dutree: A powerful Linux file system disk usage tracking tool
dutree is a fast, open source command line tool for analyzing disk usage. It is written in the Rust programming language and combines the functionality of the durep (disk usage reporting tool) and tree (listing directory contents in a tree format) command line tools. Therefore, dutree is able to report disk usage in a tree format.
As a powerful disk usage tracking tool, dutree is suitable for Linux file systems. It is free and open source and is able to display results in the form of colored output, with the color depending on the configuration of the GNU LS_COLORS environment variable. This environment variable allows setting the color of files based on their extension, permissions, and type.
dutree has the following characteristics:
- Display the tree structure of the file system.
- Supports merging small files.
- Allows comparison of disk usage of different directories.
- Supports excluding specified files or directories.
To install dutree in a Linux system, first ensure that the Rust programming language is installed on the system. If Rust is not installed yet, you can install it using the following curl command:
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % sudo curl https://sh.rustup.rs -sSf | sh
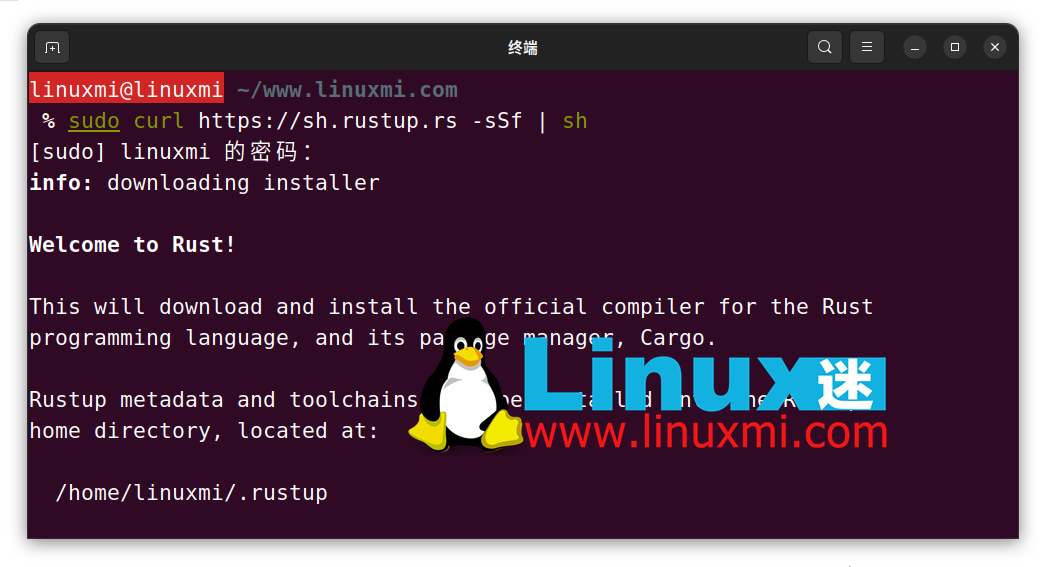
After installing Rust, you can execute the following command to install dutree in the Linux distribution, as shown below:
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % cargo install --git https://github.com/nachoparker/dutree.git
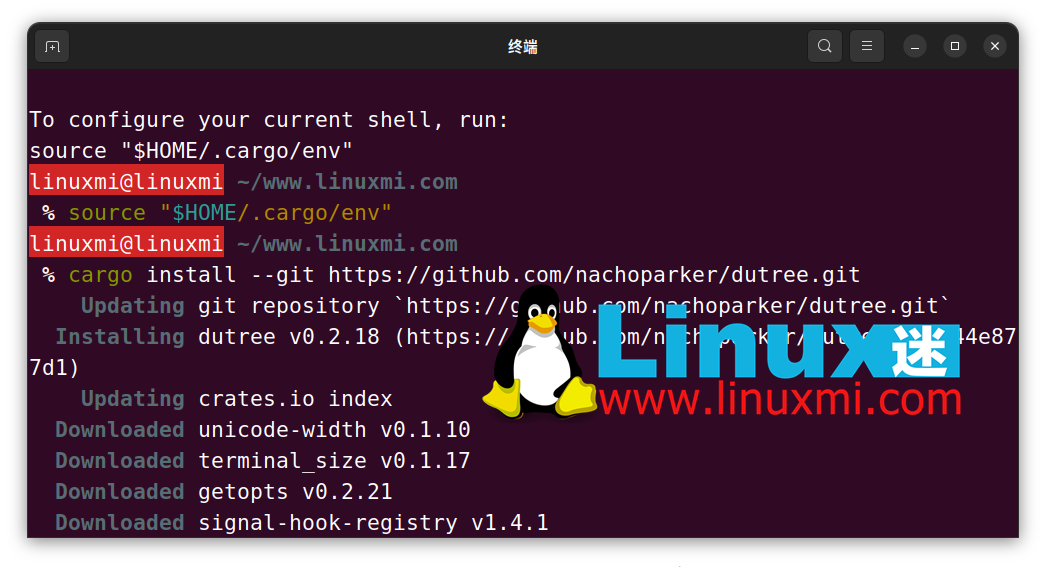
After dutree is installed, it will use environment colors based on the environment variable LS_COLORS, with the same colors as the ls –color command configured for our distribution.
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % ls --color
The easiest way to run dutree is without any parameters, so that it displays a file system tree.
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % dutree

To display actual disk usage instead of file size, use the -u flag.
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % dutree -u

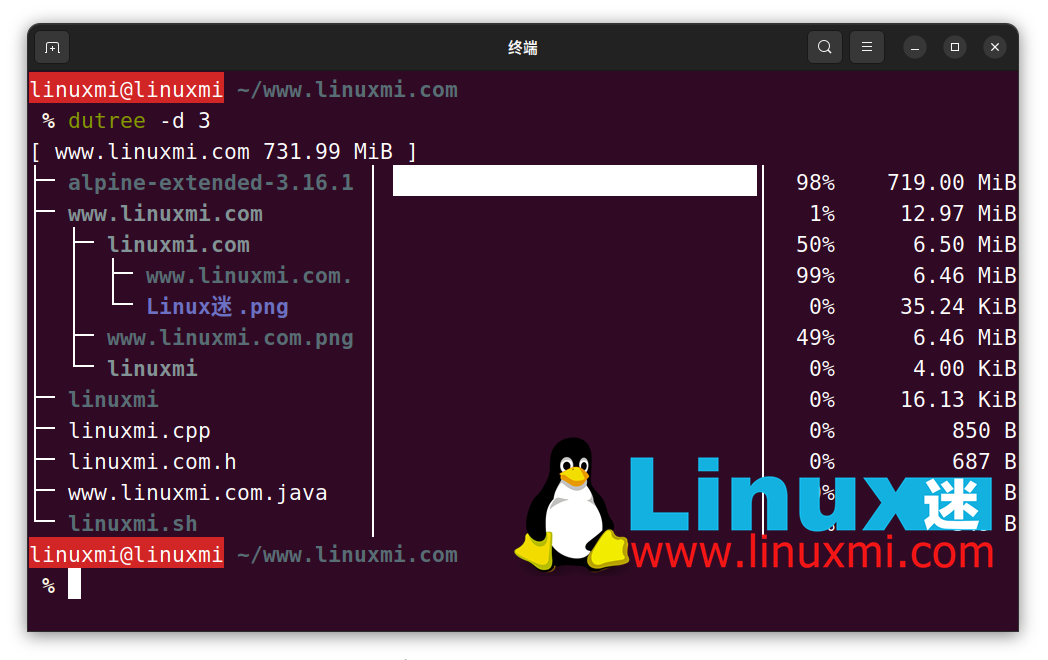
You can use the -d flag to display directories at a given depth (default is 1). The following command will display the directories at depth 3 under the current working directory.
For example, if the current working directory (~/) displays the size of ~///*, as shown in the following example screenshot.
