 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 H5 Tutorial
H5 Tutorial
 The HTTP caching mechanism you deserve to know (detailed code explanation)
The HTTP caching mechanism you deserve to know (detailed code explanation)
The HTTP caching mechanism you deserve to know (detailed code explanation)
In the previous article "In-depth analysis of the white screen problem of routing switching in vue (with code)", we learned about the white screen problem of routing switching in vue. The following article will give you a detailed explanation of the HTTP caching mechanism. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.

##Web Caching can be roughly divided into: database cache, server-side cache (proxy server cache, CDN cache ), browser cache.
HTTP cache, indexDB, cookie, localstorage, etc.
What I want to talk about here is httpcaching.
- Reduces redundant data transmission
- Alleviates network bottlenecks
- Reduced the requirements for the original server
- Reduced the distance delay
Cache hit rate: The ratio of the number of requests to get data from the cache to the number of all requests. Ideally, the higher the better.
Expired content: Content that exceeds the set validity time and is marked as "stale". Usually expired content cannot be used to reply to client requests, and new content must be requested from the origin server again or the cached content must be verified to be still ready.
Verification: Verify whether the expired content in the cache is still valid. If the verification passes, refresh the expiration time.
Invalidation: Invalidation is to remove the content from the cache. When content changes, invalid content must be removed.
Mechanism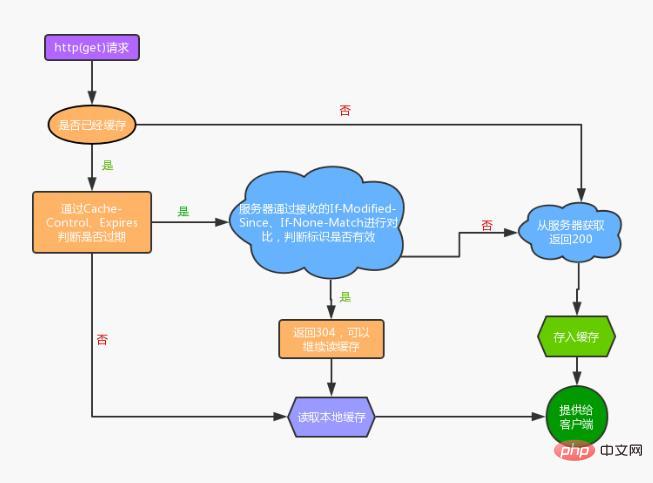
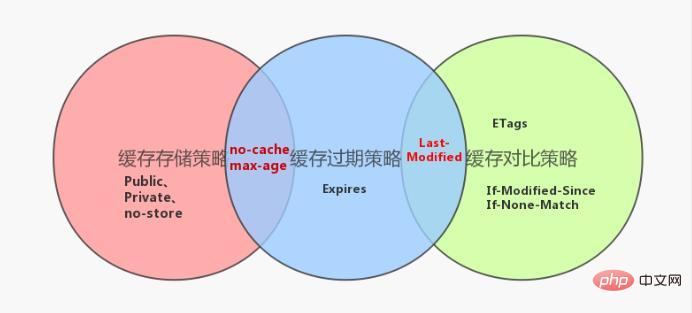
1) Cache storage strategy
Cache The storage policy determines whether the client should store theresponse of http. The http header related to cache storage is mainly the Cache-Control in the response header. The header has the following corresponding values: Public, Private, no-cache, max-age, no-store. Except for no-store, the others will indicate that response should be cached by the client.
Through the Cache-Control: Public setting we can store the HTTP response data locally, but this does not mean that subsequent browsers will read the data directly from the cache. And use, because it cannot determine whether the locally cached data is available (may have expired), it needs to be judged by the cache expiration policy
2) Cache expiration policy
The cache expiration policy determines whether the cache data stored locally by the client has expired. If it has not expired, the locally stored data can be used directly. Otherwise, a request needs to be sent to the server to try to re-obtain the data. The http header related to the cache expiration policy is Expires.
Expires indicates the absolute time when the cached data is valid, telling the client that the local cache will become invalid after this time point. During this time, the client can directly cache from the local cache without requesting the server. Use the stored results in .
It should be noted that :no-cache and max-age=xxx have higher priority than Expires. When they exist at the same time, the latter will be Cover it. Secondly, cache data expiration only tells the client that it can no longer read the cache directly from the local cache, but needs to send another request to the server for confirmation. The specific circumstances under which locally stored data can continue to be used depend on the cache comparison strategy.
