Master these methods to easily set time limits in your Linux system
As the pace of work and life accelerates, we often need to set some time limits in Linux systems to control our behavior. Whether it is to limit user login time or limit process running time, Linux systems provide a variety of methods to achieve this purpose. So, do you know how to set time limit in Linux system? This article will introduce several common methods so that you can easily master them.
timeout is a command line utility that runs a specified command and terminates it if it is still running after a given period of time. The timeout command is part of the GNU core utility package, which is installed on almost all Linux distributions
how to use
Grammar format:
timeout [OPTION] DURATION COMMAND [ARG]...
DURATION can be a positive integer or floating point number, followed by an optional suffix:
- s – seconds (default)
- m – minutes
- h – hours
- d – day
If no unit is added, the default is seconds. If DURATION is 0, the associated timeout is disabled.
Example
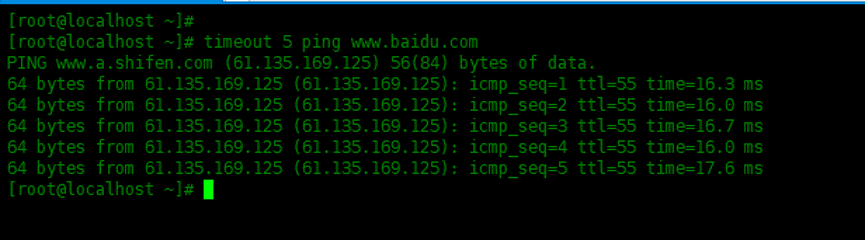
Terminate the ping operation after 5 seconds:
[root@localhost ~]# timeout 5 ping www.baidu.com PING www.a.shifen.com (61.135.169.125) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 61.135.169.125 (61.135.169.125): icmp_seq=1 ttl=55 time=16.3 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.125 (61.135.169.125): icmp_seq=2 ttl=55 time=16.0 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.125 (61.135.169.125): icmp_seq=3 ttl=55 time=16.7 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.125 (61.135.169.125): icmp_seq=4 ttl=55 time=16.0 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.125 (61.135.169.125): icmp_seq=5 ttl=55 time=17.6 ms
Terminate ping operation after 5 minutes:
[root@localhost ~]# timeout 5m ping www.baidu.com
Terminate ping operation after 1 day:
[root@localhost ~]# timeout 1d ping www.baidu.com
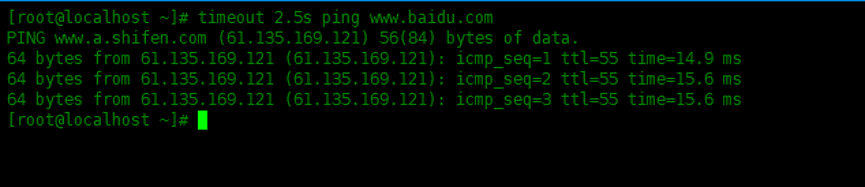
Terminate the ping operation after 2.5 seconds:
[root@localhost ~]# timeout 2.5s ping www.baidu.com PING www.a.shifen.com (61.135.169.121) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 61.135.169.121 (61.135.169.121): icmp_seq=1 ttl=55 time=14.9 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.121 (61.135.169.121): icmp_seq=2 ttl=55 time=15.6 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.121 (61.135.169.121): icmp_seq=3 ttl=55 time=15.6 ms
Send the specified signal
If no signal is given, timeout sends a SIGTERM signal to the managed command when the time limit is reached. The signal to be sent can be specified using the -s (-signal) option.