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % dutree -d 3
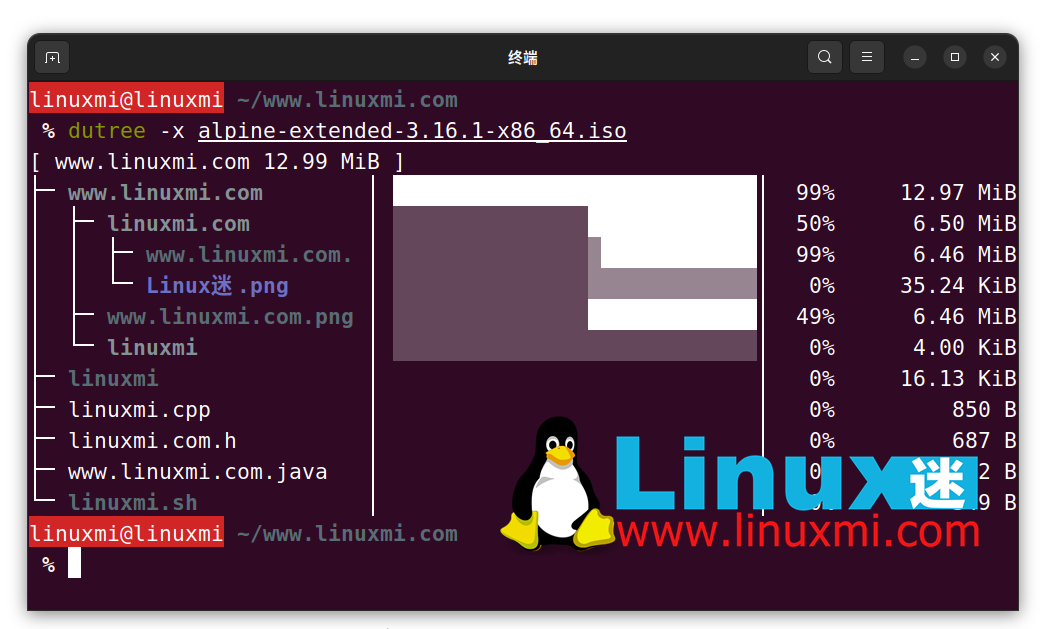
Exclude files or directories from output
To exclude items matching file or directory names, use the -x flag.
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % dutree -x alpine-extended-3.16.1-x86_64.iso
You can also quickly get a local overview by skipping directories by using the -f option as shown below.
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % dutree -f
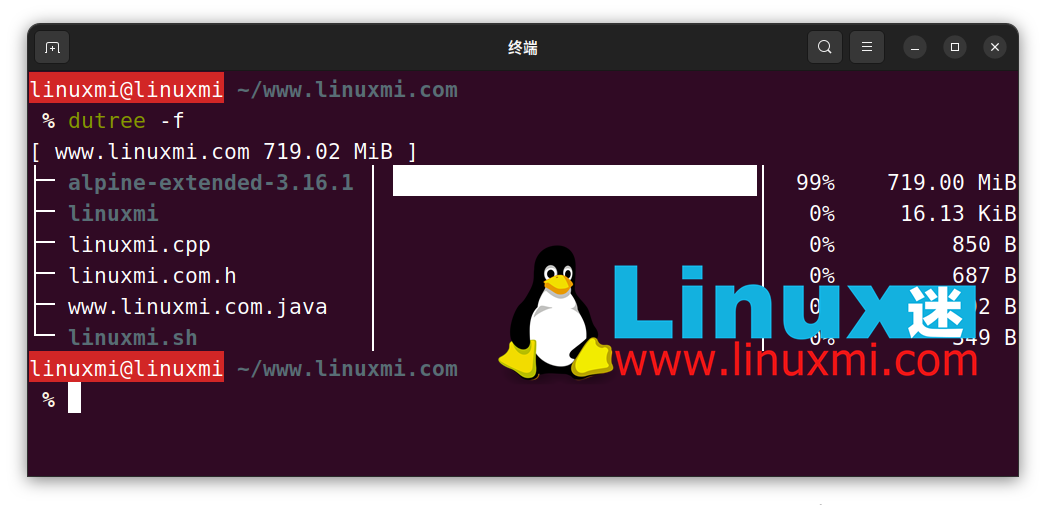
A complete summary/overview can be generated using the -s flag as shown below.
