A Linux Admin's Helper: Seven Tools to Simplify and Automate Tasks
Linux system management is a complex and tedious task, which involves many aspects, such as installation, configuration, monitoring, maintenance, backup, recovery, etc. Linux system administrators need to master a lot of knowledge and skills, and they also need to spend a lot of time and energy. Are there any tools that can help Linux system administrators simplify and automate tasks? The answer is yes. This article will introduce seven tools that can help Linux system administrators simplify and automate tasks.
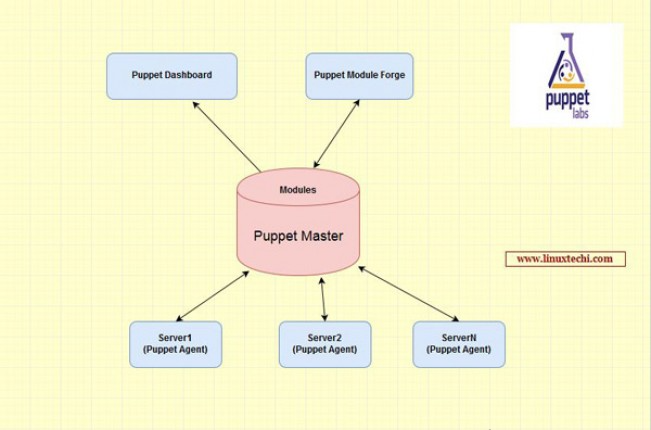
Puppet is an open source tool designed to greatly simplify automation and reporting for system administrators. It is basically a configuration management software that helps configure and maintain servers and other systems in corporate networks. System administrators often spend a large amount of time doing the same tasks over and over every day. They always want to automate these tasks so they can have more time to work on other projects or learn new concepts and scripting languages. Administrators can automate tasks by writing scripts, but in companies with large networks, scripting is not very convenient. At this time, Puppet is very useful, because with Puppet, you can:
- Define unique configuration settings for each host on the network;
- Constantly monitor the network for any changes;
- Helps create and manage users efficiently;
- Help manage configuration settings for each open source tool.
2. CHEF
Chef is another popular automation tool available for Linux system administrators. Written in Ruby and Erlang, it's a great help for configuring and maintaining your company's servers, whether your company has ten servers or hundreds. It can also help you integrate cloud servers with Amazon EC2, OpenStack, RackSpace or Google Cloud. Chef turns your infrastructure into code so that you can easily take down a server by changing just a few lines of code, making it easy for you to manage your servers. Physical nodes also mean that you can easily test changes before deploying them to production, and you can easily control the version of each update to your code. Chef DK provides you with all the tools to test and manage your configuration, and Chef Server acts as a repository for all your recipes and can manage every node connected to the server. The Chef client software runs on each client and receives information from the server from time to time to update its configuration settings.
3. CFEngine
The next automation tool for Linux system administrators is CFEngine, another leading automation system that helps you manage and automate your entire infrastructure with ease. Once you use CFEngine to define a configuration for the systems on your network, CF Engine automatically ensures that the configuration complies with the specification. Needless to say, if you have 10 or 100 nodes in your network, any or all nodes can be updated or modified in just a few seconds. CFEngine is favored by many Linux system administrators because of its low running cost, fast response speed, and self-healing function.
