 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Summary of related techniques for optimizing RequireJS projects_Basic knowledge
Summary of related techniques for optimizing RequireJS projects_Basic knowledge
Summary of related techniques for optimizing RequireJS projects_Basic knowledge
This article will demonstrate how to merge and compress a RequireJS-based project. This article will use several tools, including Node.js. Therefore, if you don’t have Node.js on hand yet, you can click here to download one.
Motivation
There have been many articles introduced about RequireJS. This tool can easily split your JavaScript code into modules and keep your code modular and maintainable. This way, you will have a number of JavaScript files that have interdependencies. Just reference a RequireJS-based script file in your HTML document, and all necessary files will be automatically referenced to the page.
However, it is a bad practice to separate all JavaScript files in a production environment. This results in many requests, even if the files are small, and wastes a lot of time. You can merge these script files to reduce the number of requests and save loading time.
Another trick to save loading time is to reduce the size of the files being loaded. Smaller files will transfer faster. This process is called minimization, and it is achieved by carefully changing the code structure of the script file without changing the code's behavior and functionality. For example: remove unnecessary spaces, shorten (mangling, or compress) variable (variables, or method) names and function (methods, or method) names, etc. This process of merging and compressing files is called code optimization. In addition to optimizing JavaScript files, this method is also suitable for optimizing CSS files.
RequireJS has two main methods: define() and require(). These two methods basically have the same declaration and they both know how to load dependencies and then execute a callback function. Unlike require(), define() is used to store code as a named module. Therefore, the callback function of define() needs to have a return value as this module definition. These similarly defined modules are called AMD (Asynchronous Module Definition, asynchronous module definition).
If you're not familiar with RequireJS or don't quite understand what I'm writing - don't worry. Here's an example of these.
Optimization of JavaScript applications
In this section I will show you how to optimize Addy Osmani's TodoMVC Backbone.js RequireJS project. Since the TodoMVC project contains many TodoMVC implementations under different frameworks, I downloaded version 1.1.0 and extracted the Backbone.js RequireJS application. Click here to download the app and unzip the downloaded zip file. The unzipped directory of todo-mvc will be the root path for our example, and I will refer to this directory as
Look at the source code of
index.html code that references the script file
<script data-main="js/main" src="js/lib/require/require.js"></script> <!--[if IE]> <script src="js/lib/ie.js"></script> <![endif]-->
其实,整个项目只需要引用require.js这个脚本文件。如果你在浏览器中运行这个项目,并且在你喜欢的(擅长的)调试工具的network标签中, 你就会发现浏览器同时也加载了其它的JavaScript文件:
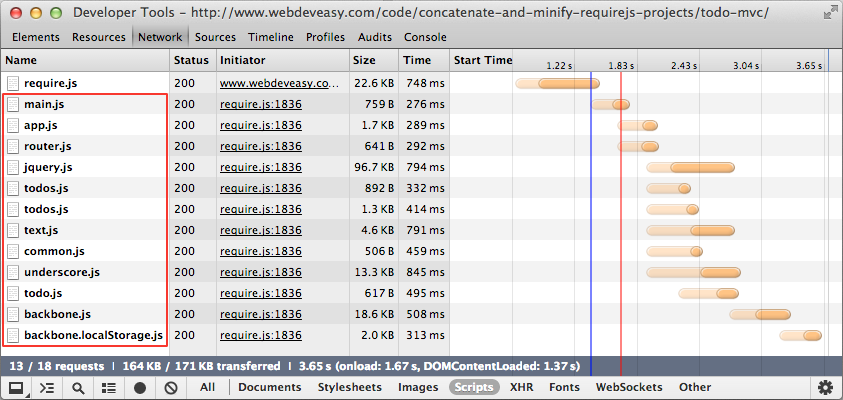
所有在红线边框里面的脚本文件都是由RequireJS自动加载的。
我们将用RequireJS Optimizer(RequireJS优化器)来优化这个项目。根据已下载的说明文件,找到r.js并将其复制到
RequireJS Optimizer有很多用处。它不仅能够优化单个JavaScript或单个CSS文件,它还可以优化整个项目或只是其中的一部分,甚至多页应用程序(multi-page application)。它还可以使用不同的缩小引擎(minification engines)或者干脆什么都不用(no minification at all),等等。本文无意于涵盖RequireJS Optimizer的所有可能性,在此仅演示它的一种用法。
正如我之前所提到的,我们将用到Node.js来运行优化器(optimizer)。用如下的命令运行它(optimizer):