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % dutree -s
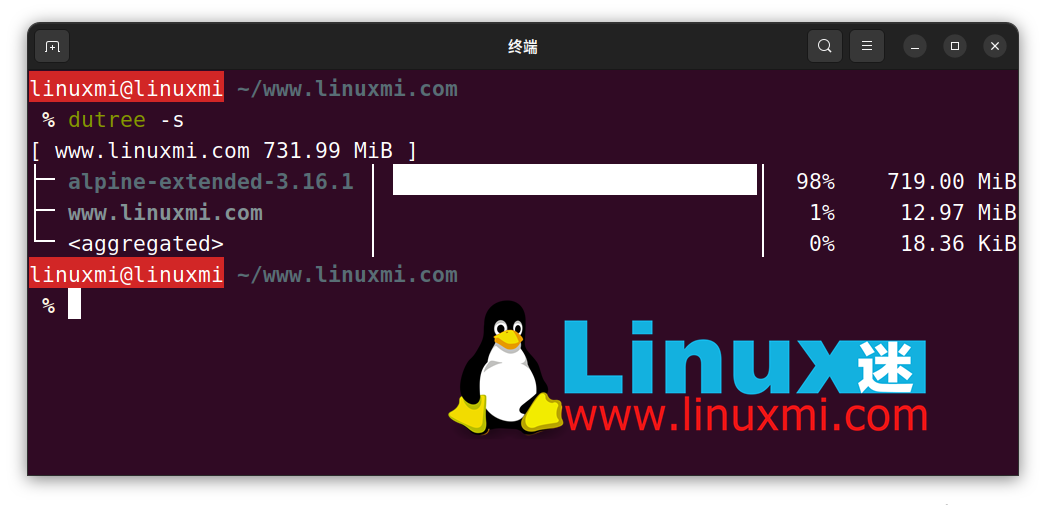
Files smaller than a certain size can be aggregated. The default value is 1M, as shown below.
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % dutree -a
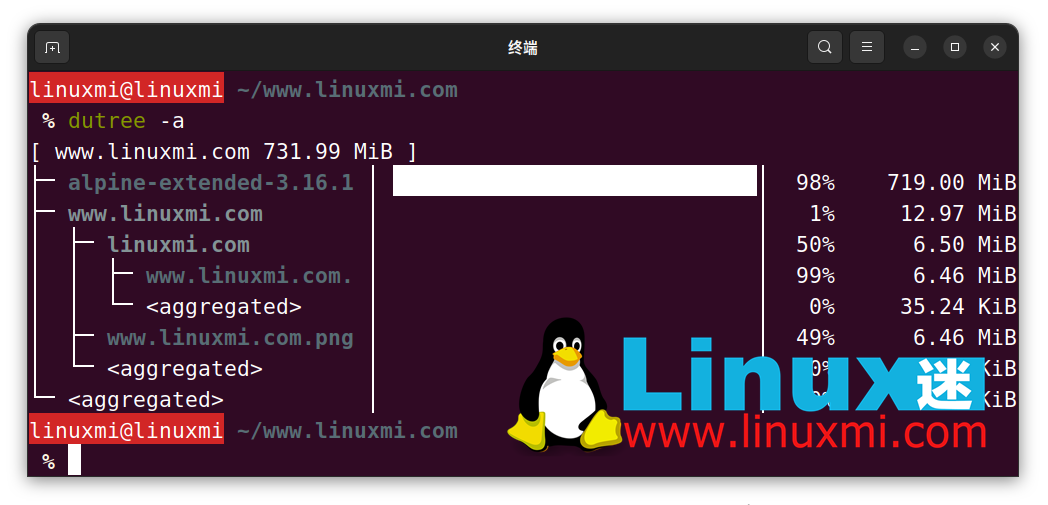
The switch to exclude hidden files is -H.
