A useful LaTeX editor on the Linux platform
Introduction: Once you get over the learning curve of LaTeX, nothing beats LaTeX. Here are the best LaTeX editors for Linux and other platforms.
LaTeX[1] is a document production system. Unlike a plain text editor, in a LaTeX editor you can't just write plain text, you also have to use some LaTeX commands in order to organize the content of the document.
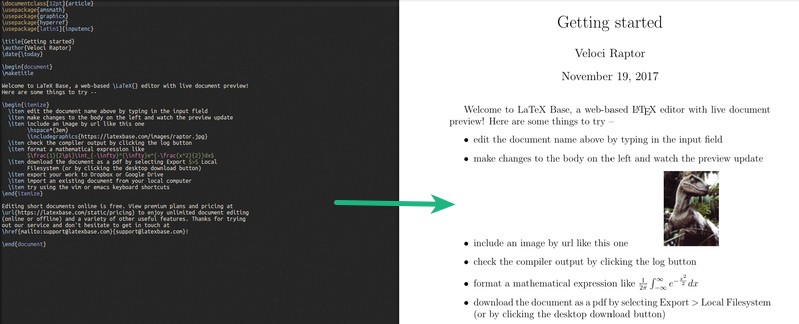
LaTeX editor is generally used for publishing scientific research documents or books for academic purposes. Most importantly, it can bring you convenience when you need to process documents containing many complex mathematical symbols. Sure, using a LaTeX editor is fun, but it's not always useful unless you have some special needs for the document you're writing.
Well, as I mentioned before, using a LaTeX editor means you have specific needs. In order to mess around with the LaTeX editor, you don't need to have a geek mind. But for those using regular text editors, it's not a very efficient solution.
If you are looking for a tool to carefully create a document, and you have no interest in spending time formatting text, then the LaTeX editor may be just the tool you are looking for. In the LaTeX editor, you only need to specify the type of document, and it will set the font type and size of the document for you accordingly. It is for this reason that it is no wonder that it is considered one of the best open source tools for writers[2].
But please be aware: The LaTeX editor is not an automated tool. You must first learn some LaTeX commands to enable it to accurately process text formatting.
Let me explain in advance that the following list does not have a clear order. The editor with serial number 3 is not necessarily better than the editor with serial number 7.
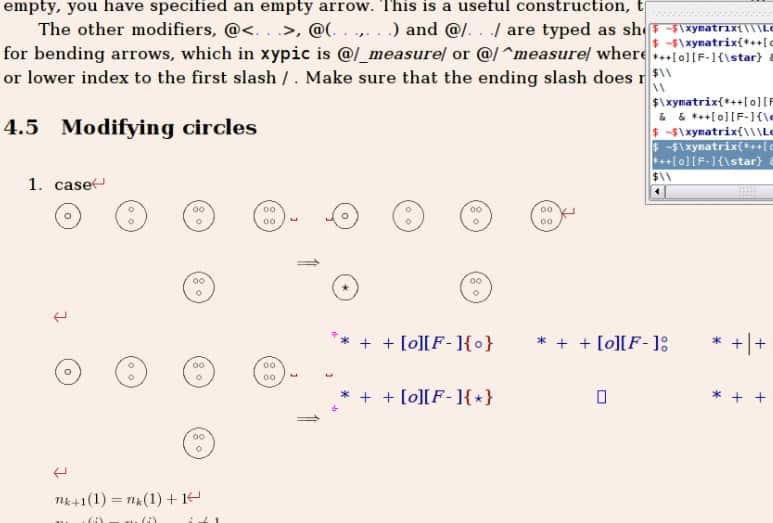
LyX[3] is an open source LaTeX editor, which means it is one of the best document processing engines available on the Internet. LyX helps you focus on your article and forget about formatting words, which is what every LaTeX editor should do. LyX allows you to manage different document contents based on different documents. Once you install it, you can control many things in your document, such as margins, headers, footers, whitespace, indents, tables, and more.
If you are busy writing carefully crafted scientific documents, research papers, or similar documents, you will be happy to experience LyX's equation editor, which is one of its features. LyX also includes a series of tutorials to get started, making getting started less hassle-free.