运行RequireJS Optimizer
$ node r.js -o <arguments>
有两种方式可以将参数传递给optimizer。一种是在命令行上指定参数:
在命令行上指定参数
$ node r.js -o baseUrl=. name=main out=main-built.js
另一种方式是构建一个配置文件(相对于执行文件夹)并包含指定的参数 :
$ node r.js -o build.js
build.js的内容:配置文件中的参数
({
baseUrl: ".",
name: "main",
out: "main-built.js"
})
我认为构建一个配置文件比在命令行中使用参数的可读性更高,因此我将采用这种方式。接下来我们就为项目创建一个
({
appDir: './',
baseUrl: './js',
dir: './dist',
modules: [
{
name: 'main'
}
],
fileExclusionRegExp: /^(r|build)\.js$/,
optimizeCss: 'standard',
removeCombined: true,
paths: {
jquery: 'lib/jquery',
underscore: 'lib/underscore',
backbone: 'lib/backbone/backbone',
backboneLocalstorage: 'lib/backbone/backbone.localStorage',
text: 'lib/require/text'
},
shim: {
underscore: {
exports: '_'
},
backbone: {
deps: [
'underscore',
'jquery'
],
exports: 'Backbone'
},
backboneLocalstorage: {
deps: ['backbone'],
exports: 'Store'
}
}
})
Understanding all the configuration options of RequireJS Optimizer is not the purpose of this article, but I want to explain (describe) the parameters I used in this article:

To learn more about RequireJS Optimizer and more advanced applications, in addition to the information provided earlier on its web page, you can click here to view detailed information on all available configuration options.
Now that you have the build file, you can run the optimizer. Enter the
Run the optimizer
$ node r.js -o build.js
A new folder will be generated:
Run the optimized project and it will look exactly like the unoptimized project. Checking the network traffic information of the page again, you will find that only two JavaScript files are loaded.
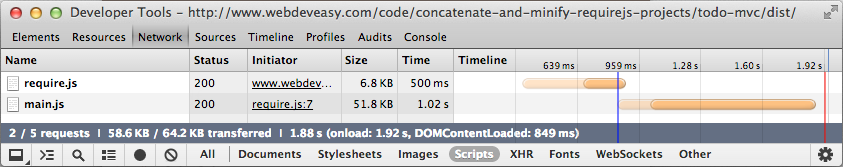
RequireJs Optimizer reduces the number of script files on the server from 13 to 2 and reduces the total file size from 164KB to 58.6KB (require.js and main.js).
Overhead
Obviously, after optimization, we no longer need to reference the require.js file. Because there are no separated script files and all files with dependencies have been loaded.
Nonetheless, the optimization process merged all our scripts into one optimized script file, which contains many define() and require() calls. Therefore, in order to ensure that the application can run properly, define() and require() must be specified and implemented somewhere in the application (that is, including these files).
This results in a well-known overhead: we always have some code implementing define() and require(). This code is not part of the application; it exists solely for our infrastructure considerations. This problem becomes especially huge when we develop a JavaScript library. These libraries are usually very small compared to RequireJS, so including it in the library creates a huge overhead.
As I write this, there is no complete solution for this overhead, but we can use almond to alleviate this problem. Almond is an extremely simple AMD loader that implements the RequireJS interface (API). Therefore, it can be used as an alternative to the RequireJS implementation in optimized code, and we can include almond in the project.
As such, I'm working on developing an optimizer that will be able to optimize RequireJS applications without the overhead, but it's still a new project (in the early stages of development) so there's nothing to show about it here .
Download and Summary

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1242
1242
 24
24
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Different JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
This article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
I built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.