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % dutree -H
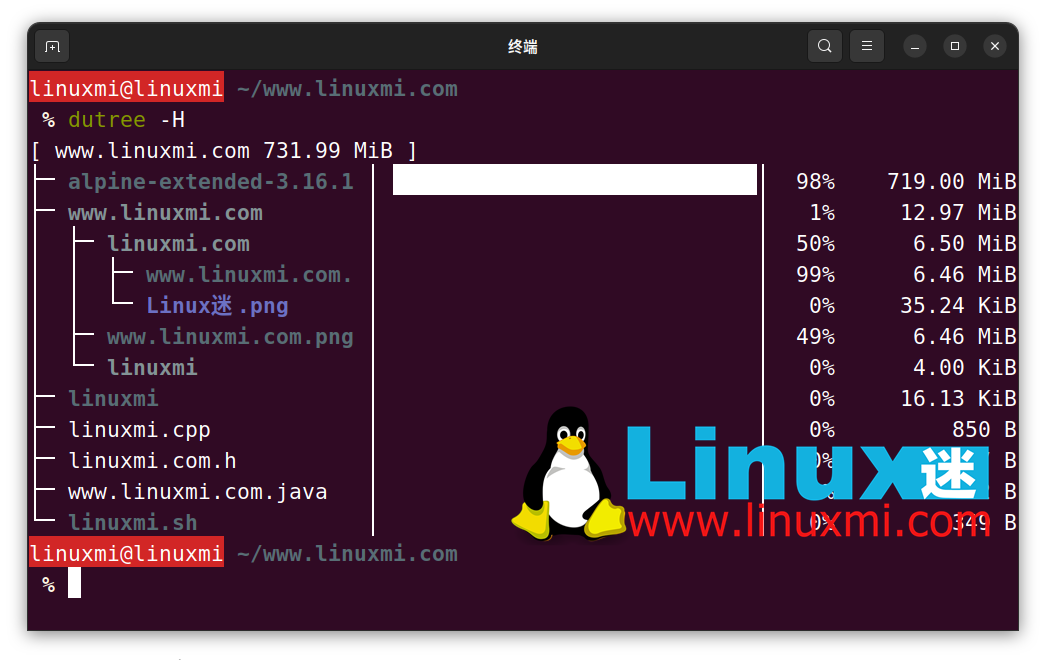
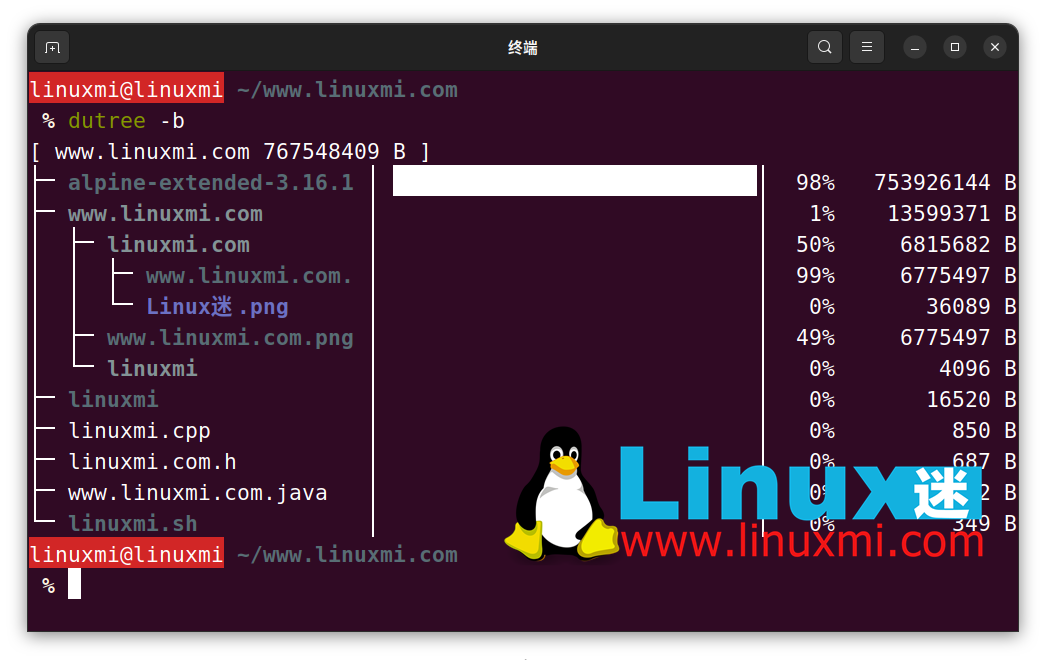
This option is used to display the size in bytes instead of kilobytes (the default). -b
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % dutree -b
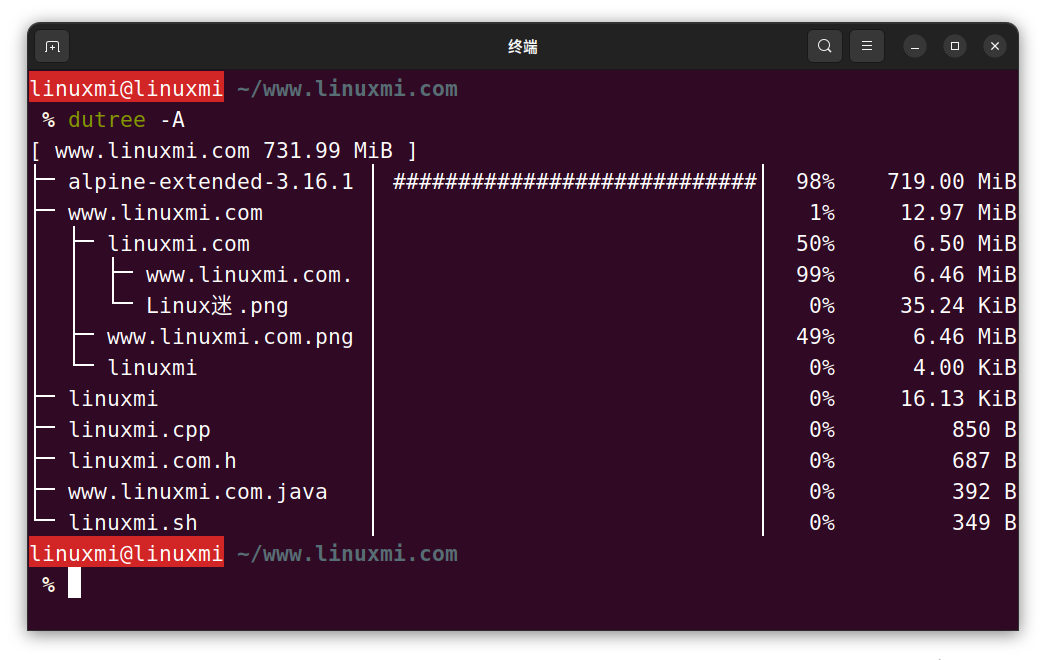
To turn off colors and display only ASCII characters, use the flag -A as shown below.
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com % dutree -a
You can use the -h option to view dutree help messages.
$ dutree -h
使用方式: dutree [选项] [..]
选项:
-d, –depth [DEPTH] 显示目录深度为 N (默认 1)
-a, –aggr [N[KMG]] 聚合小于 N B/KiB/MiB/GiB 的文件(默认 1M)
-s, –summary 等效于 -da,或 -d1 -a1M
-u, –usage 报告实际磁盘使用情况而不是文件大小
-b, –bytes 以字节打印大小
-x, –exclude NAME 排除匹配的文件或目录
-H, –no-hidden 排除隐藏文件
-A, –ascii 仅使用 ASCII 字符,不使用颜色
-h, –help 显示帮助
-v, –version 打印版本号
dutree 是一个简单而强大的命令行工具,用于在 Linux 系统上以树状格式显示文件大小和分析磁盘使用情况。如果还有什么疑问与建议,请在下面的评论栏中留言告诉我们。
The above is the detailed content of dutree: A powerful Linux file system disk usage tracking tool. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.