4. Ansible
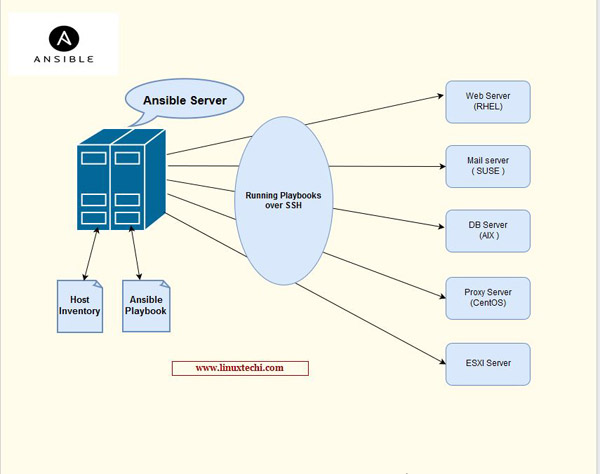
Ansible is an open source configuration management and IT enterprise automation software provided by Red Hat. It comes with a simple programming language that allows system administrators to efficiently handle the automation and configuration process. Ansible consists of control machines and nodes that control machines. Nodes are controlled via SSH. One of the main features of Ansible is that the agent is not deployed to the nodes, but communicates entirely through SSH. Ease of learning and use, consistency, high reliability and security are other features that make Ansible stand out. The only limitation of Ansible is that it cannot configure bare metal and virtual machines.
5. Foreman
Foreman is another open source configuration management tool used for forensic analysis. Foreman provides a dashboard through which we can configure bare metal servers and virtual machines. By default, whenever we install Foreman, it uses Puppet as the configuration tool. However, with the help of plug-ins, Foreman also supports integration with other configuration management tools, such as Chef, Puppet, Ansible, Salt and many other tools. Foreman automation tools also come with a variety of interfaces, including command line interfaces, web front-ends, and REST APIs. Some of Foreman’s other notable features include the following:
- Manage changes to Puppet modules and puppet classes through the dashboard;
- It's easy to manage your Puppet environment from the Foreman dashboard;
- Thanks to the dashboard, creating Hosts Groups and adding puppet modules to host groups is easy;
- Puppet modules can be easily added or pushed to nodes from the Foreman dashboard.
6. Katello
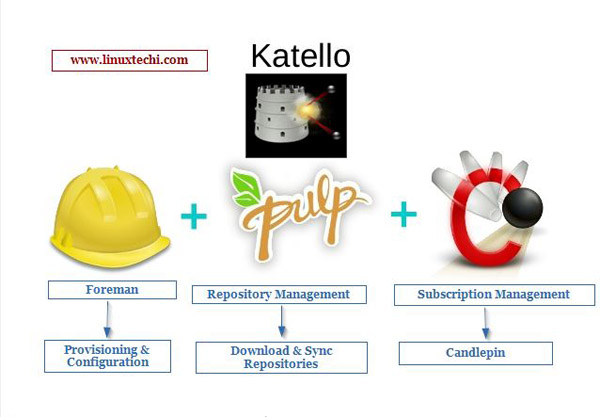
Katello is another open source automation tool. In other words, we can say that Katello is an open source version of Red Hat satellite Server; we can use it to replace Red Hat satellite server if we do not want to spend money on enterprise products and their support. Katello has been acquired by Foreman, and most of the features in Foreman are also supported in Katello. The main functions of Katello Server are as follows:
- Patching Linux-based servers (RHEL and CentOS);
- Use Pulp Service to synchronize the code base;
- Use Foreman for various configurations;
- It also handles subscription content management and audits all deployed packages;
- With Katello, you can create host groups for all hosts and perform operations in batches on a single host or a group of hosts.
7. Nagios

Nagios, now called Nagios Core, is an open source automation and monitoring tool that can manage all systems in your infrastructure. It also provides an alerting service that alerts system administrators if it detects a problem in your network. With SNMP and Nagios, system administrators can also control and manage printers, routers, and switches. Nagios allows us to create event handling tools that automatically restart the failed application and its services once an application and its services are down.
The above is the detailed content of A Linux Admin's Helper: Seven Tools to Simplify and Automate Tasks. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1313
1313
 25
25
 1262
1262
 29
29
 1235
1235
 24
24
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
VS Code One-step/Next step shortcut key usage: One-step (backward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl ←; macOS: Cmd ←Next step (forward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl →; macOS: Cmd →
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.
 laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
To install Laravel, follow these steps in sequence: Install Composer (for macOS/Linux and Windows) Install Laravel Installer Create a new project Start Service Access Application (URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000) Set up the database connection (if required)
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version