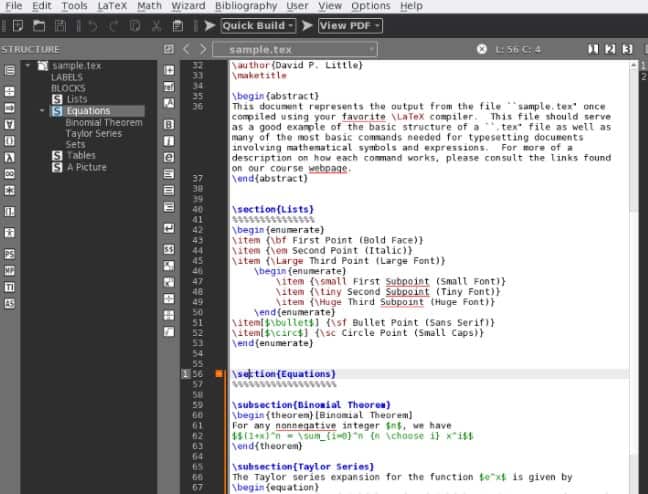
Texmaker[4] is considered one of the best LaTeX editors for the GNOME desktop environment. It presents a very nice user interface, resulting in a great user experience. It is also known as one of the most practical LaTeX editors. If you frequently convert PDFs, you will find that TeXmaker is faster than other editors. As you write, you can also preview how your document will ultimately look. At the same time, you can also observe that you can easily find the required symbols.
Texmaker also provides an extended shortcut key support. Why wouldn't you try using it?
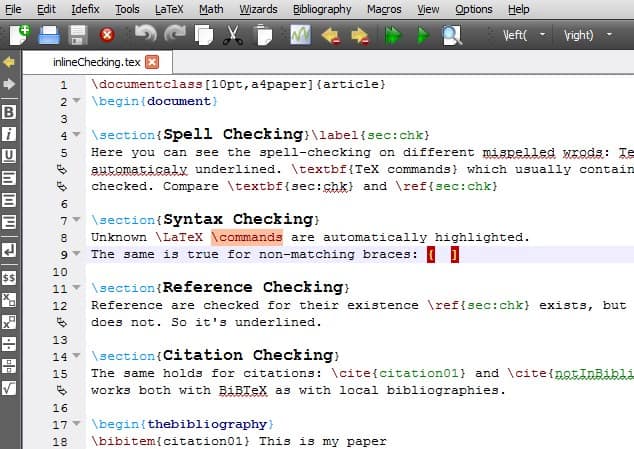
If you want a LaTeX editor that can provide you with quite good customization functions and an easy-to-use interface, then TeXstudio[5] is the one Perfect choice. Its UI is indeed simple, but not crude. TeXstudio comes with syntax highlighting, an integrated reader that allows you to check references, and other auxiliary tools.
It also supports some cool features, such as auto-completion, link overlay, bookmarks, multi-cursors, etc., which makes writing LaTeX documents easier than before.
TeXstudio is actively maintained, making it a compelling choice for novice or advanced writers.
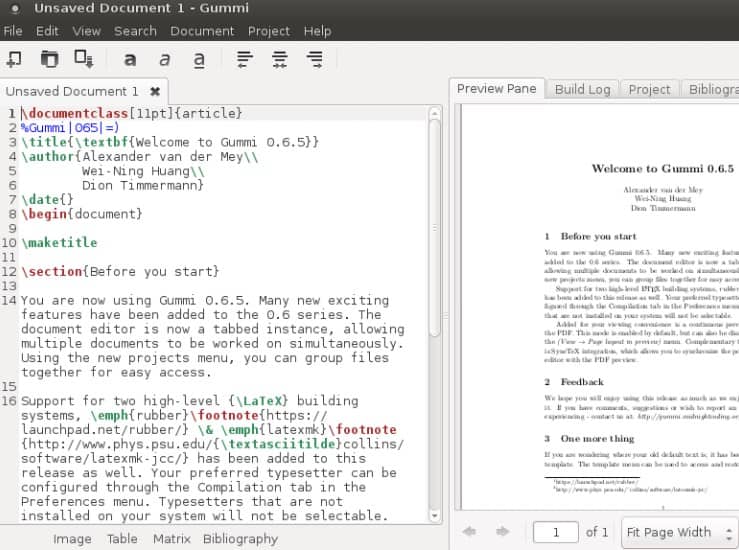
Gummi[6] is a very simple LaTeX editor based on the GTK toolbox. Of course, you won’t find many fancy options in this editor, but if you just want to be able to start writing right away, then Gummi is our recommendation for you. It supports outputting documents to PDF format, supports syntax highlighting, and helps you perform some basic error checking. Although it is no longer actively maintained on GitHub, it still works fine.
