nvtop – A great Linux task monitor
nvtop command is a great task monitor for Linux users that monitors NVIDIA, AMD and Intel GPU (graphics processing unit) usage. It is similar to the top command or htop command and can efficiently handle multiple GPUs in your system and display detailed information about them in htop format.
Next let’s take a look at how to install the nvtop command and monitor GPU tasks on your Linux distribution.
nvtop Command – A great Linux task monitor for NVIDIA, AMD and Intel GPUs
The nvtop command is a GPU status viewer based on ncurses (the new curses library that displays information in the terminal) for AMD, Intel and NVIDIA GPUs. In other words, you can use this interactive GPU process viewer on Linux to view the status of the following GPUs:
- AMD GPU using amdgpu driver.
- Intel graphics card using i915 Linux driver.
- Use NVIDIA drivers with NVIDIA GPUs GeForce 600, GeForce 800M, and their successors.
Installing nvtop command on Linux
You can also install the nvtop command on the GPU desktop or server depending on your Linux distribution.
Arch Linux
Run the following pacman command:
$ sudo pacman -Syu nvtop
Gentoo Linux
Use the following emerge command:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo layman -a guru linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo emerge -av nvtop
Ubuntu Impish (21.10), Debian Buster (stable) and newer versions
Try using apt command or apt-get command:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo apt update linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo apt install nvtop

Debian Linux 10 users please enable contrib software sources in /etc/apt/sources.list:
