Detailed explanation of LinkedList in Java collections
LinkedList is a doubly linked list that inherits AbstractSequentialList. It can also be operated as a stack, queue or double-ended queue.
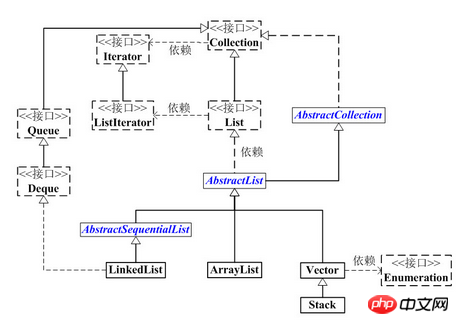
LinkedList implements the List interface and can perform queue operations on it.
LinkedList implements the Seque interface and can use LinkedList as a double-ended queue.
LinkedList implements Cloneable, covers the clone function, and can be cloned.
LinkedList implements Serializable and can be serialized.
LinkedList is not thread-safe.
LinkedList sample program:
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testLinkedListAPIs() ;
useLinkedListAsLIFO();
useLinkedListAsFIFO();
}
private static void testLinkedListAPIs()
{
String val = null;
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
//添加是哪个元素
llist.add("1");
llist.add("2");
llist.add("3");
llist.add(1, "4");//在第一个元素后面插入4
System.out.println("\nTest \"addFirst(), removeFirst(), getFirst()\"");
llist.addFirst("10");//将10插入并作为第一个元素
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
System.out.println("llist.removeFirst():"+llist.removeFirst());//删除掉第一个元素
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
System.out.println("llist.getFirst():"+llist.getFirst());//获得第一个元素
System.out.println("\nTest \"offerFirst(), pollFirst(), peekFirst()\"");
llist.offerFirst("10");//添加第一个元素
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
System.out.println("llist.pollFirst():"+llist.pollFirst());//去掉第一个元素
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
System.out.println("llist.peekFirst():"+llist.peekFirst());//读取第一个元素
System.out.println("\nTest \"addLast(), removeLast(), getLast()\"");
llist.addLast("20");//链尾添加元素20
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
System.out.println("llist.removeLast():"+llist.removeLast());//删掉链尾元素20
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
System.out.println("llist.getLast():"+llist.getLast());//读取链尾元素
System.out.println("\nTest \"offerLast(), pollLast(), peekLast()\"");
llist.offerLast("20");//添加链尾元素20
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
System.out.println("llist.pollLast():"+llist.pollLast());//删掉链尾元素20
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
System.out.println("llist.peekLast():"+llist.peekLast());//读取链尾元素
llist.set(2, "300");//替换第三个元素
System.out.println("\nget(3):"+llist.get(2));//获得第三个元素
String[] arr = (String[])llist.toArray(new String[0]);//得到数组
for (String str:arr)
{
System.out.println("str:"+str);
System.out.println("size:"+llist.size());
llist.clear();
System.out.println("isEmpty():"+llist.isEmpty()+"\n");
}
}
private static void useLinkedListAsLIFO()
{
System.out.println("\nuseLinkedListAsLIFO");
LinkedList stack = new LinkedList();
//类似于栈输入
stack.push("1");
stack.push("2");
stack.push("3");
stack.push("4");
System.out.println("stack:"+stack);
System.out.println("stack.pop():"+stack.pop());//出栈
System.out.println("stack.peek():"+stack.peek());//只输出栈顶元素并不出栈
System.out.println("stack:"+stack);
}
private static void useLinkedListAsFIFO()
{
System.out.println("\nuseLinkedListAsFIFO");
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
//类似于队列,入队
queue.add("10");
queue.add("20");
queue.add("30");
queue.add("40");
System.out.println("queue:"+queue);
System.out.println("queue.remove():"+queue.remove());//队列出队
System.out.println("queue.element():"+queue.element());//读取队头,并不删除元素
System.out.println("queue:"+queue);
}
}Output result:
Test "offerLast(), pollLast(), peekLast()" llist:[1, 4, 2, 3, 20] llist.pollLast():20 llist:[1, 4, 2, 3] llist.peekLast():3 get(3):300 str:1 size:4 isEmpty():true str:4 size:0 isEmpty():true str:300 size:0 isEmpty():true str:3 size:0 isEmpty():true useLinkedListAsLIFO stack:[4, 3, 2, 1] stack.pop():4 stack.peek():3 stack:[3, 2, 1] useLinkedListAsFIFO queue:[10, 20, 30, 40] queue.remove():10 queue.element():20 queue:[20, 30, 40]
LinkedList source code:
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
transient int size = 0; //其实大小为0
transient Node<E> first; //第一个节点
transient Node<E> last; //最后一个节点
public LinkedList() { //构造一个空LinkedList
}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { //构造一个带有输入集合的
this();
addAll(c);
}
private void linkFirst(E e) { //链接第一个节点
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
void linkLast(E e) { //链接最后一个节点
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { //在节点succ前插入一个e
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//不再链接第一个非空的节点
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//删掉最后一个节点
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//删掉节点X
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//获得第一个节点
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
//获得最后一个节点
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
//删除第一个节点
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
//删除最后一个节点
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
//在头节点插入E
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
//在尾节点插入E
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
//是否包含某个对象
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
//链表长度
public int size() {
return size;
}
//在链表中添加节点
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
//删掉某个节点
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//在链表尾追加集合
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
//在某个节点之后追加集合
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
//清空链表
public void clear() {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) {
Node<E> next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
//获得第几个节点
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
//对某个节点修改
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
//在index节点之前插入一个节点element
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
//删除掉下标为index的节点
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
//测试此index下是否有节点
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
//下标位置在链表内
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
//下标越界
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
