 Software Tutorial
Software Tutorial
 Computer Software
Computer Software
 How to change to the next line in matlab-How to change to the next line in matlab
How to change to the next line in matlab-How to change to the next line in matlab
How to change to the next line in matlab-How to change to the next line in matlab
php editor Zimo will introduce to you how to change to the next line in matlab. In matlab, you can use the semicolon ";" to implement the line break operation, just add a semicolon at the end of each statement. This can make the code clearer and easier to read and improve the maintainability of the code. In addition, you can also use the "..." symbol to indicate line breaks and divide long codes into multiple lines, making it easier to view and edit. Both of the above methods can very well help you implement line break operations in matlab and improve code writing efficiency.
1. First open matlab and click Preset, as shown in the figure below.
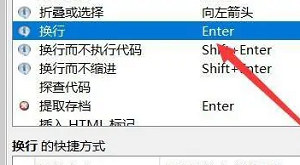
2. Then select Keyboard and click Shortcut, scroll down in the right window to find Line Break, make sure the key is Enter and click OK, as shown in the figure below.
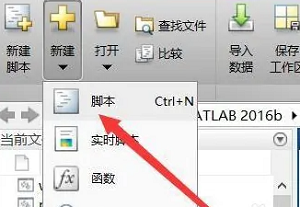
3. Click New on the home page and select Script, as shown in the figure below.
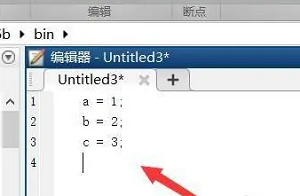
4. Enter the code in the editor and use the Enter key to change the line. Then enter the next line of code, as shown in the figure below.
The above is the entire content of how to change to the next line in matlab brought by the editor. I hope it can be helpful to everyone.
The above is the detailed content of How to change to the next line in matlab-How to change to the next line in matlab. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 The difference between scilab and matlab
Dec 11, 2023 am 11:13 AM
The difference between scilab and matlab
Dec 11, 2023 am 11:13 AM
The difference between scilab and matlab: 1. Annotation symbols; 2. Representation of preset variables; 3. Usage of operators; 4. Definition and calling of matrices; 5. Editing and execution of programs; 6. Data types; 7. Functions Library; 8. Graphical interface; 9. Community support and ecosystem; 10. Cross-platform compatibility; 11. Price. Detailed introduction: 1. Comment symbols. In Scilab, comments are guided by "//", while in Matlab, comments are guided by "%"; 2. Representation of preset variables in Scilab, etc.
 What are the Java operations that come with Matlab?
May 03, 2023 pm 04:07 PM
What are the Java operations that come with Matlab?
May 03, 2023 pm 04:07 PM
1. Get the full-screen position of the mouse. The upper left corner of the screen is the coordinate origin. To get the mouse position and get the mouse pixel color, it is recommended to use it in conjunction with a while loop or timer function: importjava.awt.MouseInfo;mousepoint=MouseInfo.getPointerInfo().getLocation();mousepoint =[mousepoint.x,mousepoint.y]2 Get the current clipboard content importjava.awt.Toolkitimportjava.awt.datatransfer.DataFlavorclip=
 How to modify coordinates in matlab
Dec 15, 2023 am 10:40 AM
How to modify coordinates in matlab
Dec 15, 2023 am 10:40 AM
In MATLAB, you can use the "set" function to modify the axis properties of a graph. Detailed introduction: 1. Modify the range of the coordinate axis: set(gca, 'XLim', [0 10], 'YLim', [0 10]); 2. Modify the label of the coordinate axis: set(gca, 'XLabel', 'My X-axis', 'YLabel', 'My Y-axis'); 3. Modify the scale of the coordinate axis, etc.
 How to stop running commands in matlab
Jan 14, 2021 am 11:46 AM
How to stop running commands in matlab
Jan 14, 2021 am 11:46 AM
How to stop running commands in matlab: 1. Select a program and click the run icon; 2. Click the pause icon above to temporarily stop the program from running; 3. Click to exit debugging to force stop the busy program.
 How to use fprintf in matlab
Sep 28, 2023 pm 04:28 PM
How to use fprintf in matlab
Sep 28, 2023 pm 04:28 PM
fprintf is a function in MATLAB used to format output. The basic syntax of fprintf is "fprintf(fileID, format, A)", where fileID is an identifier used to specify the file to be written. If you want to write data to the command window, you can use 1 as fileID The value of format is a string used to specify the output format, and A is the data to be output.
 How to run m-file in matlab - Tutorial on running m-file in matlab
Mar 04, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to run m-file in matlab - Tutorial on running m-file in matlab
Mar 04, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
Do you know how to run m files in matlab? Below, the editor will bring you a tutorial on how to run m files in matlab. I hope it will be helpful to you. Let’s learn with the editor! 1. First open the matlab software and select the upper left "Open" the corner, as shown in the picture below. 2. Then select the m file to be run and open it, as shown in the figure below. 3. Press F5 in the window to run the program, as shown in the figure below. 4. We can view the running results in the command line window and workspace, as shown in the figure below. 5. You can also run the file by clicking "Run" directly, as shown in the figure below. 6. Finally, you can view the running results of the m file in the command line window and workspace, as shown in the figure below. The above is the matlab method that the editor brought to you
 How to wrap lines in BarTender - How to wrap lines in BarTender
Mar 05, 2024 pm 07:52 PM
How to wrap lines in BarTender - How to wrap lines in BarTender
Mar 05, 2024 pm 07:52 PM
Many users use the BarTender software in their offices. Recently, some new users have asked how to wrap lines in BarTender. Below, the editor will bring you the method of wrapping lines in BarTender. Let us take a look below. 1. In BarTender, click the Create Text button in the toolbar, select Create Single Line Text, and enter the text content. 2. Double-click the created text object to open the text properties dialog box. Switch to the "Text Format" tab and select "Paragraph" for "Type" on the right. 3. Click Close, adjust the size of the text box or enter more text, or wrap the text according to actual requirements.
 How would you convert MATLAB code to Python code?
Aug 19, 2023 pm 10:53 PM
How would you convert MATLAB code to Python code?
Aug 19, 2023 pm 10:53 PM
MATLAB is a popular programming language widely used in engineering and scientific fields, but Python is quickly becoming the language of choice for many programmers due to its flexibility and adaptability. If you want to convert MATLAB code to Python code, it may feel very difficult at first. However, with the right knowledge and approach, you can make the process much easier. Here are some steps to help you convert MATLAB code to Python: Step 1: Familiarize yourself with Python syntax Python and MATLAB have unique syntax, so you need to be familiar with Python syntax before you start converting your code. Spend some time understanding the basics of Python syntax, including variables and data types





