Linux memory management artifact: smem tool
Hi everybody, I'm.
Today I want to introduce to you a very practical memory management tool in Linux systems: smem.
smem is a command line tool that can generate a variety of memory usage reports. Unlike other existing tools, smem can report PSS (Proportional Set Size, proportional occupied size), which is a more meaningful metric. It accurately measures the amount of memory used by libraries and applications in a virtual memory system.
Traditionally, since most physical memory is often shared among multiple applications, using resident set size (RSS) as a measure of memory usage overestimates actual memory consumption. In contrast, the PSS parameter measures the memory allocated by each application in each shared memory region, which provides a more realistic and accurate metric.
1. Install smem tool
If you are using Fedora 19 or above, smem is in the repository by default, so you can install it using yum:
$ sudo yum install smem
For Ubuntu users, you can use the apt-get command to install smem:
$ sudo apt-get install smem
If it cannot be installed normally, you can download its source code and install it directly at the address: https://www.selenic.com/smem/download/
2. Common usage of smem tool
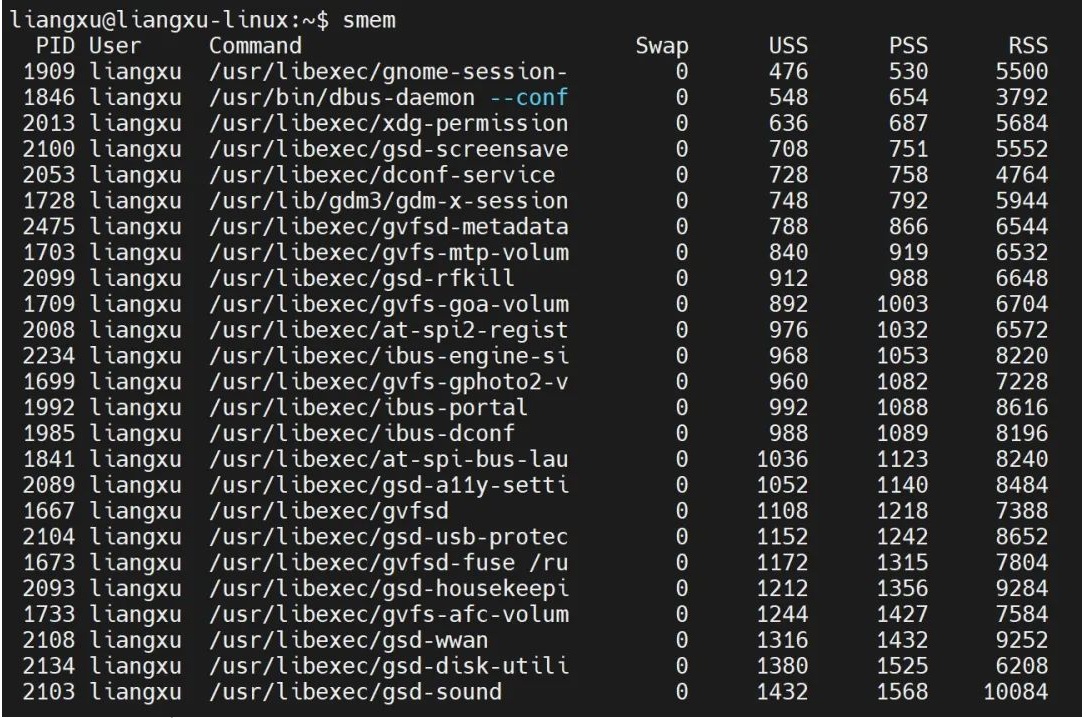
By default, smem will display each running process and the memory used. Here, you can note the size of RSS relative to USS and PSS, and you can see that it is significantly higher than the other two.
$ smem
In addition, smem can also display the memory used by each library. This result is relatively long and may take some time, depending on your system.