//检查下标下的节点
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
//判断下标位置
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
//返回下标节点
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
//查找是否存在节点并返回下标,不存在返回-1
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
//返回最后一个相同的节点的下标
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
//返回表头数据并不删除
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
//返回表头数据
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
//获得表头数据,并删除表头
public E poll() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
//删除表头
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
//在表尾添加数据
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
//在表头添加数据
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
//在表尾添加数据
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
//获得第一个数据,并不删除
public E peekFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
//获得最后一个数据,并不删除
public E peekLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
//获得第一个节点并删除
public E pollFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
//获得最后一个节点并删除
public E pollLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
//入栈
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
//出栈
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
//删除第一次出现的对象
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
return remove(o);
}
//删除最后一次出现的对象
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//迭代器
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
private Node<E> lastReturned;
private Node<E> next;
private int nextIndex;
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
ListItr(int index) {
// assert isPositionIndex(index);
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
nextIndex = index;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex < size;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return nextIndex > 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasPrevious())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return nextIndex;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return nextIndex - 1;
}
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;
unlink(lastReturned);
if (next == lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.item = e;
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = null;
if (next == null)
linkLast(e);
else
linkBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) {
action.accept(next.item);
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
}
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
/**
* @since 1.6
*/
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingIterator();
}
/**
* Adapter to provide descending iterators via ListItr.previous
*/
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> {
private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private LinkedList<E> superClone() {
try {
return (LinkedList<E>) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
public Object clone() {
LinkedList<E> clone = superClone();
// Put clone into "virgin" state
clone.first = clone.last = null;
clone.size = 0;
clone.modCount = 0;
// Initialize clone with our elements
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
clone.add(x.item);
return clone;
}
//生成对象数组
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] result = new Object[size];
int i = 0;
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
return result;
}
//泛型数组
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
int i = 0;
Object[] result = a;
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 876323262645176354L;
//序列化写对象
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
s.writeObject(x.item);
}
//序列化读对象
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in size
int size = s.readInt();
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
linkLast((E)s.readObject());
}
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new LLSpliterator<E>(this, -1, 0);
}
/** A customized variant of Spliterators.IteratorSpliterator */
static final class LLSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {
static final int BATCH_UNIT = 1 << 10; // batch array size increment
static final int MAX_BATCH = 1 << 25; // max batch array size;
final LinkedList<E> list; // null OK unless traversed
Node<E> current; // current node; null until initialized
int est; // size estimate; -1 until first needed
int expectedModCount; // initialized when est set
int batch; // batch size for splits
LLSpliterator(LinkedList<E> list, int est, int expectedModCount) {
this.list = list;
this.est = est;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
final int getEst() {
int s; // force initialization
final LinkedList<E> lst;
if ((s = est) < 0) {
if ((lst = list) == null)
s = est = 0;
else {
expectedModCount = lst.modCount;
current = lst.first;
s = est = lst.size;
}
}
return s;
}
public long estimateSize() { return (long) getEst(); }
public Spliterator<E> trySplit() {
Node<E> p;
int s = getEst();
if (s > 1 && (p = current) != null) {
int n = batch + BATCH_UNIT;
if (n > s)
n = s;
if (n > MAX_BATCH)
n = MAX_BATCH;
Object[] a = new Object[n];
int j = 0;
do { a[j++] = p.item; } while ((p = p.next) != null && j < n);
current = p;
batch = j;
est = s - j;
return Spliterators.spliterator(a, 0, j, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
return null;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Node<E> p; int n;
if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if ((n = getEst()) > 0 && (p = current) != null) {
current = null;
est = 0;
do {
E e = p.item;
p = p.next;
action.accept(e);
} while (p != null && --n > 0);
}
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Node<E> p;
if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if (getEst() > 0 && (p = current) != null) {
--est;
E e = p.item;
current = p.next;
action.accept(e);
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
}The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of LinkedList in Java collections. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.