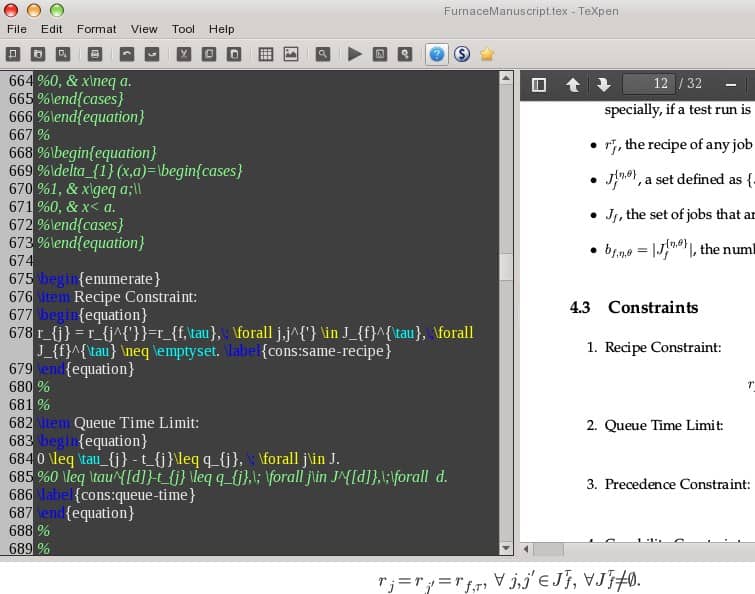
TeXpen[7] is another simple LaTeX editor. It provides you with auto-completion functionality. But the user interface may not impress you. If you don't care about the user interface and want a super easy LaTeX editor, TeXpen will meet your needs. At the same time, TeXpen can also correct or improve the English grammar and expressions used in the document for you.
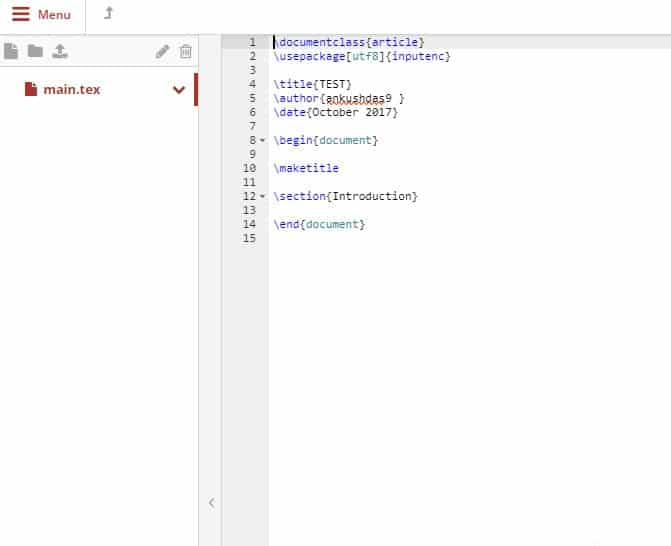
ShareLaTeX[8] is an online LaTeX editor. If you want to collaborate on a document with someone or a group of friends, then this is what you need.
It offers a free plan and several paid plans. Even students from Harvard and Oxford universities use it for personal projects. Its free plan also allows you to add a collaborator.
Its paid plan allows you to synchronize with GitHub and Dropbox, and can record the complete document modification history. You can select multiple collaborators for each of your projects. For students, it also offers separate billing plans.
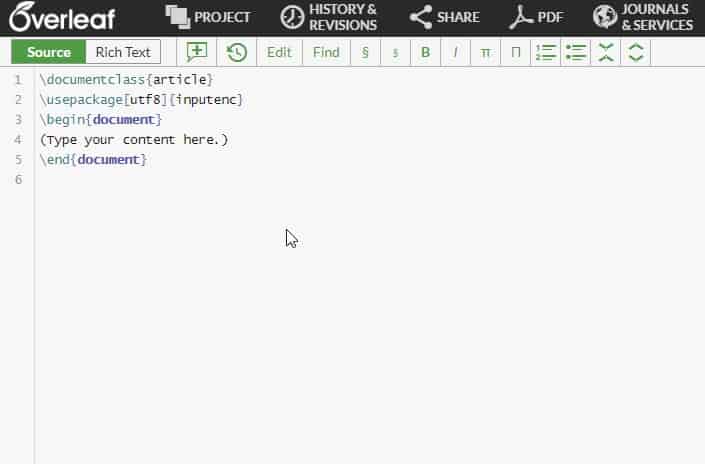
Overleaf[9] is another online LaTeX editor. It is similar to ShareLaTeX in that it offers different billing plans for experts and students. It also offers a free plan with which you can sync with GitHub, check your revision history, or add multiple collaborators.