$ smem -m
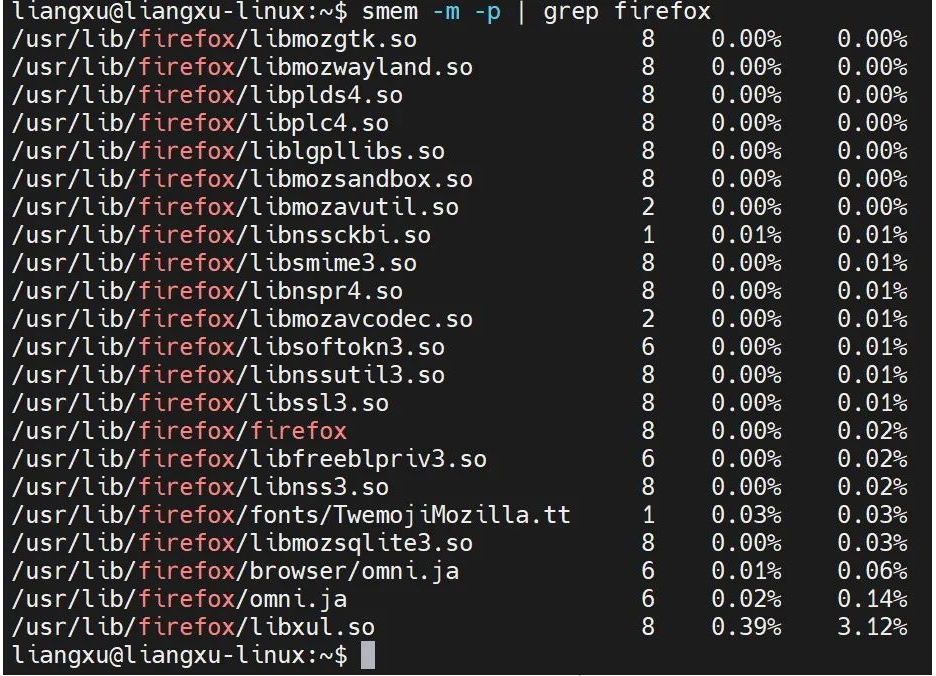
This command produces too many results. If we want to check the memory usage of a specific application, such as Firefox, then we can use it with the grep command and use -p## at the same time. # option to view memory usage as a percentage.
$ smem -m -p | grep firefox
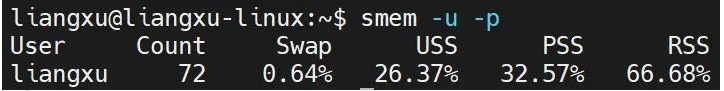
smem The command can also display the memory usage of each user. You need to use the -u option:
$ smem -u -p
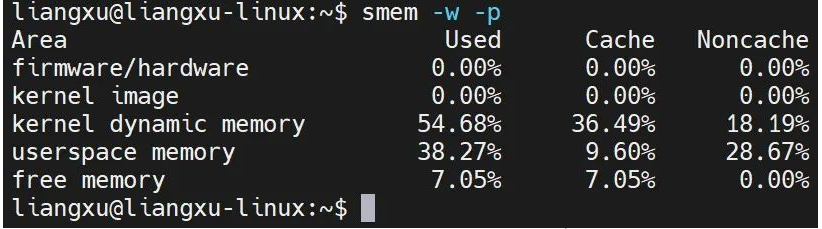
你还可以使用 -w 选项查看系统内存使用情况:
$ smem -w -p
3. 结果可视化输出
显示数字毕竟不直观,我们还可以使用 smem 生成图形图表来显示内存使用情况,一目了然。要达到这个目的,我们需要使用到除了不能生孩子啥都可以干的 Python 。
但光有 Python 还不行,还需要安装用于生成图表的 matplotlib 库。
Fedora 用户可以通过运行以下命令来安装它:
$ sudo yum install python-matplotlib
Ubuntu 用户可以通过运行下面命令获得它:
$ sudo apt-get install python-matplotlib
库安装之后,现在就可以以条形图或饼图的形式将获得的内存使用情况以可视化表示。
3.1 饼形图
使用 smem 以饼图的形式查看内存使用情况,需要加上 --pie 选项,如下所示:
$ smem --pie name -s pss
命令运行之后将生成一个饼图。请注意,这条命令里我们还加了 -s pss ,意思是显示 PSS 的内存使用情况。要获取 USS 和 RSS 的饼图,只需将命令中的 pss 替换为 uss 或 rss 即可。
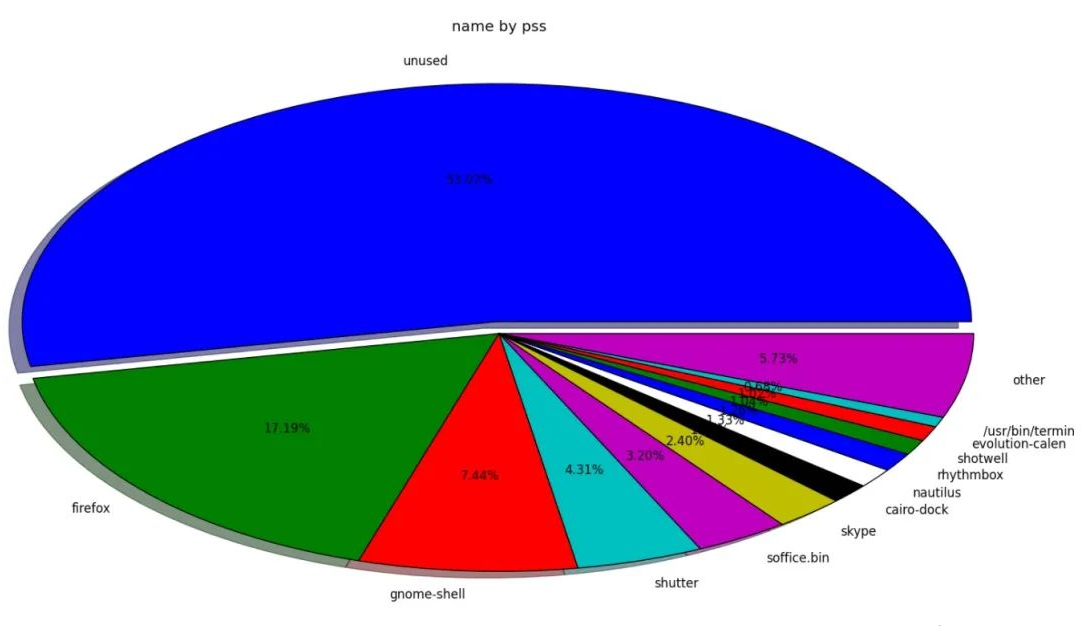
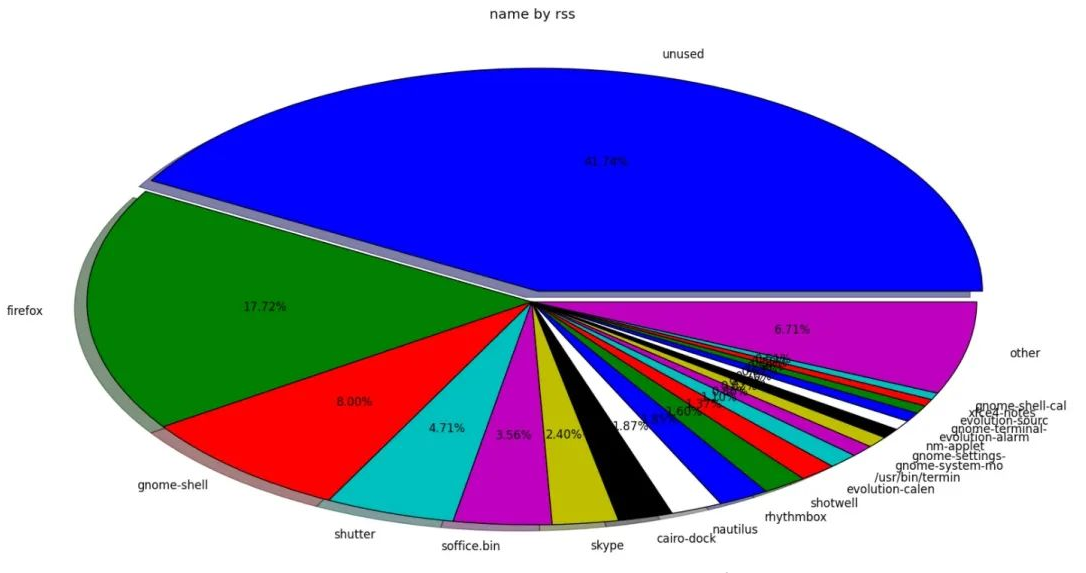