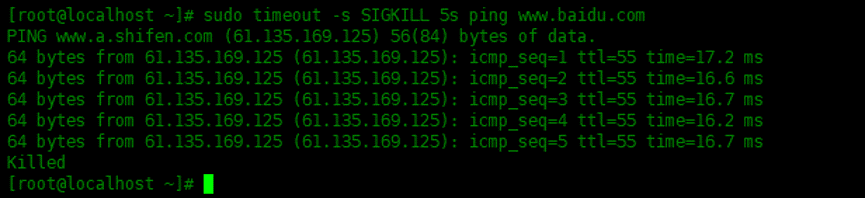
Send SIGKILL signal to ping command, terminate after 5 seconds:
[root@localhost ~]# sudo timeout -s SIGKILL 5s ping www.baidu.com PING www.a.shifen.com (61.135.169.125) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 61.135.169.125 (61.135.169.125): icmp_seq=1 ttl=55 time=17.2 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.125 (61.135.169.125): icmp_seq=2 ttl=55 time=16.6 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.125 (61.135.169.125): icmp_seq=3 ttl=55 time=16.7 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.125 (61.135.169.125): icmp_seq=4 ttl=55 time=16.2 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.125 (61.135.169.125): icmp_seq=5 ttl=55 time=16.7 ms Killed
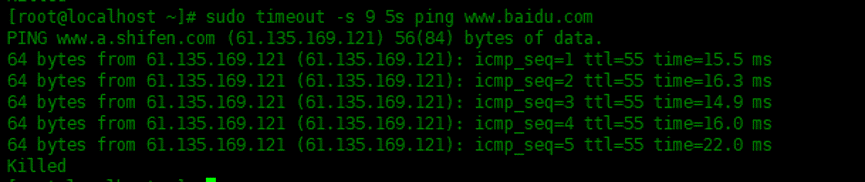
A signal can be assigned its name or its sequence number. The SIGKILL serial number used below will terminate the operation after 5 seconds:
[root@localhost ~]# sudo timeout -s 9 5s ping www.baidu.com PING www.a.shifen.com (61.135.169.121) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 61.135.169.121 (61.135.169.121): icmp_seq=1 ttl=55 time=15.5 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.121 (61.135.169.121): icmp_seq=2 ttl=55 time=16.3 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.121 (61.135.169.121): icmp_seq=3 ttl=55 time=14.9 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.121 (61.135.169.121): icmp_seq=4 ttl=55 time=16.0 ms 64 bytes from 61.135.169.121 (61.135.169.121): icmp_seq=5 ttl=55 time=22.0 ms Killed
To see all available signals, use the kill -l command to view all signals.
[root@localhost ~]# kill -l 1) SIGHUP 2) SIGINT 3) SIGQUIT 4) SIGILL 5) SIGTRAP 6) SIGABRT 7) SIGBUS 8) SIGFPE 9) SIGKILL 10) SIGUSR1 11) SIGSEGV 12) SIGUSR2 13) SIGPIPE 14) SIGALRM 15) SIGTERM 16) SIGSTKFLT 17) SIGCHLD 18) SIGCONT 19) SIGSTOP 20) SIGTSTP 21) SIGTTIN 22) SIGTTOU 23) SIGURG 24) SIGXCPU 25) SIGXFSZ 26) SIGVTALRM 27) SIGPROF 28) SIGWINCH 29) SIGIO 30) SIGPWR 31) SIGSYS 34) SIGRTMIN 35) SIGRTMIN+1 36) SIGRTMIN+2 37) SIGRTMIN+3 38) SIGRTMIN+4 39) SIGRTMIN+5 40) SIGRTMIN+6 41) SIGRTMIN+7 42) SIGRTMIN+8 43) SIGRTMIN+9 44) SIGRTMIN+10 45) SIGRTMIN+11 46) SIGRTMIN+12 47) SIGRTMIN+13 48) SIGRTMIN+14 49) SIGRTMIN+15 50) SIGRTMAX-14 51) SIGRTMAX-13 52) SIGRTMAX-12 53) SIGRTMAX-11 54) SIGRTMAX-10 55) SIGRTMAX-9 56) SIGRTMAX-8 57) SIGRTMAX-7 58) SIGRTMAX-6 59) SIGRTMAX-5 60) SIGRTMAX-4 61) SIGRTMAX-3 62) SIGRTMAX-2 63) SIGRTMAX-1 64) SIGRTMAX [root@localhost ~]#
Stop the stuck process
SIGTERM, the default signal sent when the time limit is exceeded, can be caught or ignored by some processes. In this case, the process continues running after sending the termination signal.
To ensure that the executed command is terminated, please use the -k (-kill after) option followed by a time. It will be forced to end when the given time limit is reached.
In the following example, the timeout command runs for one minute, and if the command does not end, the command will be terminated after 10 seconds:
[root@localhost ~]# timeout -k 10s 1m sh test.sh
Run in the foreground
By default, timeout runs managed commands in the background. If you want to run the command in the foreground, use the --foreground option:
[root@localhost ~]# timeout --foreground 5m ./script.sh
Summarize
This article introduces several common methods of setting time limits in Linux systems, including using the ulimit command, using the pam_time module, using cron scheduled tasks, etc. By understanding these methods, you can better control user behavior, optimize system performance, prevent resource waste, etc. I hope readers can choose a method that suits them based on actual needs and apply it.
The above is the detailed content of Master these methods to easily set time limits in your Linux system. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.