In each project, it has a limit on the number of files. So in most cases this won't be an inconvenience for you if you are very familiar with LaTeX files.

Authorea[10] is a wonderful online LaTeX editor. Of course, if you take the price into consideration, it might not be the best one. For the free plan, it has a 100 MB data upload limit and the ability to create only one private document at a time. The paid plan, on the other hand, offers more perks, but if you consider the price, it might not be the cheapest. The only reason you should choose Authorea should be because of its user interface. If you love using a tool that offers an impressive user interface, don't miss it.
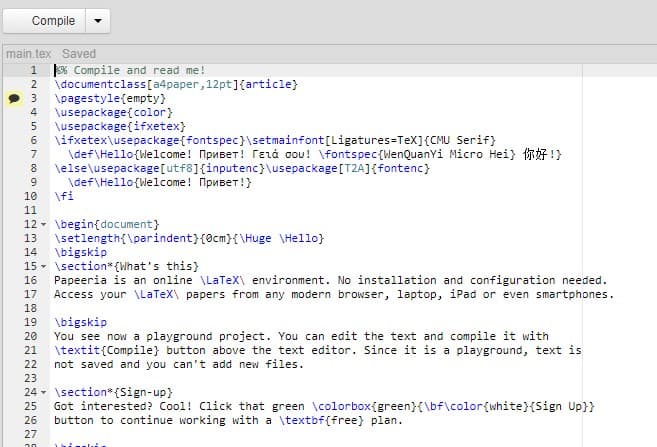
Papeeria[11] is the cheapest LaTeX online editor you can find on the Internet, considering that it is as reliable as other editors. If you want to use it for free, you cannot use it for private projects. However, if you prefer public projects, it allows you to create an unlimited number of projects and add an unlimited number of collaborators. It features a very simple paint builder and uses Git synchronization at no additional cost. If you prefer the paid plan, it gives you the ability to create 10 private projects.
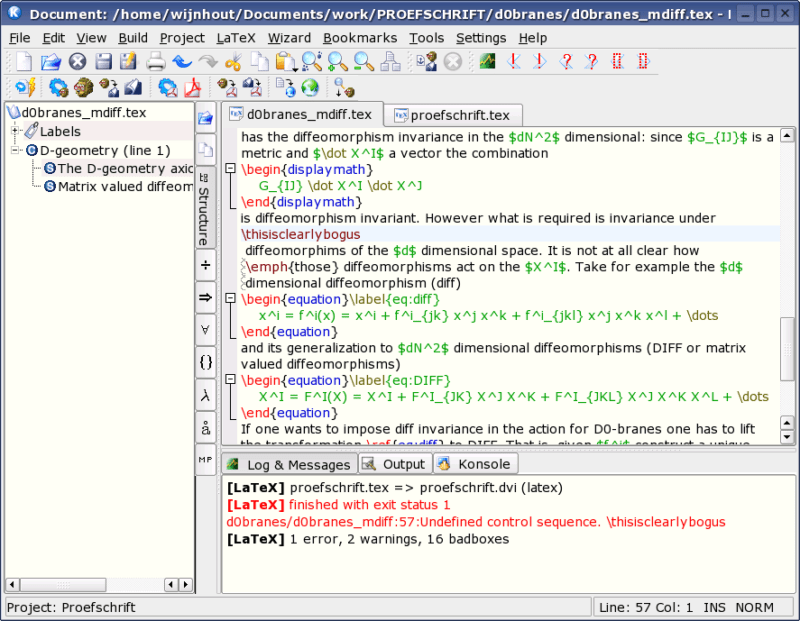
Finishing last on our list of the best LaTeX editors is the Kile[12] editor. Some friends highly praise Kile, largely because of the features it provides.
Kile is not just an editor, it is an IDE tool similar to Eclipse, providing a complete environment for documents and projects. In addition to quick compilation and preview functions, you can also use functions such as automatic completion of commands, inserting references, and organizing documents according to chapters. You really should use Kile to see its potential.
Kile is available on both Linux and Windows platforms.
So the above are our recommended LaTeX editors that you can use in Ubuntu or other Linux distributions.
The above is the detailed content of A useful LaTeX editor on the Linux platform. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.