3) Cache comparison strategy
Send the data identifier cached on the client to the server. The server uses the identifier to determine whether the client cached data is still valid, and then Decide whether to resend the data. After the client detects that the data has expired or the browser is refreshed, it will re-initiate an http request to the server. The server is not eager to return the data at this time, but looks at whether the request header has an identifier (If-Modified-Since, If -None-Match), if the judgment flag is still valid, return 304 to tell the client to fetch the local cached data and use it (note here that you must output it in the first response Corresponding header information (Last-Modified, ETags) to the client). Even if the locally cached data is considered expired, it does not mean that the data is no longer useful.
Cache expiration value
In the storage policy, no-cache is equivalent to max-age=0, if there is no response in the response returned by the server When specifying max-age, no-cache or Expires, will the client cache the http response? Through packet capture tools such as Fiddler and Charles, we can find that the client will also cache
whose value is the Date## in the response header. 10% of the difference between # and Last-Modified is used as the cache validity time
Caching panel of Fiddler
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
1) Forced caching
can be set throughExpires, Cache-Control, Expires refers to the cache expiration time, and if it exceeds this time point, it means that the resource Expired. One problem is that due to the use of specific times, if the time is represented incorrectly or is not converted to the correct time zone, it may cause errors in the cache life cycle.
And Expires is the standard of HTTP/1.0, now it is more inclined to use Cache-Control defined in HTTP/1.1. When both exist at the same time, Cache-Control has a higher priority.
2) Negotiate cache
The expiration of cached resources does not mean that the resource content has changed. If there is no difference from the resources on the server, in fact There is no need to request again. The client and server verify whether the currently requested resource can use the cache through some verification mechanism. After the browser requests data for the first time, it will store the data and the cache identifier of the response header. When requesting again, the stored header field will be brought, and the server will verify whether it is available. If304 Not Modified is returned, it means that the resource has not changed and you can use cached data to obtain a new expiration time. On the contrary, returning 200 is equivalent to requesting the resource again and replacing the old resource.
Last-modified/If-Modified-Since
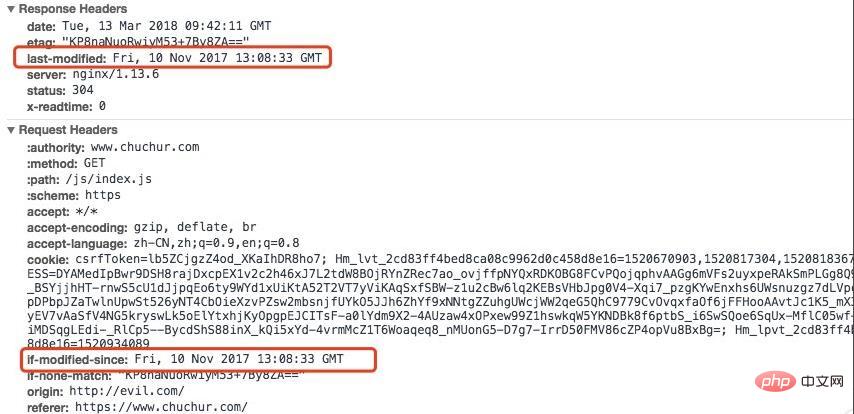
Last-modified: The last modification time of the server-side resource, the response header will contain on this logo. After the first request, the browser records this time. When requesting again, the request header will contain If-Modified-Since, which is the previously recorded time. After receiving the request with If-Modified-Since, the server will compare it with the last modification time of the resource. If it has been modified, the latest resource will be returned with status code 200. If it has not been modified, it will be returned to 304.
Etag/If-None-Match
A hash string generated by the server. The response header will have ETag: abcd in the first request, and If- in subsequent requests. None-Match: abcd, the server checks ETag and returns 304 or 200.
About the difference between last-modified and Etag
Some servers cannot accurately obtain the last modification time of the resource, so it is impossible to determine whether the resource has been updated based on the last modification time.
Last-modifiedcan only be accurate to seconds.The last modification time of some resources has changed, but the content has not changed. Using
Last-modifieddoes not show that the content has not changed. The accuracy ofEtagis higher than that ofLast-modified. It is a strong verification and requires consistent resource byte level and high priority. If the server providesETag, it must first perform aConditional RequestforETag.
Note: In actual use of ETag/Last-modified, pay attention to maintaining consistency. Inconsistencies may occur when doing load balancing and reverse proxying. Calculating ETag also requires resources. If the modification is not too frequent, see if your needs can be met by using Cache-Control.
Practical Application
First of all, it is necessary to clarify which content is suitable for caching and which is not.
