:Linux process freezing technology: Make your system more stable
Have you ever encountered various problems that occur when the system is hibernating? For example, the file system is damaged, hibernation image creation fails, device suspend is abnormal, etc. These problems can be solved through Linux process freezing technology.
- Process freezing technology (freezing of tasks) refers to placing user processes and some kernel threads in a "controllable" pause state when the system hibernates or suspends.
-
Without freezing technology, the process can be suspended at any schedulable point, and will not be suspended and migrated until cpu_down. This can cause a lot of problems for the system:
- It is possible to corrupt the file system. Between the time the system creates the hibernate image and the time the CPU goes down, if there are processes that are still modifying the contents of the file system, this will result in the file system being unable to be fully restored after the system is restored;
- It may cause the creation of hibernation image to fail. Creating a hibernation image requires sufficient memory space, but if there are still processes applying for memory during this period, the creation may fail;
- It is possible to interfere with the device's suspend and resume. Before the CPU is down, during device suspend, if the process is still accessing the device, especially when accessing competing resources, it may cause a device suspend exception;
- It may cause the process to sense system hibernation. The ideal state of system hibernation is that all tasks are unaware of the hibernation process and automatically resume work after waking up. However, some processes, such as a certain process, require all CPUs to be online to work properly. If the process does not freeze, it will Work abnormally.
- Frozen objects are entities in the kernel that can be scheduled for execution, including user processes, kernel threads, and work_queue. User processes can be frozen by default, which is implemented by borrowing the signal processing mechanism; kernel threads and work_queue cannot be frozen by default. A few kernel threads and work_queue specify the freezeable flag when they are created. These tasks need to judge the freeze status. When the system When entering freezing, the operation is automatically suspended. Kernel threads can determine the freezing status by calling kthread_freezable_should_stop, and actively call __refrigerator to enter freezing; work_queue determines the max_active attribute. If max_active=0, new work cannot be queued, and all work is delayed.
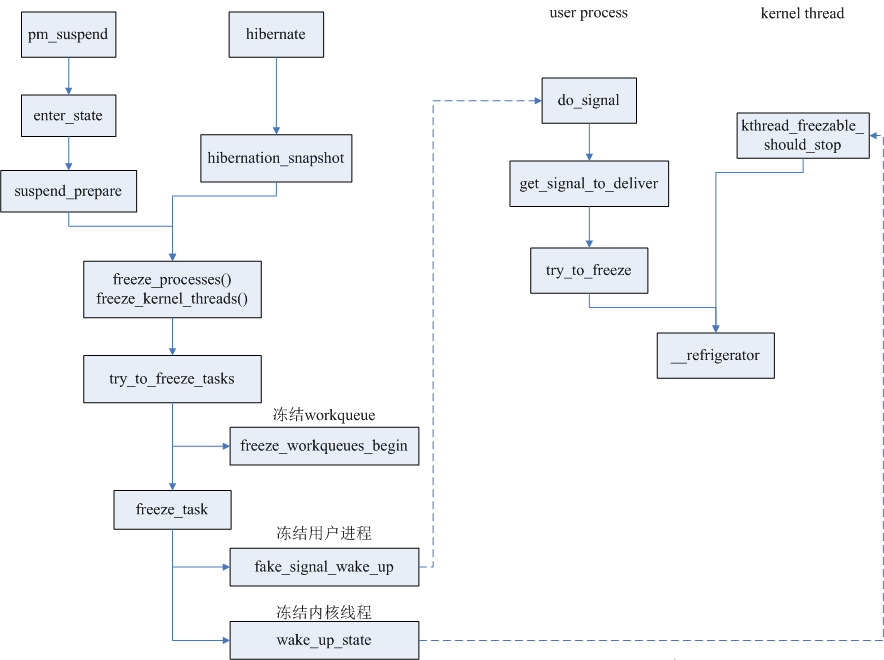
There are three important global variables that mark the system freeze status: pm_freezing, system_freezing_cnt and pm_nosig_freezing. If they are all 0, it means that the system has not entered freezing; system_freezing_cnt>0 means that the system has entered freezing, and pm_freezing=true means Freeze the user process. pm_nosig_freezing=true means freezing the kernel thread and workqueue. They will be set in freeze_processes and freeze_kernel_threads, and cleared in thaw_processes and thaw_kernel_threads.
The fake_signal_wake_up function cleverly makes use of the signal processing mechanism. It only sets the TIF_SIGPENDING bit of the task, but does not pass any signal, and then wakes up the task; in this way, the task will enter the signal processing process when returning to user mode, check the freeze status of the system, and handle it accordingly. .
The code for the task to actively call try_to_freeze is as follows:
```
```
1. static inline bool try_to_freeze_unsafe(void)
2. {
3. if (likely(!freezing(current))) //检查系统是否处于freezing状态
4. return false;
5. return __refrigerator(false); //主动进入冻结
6. }
7.
8. static inline bool freezing(struct task_struct *p)
9. {
10. if (likely(!atomic_read(&system_freezing_cnt))) //系统总体进入freezing
11. return false;
12. return freezing_slow_path(p);
13. }
14.
15. bool freezing_slow_path(struct task_struct *p)
16. {
17. if (p->flags & PF_NOFREEZE) //当前进程是否允许冻结
18. return false;
19.
20. if (pm_nosig_freezing || cgroup_freezing(p)) //系统冻结kernel threads
21. return true;
22.
23. if (pm_freezing && !(p->flags & PF_KTHREAD)) //系统冻结用户进程
24. return true;
25.
26. return false;
27. }
The main function to enter the frozen state until recovery: bool __refrigerator(bool check_kthr_stop)
1. {
2. ...
3. for (;;) {
4. set_current_state(TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE); //设置进程为UNINTERRUPTIBLE状态
5.
6. spin_lock_irq(&freezer_lock);
7. current->flags |= PF_FROZEN; //设置已冻结状态
8. if (!freezing(current) ||
9. (check_kthr_stop && kthread_should_stop())) //判断系统是否还处于冻结
10. current->flags &= ~PF_FROZEN; //如果系统已解冻,则取消冻结状态
11. spin_unlock_irq(&freezer_lock);
12.
13. if (!(current->flags & PF_FROZEN)) //如果已取消冻结,跳出循环,恢复执行
14. break;
15. was_frozen = true;
16. schedule();
17. }
18. ......
19. }
In short, Linux process freezing technology is a very useful technology that can help you avoid some potential problems and make your system more stable. If you want to learn more about this technology, check out the resources provided in this article.
The above is the detailed content of :Linux process freezing technology: Make your system more stable. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
Causes and solutions for the VS Code terminal commands not available: The necessary tools are not installed (Windows: WSL; macOS: Xcode command line tools) Path configuration is wrong (add executable files to PATH environment variables) Permission issues (run VS Code as administrator) Firewall or proxy restrictions (check settings, unrestrictions) Terminal settings are incorrect (enable use of external terminals) VS Code installation is corrupt (reinstall or update) Terminal configuration is incompatible (try different terminal types or commands) Specific environment variables are missing (set necessary environment variables)






