在使用linux系统的过程中,经常会遇到磁盘空间不足的情况。当磁盘空间不足时,系统的运行会变得异常缓慢,甚至会出现崩溃等问题。而使用linux命令清理硬盘空间,是一种非常简单和有效的方法,可以让你的系统重获新生。在本文中,我们将介绍几种常用的linux命令,帮助你清理硬盘空间,提高系统的性能和稳定性。
如果在 Linux 命令行上工作,你应该熟悉 du 命令。 了解诸如 du 之类的命令,它可以快速返回有关磁盘使用情况的信息,是命令行提高程序员工作效率的方法之一。 然而,如果你正在寻找一种节省更多时间并使你的生活更轻松的方法,那么请查看dust,它是用 Rust 编写的更直观的 du 命令。
简而言之,dust 是一种提供文件类型和元数据的工具。 如果你在一个目录中的运行 dust,它会以多种方式报告该目录的磁盘利用率。 它提供了一个非常有用的图表,告诉您哪个文件夹使用的磁盘空间最多。 如果有嵌套文件夹,您可以看到每个文件夹使用的空间百分比。
安装dust
你可以使用 Rust 的 Cargo 包管理器安装dust:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ cargo install du-dust
或者,您可能会在 Linux 上的软件存储库中找到它,在 macOS 上,使用MacPorts或Homebrew。
探索dust
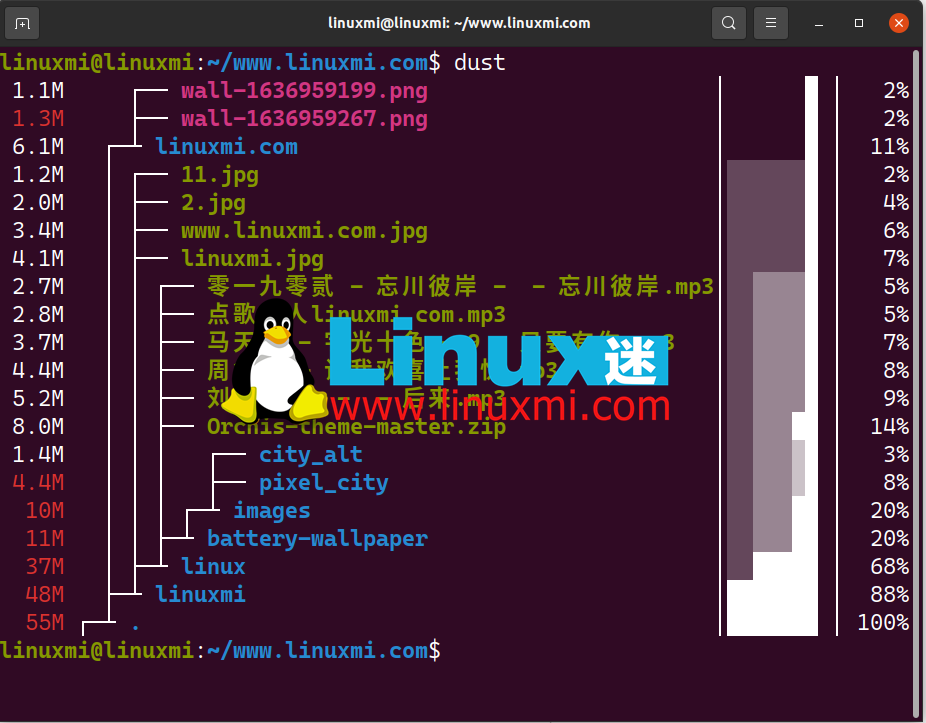
dust在目录上发出命令会返回一个图表,该图表显示其内容以及每个项目以树格式显示的百分比。
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ dust
应用dust到特定目录:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ dust /usr/games

-r 选项以相反的顺序显示输出,根在底部:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ dust -r /usr/games
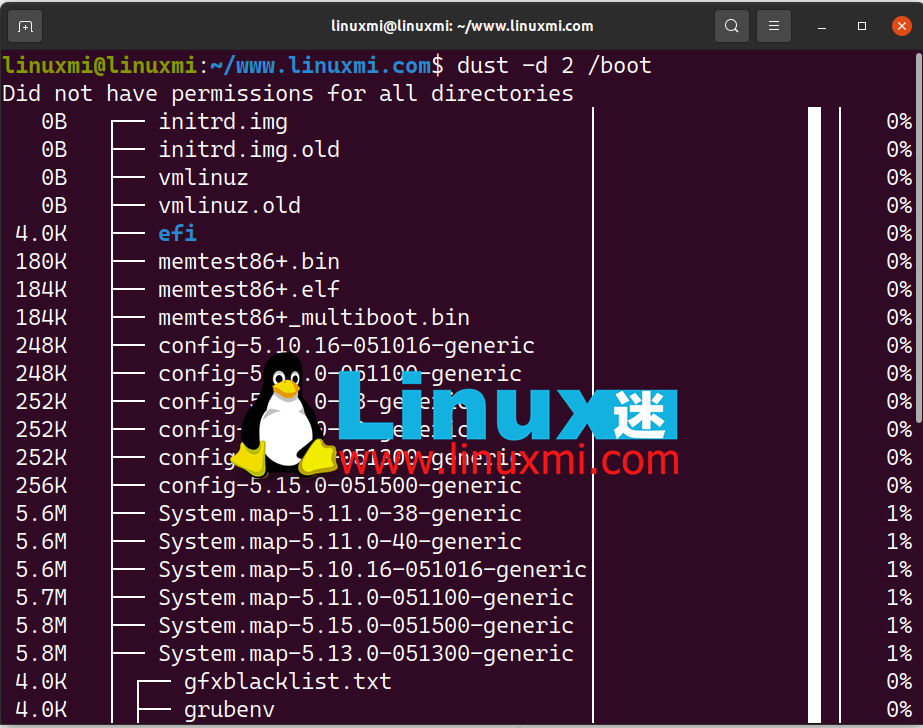
使用 dust -d 2 返回两个级别的子目录及其磁盘利用率:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ dust -d 2 /boot
结论
dust的美妙之处在于它是一个小巧、简单且易于理解的命令。 它使用配色方案来表示最大的子目录,从而可以轻松地可视化你的目录。 这是一个受欢迎的项目,欢迎贡献。
通过本文的介绍,相信你已经了解到了几种常用的Linux命令,可以帮助你清理硬盘空间,提高系统的性能和稳定性。当你的系统出现磁盘空间不足的情况时,不要慌张,使用这些命令可以帮助你轻松解决问题。同时,在平时的使用中,也应该注意清理系统中不必要的文件和数据,保持磁盘空间的充足。这样,你的系统将会更加稳定、高效。
以上就是如何用Linux命令清理硬盘空间,让你的系统重获新生的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号