从两个饼图中,可以看到 RSS 报告还有 41.74% 的未使用内存,而 PSS 报告有 53.02% 的未使用内存。可以看出来,RSS 显示的可用内存偏小,但实际还有很充足的内存空间。
3.2 柱状图
smem 的另一个很酷的特性是以柱状图的形式生成输出。有了这个功能,你可以一次性查看 USS、PSS 和 RSS 报告的内存使用情况。
要实现这个功能,需要加上 --bar 选项:
$ smem --bar pid -c "pss uss rss"
上面的命令将给出带有进程 ID 号的内存使用情况的输出结果。如果想要查看进程的名称,可以将 pid 替换为 name 即可。
命令运行之后,可以生成如下图所示的条柱状图。

The above is the detailed content of Linux memory management artifact: smem tool. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
Causes and solutions for the VS Code terminal commands not available: The necessary tools are not installed (Windows: WSL; macOS: Xcode command line tools) Path configuration is wrong (add executable files to PATH environment variables) Permission issues (run VS Code as administrator) Firewall or proxy restrictions (check settings, unrestrictions) Terminal settings are incorrect (enable use of external terminals) VS Code installation is corrupt (reinstall or update) Terminal configuration is incompatible (try different terminal types or commands) Specific environment variables are missing (set necessary environment variables)






