameter configuration in @SessionAttributes:
1. The configuration parameters provide value and type, which are stored in ArrayType. (When there is only one parameter, there is no need to write it in array form, such as @SessionAttributes(value="test1", types=Integer.class))
2. Use value to configure parameters similar to the key-value pairs in Map key
3. After configuring the parameters of the practical type, the key saved in the background is its type. Personally, I feel that it is only useful when saving custom classobject, such as types=User.class , for general common class objects such as String, I think it is better to use value key-value pairs. Of course, specific situations still need to be analyzed on a case-by-case basis.
【Related Recommendations】
2.Java Video Tutorial on Implementing Equal-proportion Thumbnails of Pictures
The above is the detailed content of Briefly describe session usage and detailed records in java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1677
1677
 14
14
 1430
1430
 52
52
 1333
1333
 25
25
 1278
1278
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 A new programming paradigm, when Spring Boot meets OpenAI
Feb 01, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
A new programming paradigm, when Spring Boot meets OpenAI
Feb 01, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
In 2023, AI technology has become a hot topic and has a huge impact on various industries, especially in the programming field. People are increasingly aware of the importance of AI technology, and the Spring community is no exception. With the continuous advancement of GenAI (General Artificial Intelligence) technology, it has become crucial and urgent to simplify the creation of applications with AI functions. Against this background, "SpringAI" emerged, aiming to simplify the process of developing AI functional applications, making it simple and intuitive and avoiding unnecessary complexity. Through "SpringAI", developers can more easily build applications with AI functions, making them easier to use and operate.
 Use Spring Boot and Spring AI to build generative artificial intelligence applications
Apr 28, 2024 am 11:46 AM
Use Spring Boot and Spring AI to build generative artificial intelligence applications
Apr 28, 2024 am 11:46 AM
As an industry leader, Spring+AI provides leading solutions for various industries through its powerful, flexible API and advanced functions. In this topic, we will delve into the application examples of Spring+AI in various fields. Each case will show how Spring+AI meets specific needs, achieves goals, and extends these LESSONSLEARNED to a wider range of applications. I hope this topic can inspire you to understand and utilize the infinite possibilities of Spring+AI more deeply. The Spring framework has a history of more than 20 years in the field of software development, and it has been 10 years since the Spring Boot 1.0 version was released. Now, no one can dispute that Spring
 What are the implementation methods of spring programmatic transactions?
Jan 08, 2024 am 10:23 AM
What are the implementation methods of spring programmatic transactions?
Jan 08, 2024 am 10:23 AM
How to implement spring programmatic transactions: 1. Use TransactionTemplate; 2. Use TransactionCallback and TransactionCallbackWithoutResult; 3. Use Transactional annotations; 4. Use TransactionTemplate in combination with @Transactional; 5. Customize the transaction manager.
 How to set transaction isolation level in Spring
Jan 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
How to set transaction isolation level in Spring
Jan 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
How to set the transaction isolation level in Spring: 1. Use the @Transactional annotation; 2. Set it in the Spring configuration file; 3. Use PlatformTransactionManager; 4. Set it in the Java configuration class. Detailed introduction: 1. Use the @Transactional annotation, add the @Transactional annotation to the class or method that requires transaction management, and set the isolation level in the attribute; 2. In the Spring configuration file, etc.
 PHP MVC Architecture: Building Web Applications for the Future
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:01 AM
PHP MVC Architecture: Building Web Applications for the Future
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:01 AM
Introduction In today's rapidly evolving digital world, it is crucial to build robust, flexible and maintainable WEB applications. The PHPmvc architecture provides an ideal solution to achieve this goal. MVC (Model-View-Controller) is a widely used design pattern that separates various aspects of an application into independent components. The foundation of MVC architecture The core principle of MVC architecture is separation of concerns: Model: encapsulates the data and business logic of the application. View: Responsible for presenting data and handling user interaction. Controller: Coordinates the interaction between models and views, manages user requests and business logic. PHPMVC Architecture The phpMVC architecture follows the traditional MVC pattern, but also introduces language-specific features. The following is PHPMVC
 Spring Annotation Revealed: Analysis of Common Annotations
Dec 30, 2023 am 11:28 AM
Spring Annotation Revealed: Analysis of Common Annotations
Dec 30, 2023 am 11:28 AM
Spring is an open source framework that provides many annotations to simplify and enhance Java development. This article will explain commonly used Spring annotations in detail and provide specific code examples. @Autowired: Autowired @Autowired annotation can be used to automatically wire beans in the Spring container. When we use the @Autowired annotation where dependencies are required, Spring will find matching beans in the container and automatically inject them. The sample code is as follows: @Auto
 An advanced guide to PHP MVC architecture: unlocking advanced features
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:23 AM
An advanced guide to PHP MVC architecture: unlocking advanced features
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:23 AM
The MVC architecture (Model-View-Controller) is one of the most popular patterns in PHP development because it provides a clear structure for organizing code and simplifying the development of WEB applications. While basic MVC principles are sufficient for most web applications, it has some limitations for applications that need to handle complex data or implement advanced functionality. Separating the model layer Separating the model layer is a common technique in advanced MVC architecture. It involves breaking down a model class into smaller subclasses, each focusing on a specific functionality. For example, for an e-commerce application, you might break down the main model class into an order model, a product model, and a customer model. This separation helps improve code maintainability and reusability. Use dependency injection
 Spring Security permission control framework usage guide
Feb 18, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Spring Security permission control framework usage guide
Feb 18, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
In back-end management systems, access permission control is usually required to limit different users' ability to access interfaces. If a user lacks specific permissions, he or she cannot access certain interfaces. This article will use the waynboot-mall project as an example to introduce how common back-end management systems introduce the permission control framework SpringSecurity. The outline is as follows: waynboot-mall project address: https://github.com/wayn111/waynboot-mall 1. What is SpringSecurity? SpringSecurity is an open source project based on the Spring framework, aiming to provide powerful and flexible security for Java applications.