Consider cached content: css style files, js files, logo, icons, html files, you can Some downloaded content should not be cached: business-sensitive GET requests
Cacheable content is divided into several different situations:
Files that do not change frequently: tomax-ageSet a larger value, generally set max-age=31536000For example, some third-party files introduced and packaged have hash suffixcss, js files. Generally speaking, if the file content changes, the version number and hash value will be updated, which is equivalent to requesting another file. The standard stipulates that the value of max-age cannot exceed one year, so it is set to max-age=31536000. As for expired content, the cache area will delete files that have not been used for a period of time.
[End]
Recommended learning: Html5 video tutorial
| All content All will be cached (both the client and the proxy server can cache) | |
| The content will only be cached in the private cache (only the client can cache, not the proxy server) Cache) | |
| The cached content will expire after xxx seconds. Before the expiration, you can directly use the local cache. After the expiration, You must confirm with the server whether the resource has changed. | |
| Not cached at all on the client side | |
| can be considered equivalent In the case of max-age=0, the response will be cached on the client, but every time thereafter, it will confirm with the server whether the resource has changed |
The above is the detailed content of The HTTP caching mechanism you deserve to know (detailed code explanation). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1318
1318
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1248
1248
 24
24
 Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand the meaning of HTTP 301 status code: common application scenarios of web page redirection. With the rapid development of the Internet, people's requirements for web page interaction are becoming higher and higher. In the field of web design, web page redirection is a common and important technology, implemented through the HTTP 301 status code. This article will explore the meaning of HTTP 301 status code and common application scenarios in web page redirection. HTTP301 status code refers to permanent redirect (PermanentRedirect). When the server receives the client's
 PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools. In today's era of rapid development of the Internet, front-end development has become increasingly important. As users have higher and higher requirements for the experience of websites and applications, front-end developers need to use more efficient and flexible tools to create responsive and interactive interfaces. As two important technologies in the field of front-end development, PHP and Vue.js can be regarded as perfect tools when paired together. This article will explore the combination of PHP and Vue, as well as detailed code examples to help readers better understand and apply these two
 Exploring Go language front-end technology: a new vision for front-end development
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
Exploring Go language front-end technology: a new vision for front-end development
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
As a fast and efficient programming language, Go language is widely popular in the field of back-end development. However, few people associate Go language with front-end development. In fact, using Go language for front-end development can not only improve efficiency, but also bring new horizons to developers. This article will explore the possibility of using the Go language for front-end development and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand this area. In traditional front-end development, JavaScript, HTML, and CSS are often used to build user interfaces
 How to implement HTTP streaming using C++?
May 31, 2024 am 11:06 AM
How to implement HTTP streaming using C++?
May 31, 2024 am 11:06 AM
How to implement HTTP streaming in C++? Create an SSL stream socket using Boost.Asio and the asiohttps client library. Connect to the server and send an HTTP request. Receive HTTP response headers and print them. Receives the HTTP response body and prints it.
 Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
In front-end development interviews, common questions cover a wide range of topics, including HTML/CSS basics, JavaScript basics, frameworks and libraries, project experience, algorithms and data structures, performance optimization, cross-domain requests, front-end engineering, design patterns, and new technologies and trends. . Interviewer questions are designed to assess the candidate's technical skills, project experience, and understanding of industry trends. Therefore, candidates should be fully prepared in these areas to demonstrate their abilities and expertise.
 What status code is returned for an HTTP request timeout?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
What status code is returned for an HTTP request timeout?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
The HTTP request times out, and the server often returns the 504GatewayTimeout status code. This status code indicates that when the server executes a request, it still fails to obtain the resources required for the request or complete the processing of the request after a period of time. It is a status code of the 5xx series, which indicates that the server has encountered a temporary problem or overload, resulting in the inability to correctly handle the client's request. In the HTTP protocol, various status codes have specific meanings and uses, and the 504 status code is used to indicate request timeout issues. in customer
 How to implement h5 to slide up on the web side to load the next page
Mar 11, 2024 am 10:26 AM
How to implement h5 to slide up on the web side to load the next page
Mar 11, 2024 am 10:26 AM
Implementation steps: 1. Monitor the scroll event of the page; 2. Determine whether the page has scrolled to the bottom; 3. Load the next page of data; 4. Update the page scroll position.
 Combination of Golang and front-end technology: explore how Golang plays a role in the front-end field
Mar 19, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Combination of Golang and front-end technology: explore how Golang plays a role in the front-end field
Mar 19, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Combination of Golang and front-end technology: To explore how Golang plays a role in the front-end field, specific code examples are needed. With the rapid development of the Internet and mobile applications, front-end technology has become increasingly important. In this field, Golang, as a powerful back-end programming language, can also play an important role. This article will explore how Golang is combined with front-end technology and demonstrate its potential in the front-end field through specific code examples. The role of Golang in the front-end field is as an efficient, concise and easy-to-learn