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian buster main non-free contrib deb http://deb.debian.org/debian buster-updates main non-free contrib deb http://deb.debian.org/debian-security/ buster/updates main non-free contrib
Then search for it using apt-cache command and install it using sudo apt install nvtop command:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo apt update linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo apt search nvtop linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo apt-cache policy nvtop
All other Linux distributions
Try using the snap command. For example:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ snap search nvtop linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo snap install nvtop
Next, add the function to kill GPU processes in nvtop:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo snap connect nvtop:process-control
You can also easily add the ability to view GPU information (fans, PCIe, power supplies, etc.) as follows:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo snap connect nvtop:hardware-observe
Here's how to add AMD GPU process list support:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$sudo snap connect nvtop:system-observe
You may need a workaround to get per-process GPU usage. For example:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo snap connect nvtop:kubernetes-support
How to use Docker nvtop image
Please try the following commands in a Linux terminal. You must have a working Docker installation. For example:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$git clone https://github.com/Syllo/nvtop.git linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$cd nvtop linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com/nvtop$ sudo docker build --tag nvtop . linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com/nvtop$ sudo docker run -it --rm --runtime=nvidia --gpus=all --pid=host nvtop
Getting started with nvtop
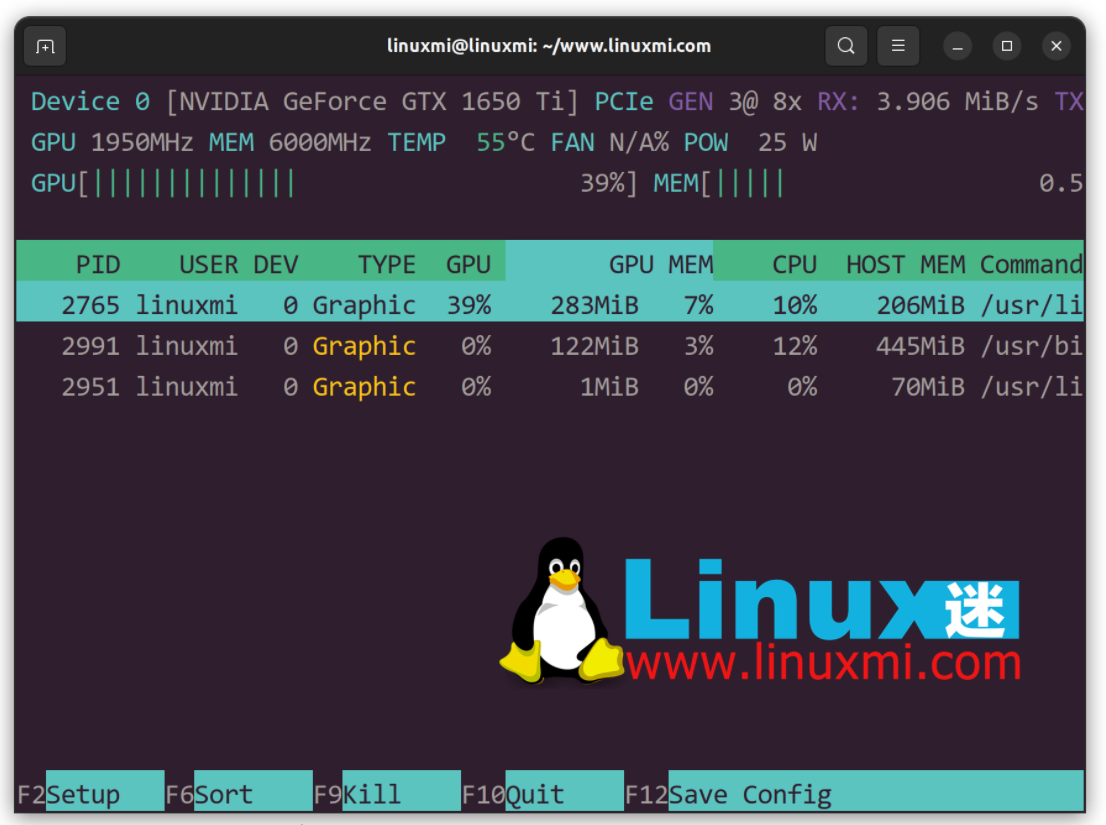
Now that the tool is installed, it’s time to try it out. You just need to enter the following command:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ nvtop
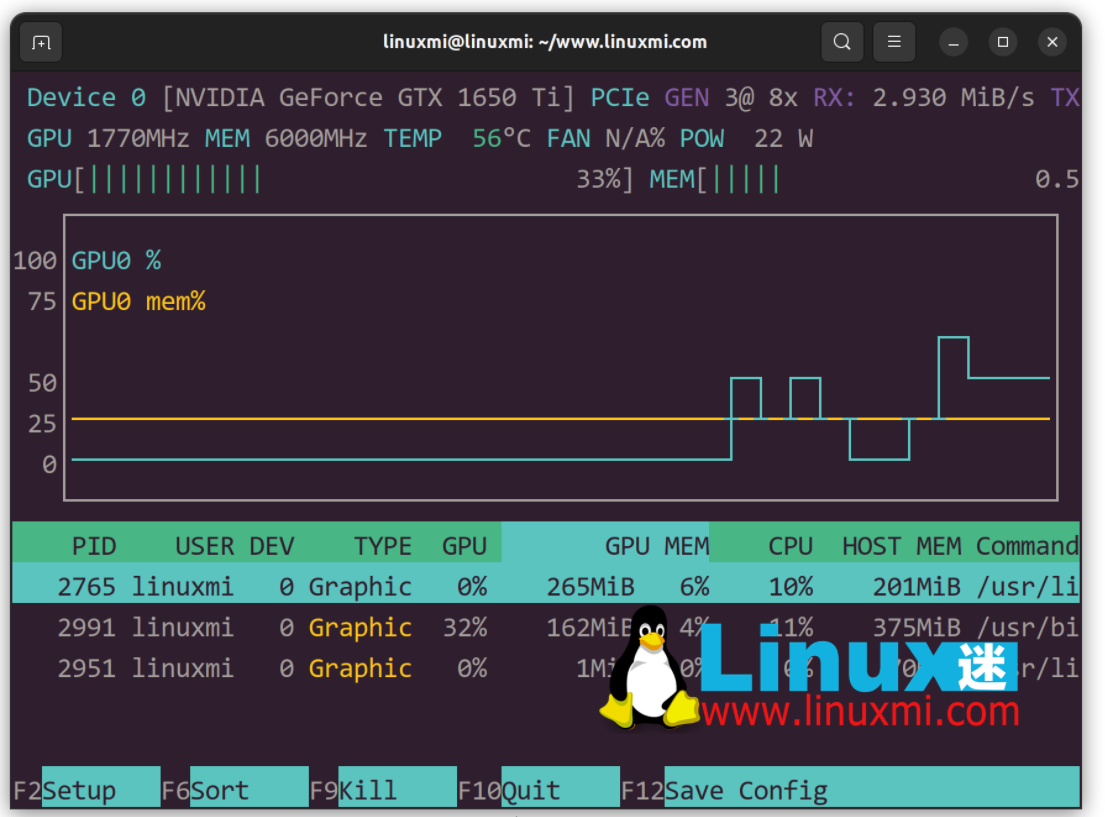
You can also specify the delay between updates in tenths of a second. For example:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$nvtop -d 0.25
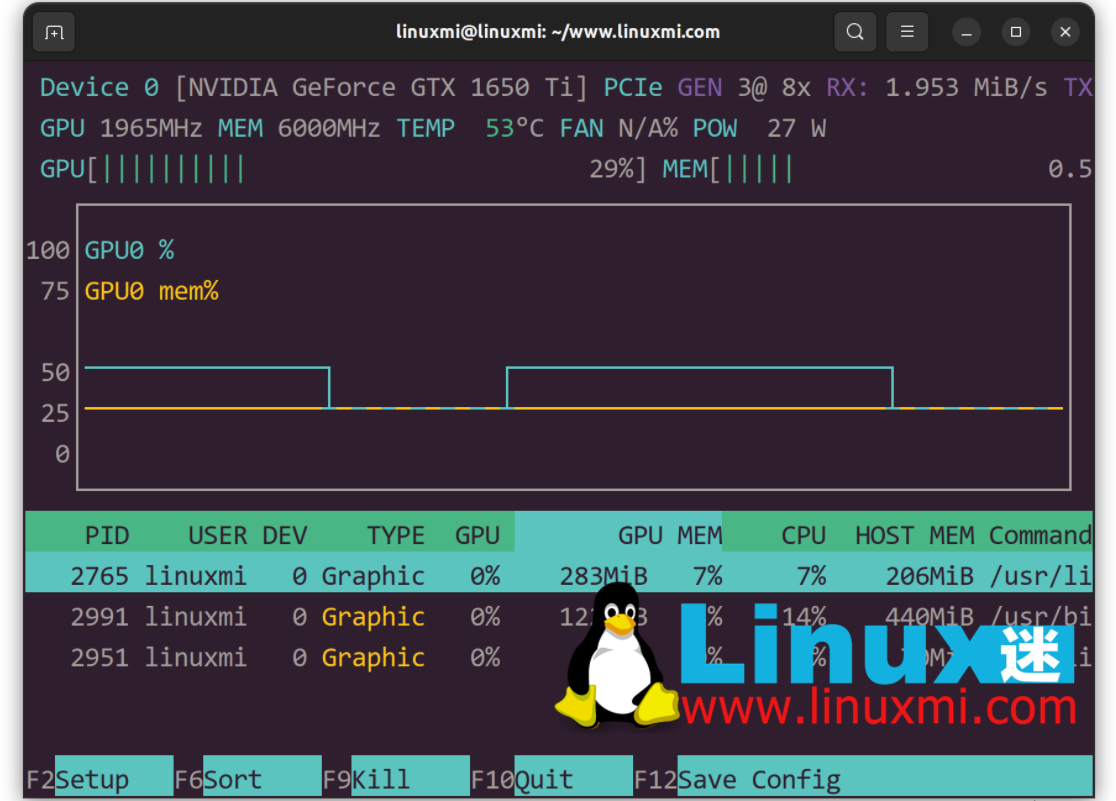
Do you want monochrome mode? Here's how to disable colored output:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ nvtop -C
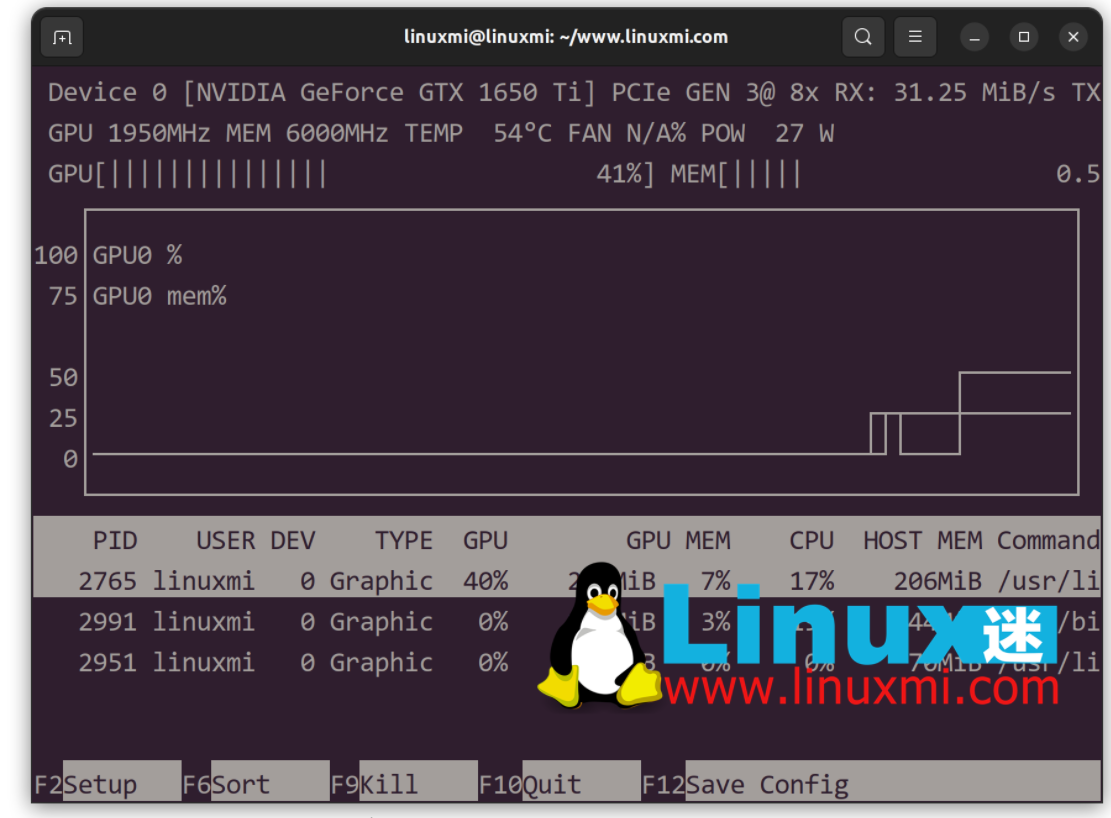
Here's how to display only one bar, corresponding to the maximum value across all GPUs:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ nvtop -p
Keyboard shortcuts for the nvtop command
| shortcut key | illustrate |
|---|---|
Up |
Select (highlight) the previous process. |
Down |
Select (highlight) the previous process. |
Left / Right |
Scroll in process line |
|
Sort in ascending order, that is, sort from small to large. |
- |
Sort in descending order, that is, from large to small. |
F2 |
Enter the setting tool to modify the interface options. |
F12 |
Save the current interface options to persistent storage. |
F9 |
"Kill" process: Select the signal to be sent to the highlighted process. |
F6 |
Sort: Select the field to sort. The current sort field will be highlighted in the title bar. |
F10, q, Esc |
Exit the nvtop command. |
Show details
in conclusion:
I find nvtop very useful when I need to see what is stress testing my GPU and key information like GPU temperature or fan speed. You can use this tool to quickly kill a process that is using up all GPU resources without having to use the ps command/grep command and then kill the PID. Most modern applications such as Firefox, Chrome, and code written in Python can use dedicated NVIDIA or AMD GPUs. Therefore, it is very useful to have this gadget. Might as well give it a try.
Get help with nvtop
You can read the nvtop manual page in the project repository offline or online. For example, try using the man command or passing the -h option like this:
nvtop -h
The above is the detailed content of nvtop – A great Linux task monitor. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1306
1306
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
Causes and solutions for the VS Code terminal commands not available: The necessary tools are not installed (Windows: WSL; macOS: Xcode command line tools) Path configuration is wrong (add executable files to PATH environment variables) Permission issues (run VS Code as administrator) Firewall or proxy restrictions (check settings, unrestrictions) Terminal settings are incorrect (enable use of external terminals) VS Code installation is corrupt (reinstall or update) Terminal configuration is incompatible (try different terminal types or commands) Specific environment variables are missing (set necessary environment variables)
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.