How to safely delete files and directories in Linux
Have you ever had the experience of deleting some sensitive or important files in your Linux system, but later found that these files did not really disappear, but were restored or stolen by others? If so, then you definitely need to know how to delete files safely in Linux system. This article will teach you how to completely delete files with simple commands to make your data more secure.

In most cases, we are accustomed to using Delete key, trash or rm command to delete files from our computer, but this is not a permanent and safe way to delete files from hard drive (or any storage media) method.
This file is just hidden from the user, it resides somewhere on the hard drive. It can be recovered by data thieves, law enforcement or other means.
Assuming the file contains classified or confidential content, such as usernames and passwords for secure systems, an attacker with the necessary knowledge and skills can easily recover a deleted copy of the file and access those user credentials (you can guess the consequences of this scenario) ).
In this article, we will explain some command line tools for permanently and safely deleting files in Linux.
1.shred – overwrite the file to hide the content
shred will overwrite the file to hide its contents, and optionally delete it.
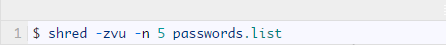
In the following command, the options are:
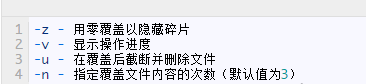
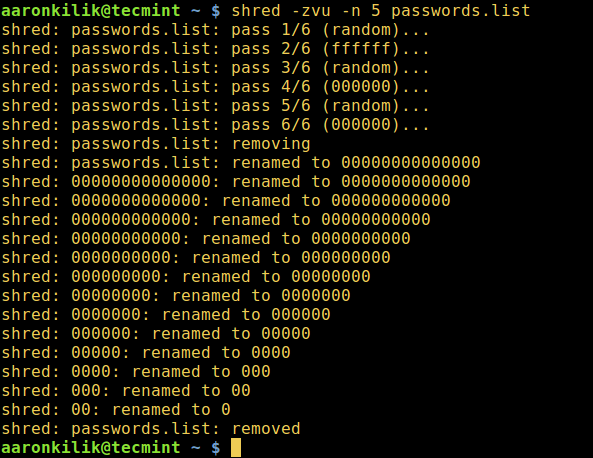
You can find more usage options and information in shred's help page: 
2.wipe – Safely delete files in Linux
The wipe command securely wipes files from disk, making it impossible to recover deleted files or directory contents.
First, you need to install the wipe tool, run the following appropriate command: 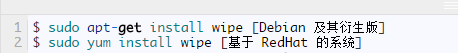
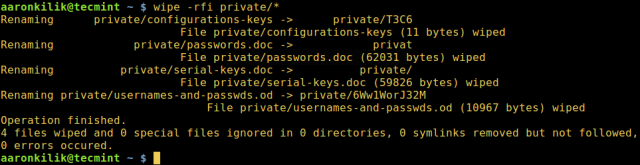
The following command will destroy all files in the private directory.
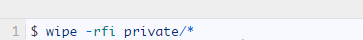
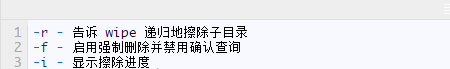
When using the following flags:
Note: wipe only works reliably on magnetic storage, so use other methods for solid state disks (memory).
Read the wipe manual for additional usage options and instructions:

3. Safe removal toolset in Linux
secure-delete is a collection of secure file deletion tools, which includes the srm (secure_deletion) tool for secure file deletion.
First, you need to install it using the following relevant commands:
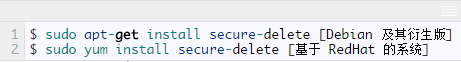
After the installation is complete, you can use the srm tool to safely delete files and directories in Linux.

The following are the options used:
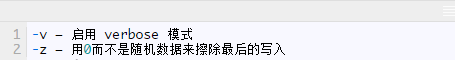
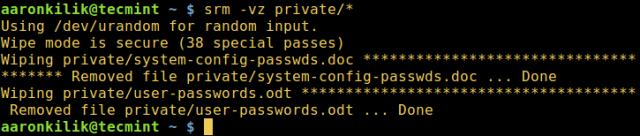
Read the srm manual for more usage options and information:
4.sfill - Safe and Free Disk/inode Space Eraser
sfill, part of the secure-deletetion toolkit, is a secure and free disk and inode space eraser that securely deletes files from available disk space. sfill checks the available space on the specified partition and fills it with random data from /dev/urandom.
The following command will execute sfill on my root partition, using the -v option to enable verbose mode:
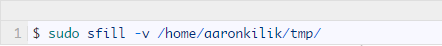
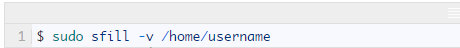
Assuming you created a separate partition /home to store the normal system user home directory, you can specify a directory on that partition to apply sfill on:
You can see some restrictions in the sfill manual, and you can also see additional usage flags and commands:

Note: The other two tools in the secure-deletetion toolkit (sswap and sdmem) are not directly relevant to the scope of this guide, however, for future use and the purpose of spreading knowledge, we will introduce them below they.
5.sswap – Secure swap wiper
It is a secure partition eraser, sswap deletes the data present on the swap partition in a safe way.
Warning: Please remember to unmount the swap partition before using sswap! Otherwise your system may crash!
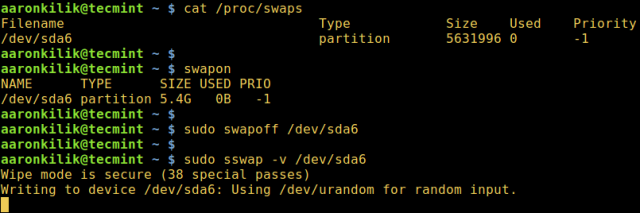
To find the swap partition (and to check whether paging and swap devices/files are already in use, use the swapon command), next, use the swapoff command to disable paging and swap devices/files (making the swap partition unavailable).
Then run the sswp command on the (closed) swap partition:
Read the sswap manual for more options and information:
6. sdmem – Secure Memory Eraser
sdmem is a secure memory eraser designed to delete data in memory (RAM) in a safe manner.
It was originally named smem, but because on Debain systems there existed another package smem - which reports per-process and per-user memory consumption, the developers decided to rename it to sdmem.

For more usage information, read the sdmen manual:
Through this article, you have learned how to delete files safely in Linux system. You can choose to use the rm or shred command to achieve this purpose according to your own needs. Whether it is rm or shred, you need to pay attention to the use of some parameters and options, as well as some possible problems and solutions.
The above is the detailed content of How to safely delete files and directories in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1670
1670
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1276
1276
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
To install Laravel, follow these steps in sequence: Install Composer (for macOS/Linux and Windows) Install Laravel Installer Create a new project Start Service Access Application (URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000) Set up the database connection (if required)
 git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Installing Git software includes the following steps: Download the installation package and run the installation package to verify the installation configuration Git installation Git Bash (Windows only)
 How to set important Git configuration global properties
Apr 17, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to set important Git configuration global properties
Apr 17, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
There are many ways to customize a development environment, but the global Git configuration file is one that is most likely to be used for custom settings such as usernames, emails, preferred text editors, and remote branches. Here are the key things you need to know about global Git configuration files.




