 System Tutorial
System Tutorial
 LINUX
LINUX
 Understanding and Implementation of Finite State Machine FSM in Linux Programming
Understanding and Implementation of Finite State Machine FSM in Linux Programming
Understanding and Implementation of Finite State Machine FSM in Linux Programming
Finite State Machine (FSM for short) refers to a mathematical model consisting of a limited number of states and behaviors such as transitions and actions between these states. It has been widely used in the computer field. FSM is an efficient programming method used to implement the processing logic of a program within a logical unit. Especially in server programming, by performing corresponding processing based on different states or message types, the logic of the program can be made clearer and easier to understand. .
So, where are finite state machines usually used?
It can be applied to tokenizers (tokenizers) that process programming languages or natural languages, and implement grammar parsing and analysis through bottom-up grammar parsers (parser). In various communication protocols, the sender and receiver Processing messages by passing data between them, in game artificial intelligence, etc.
For the implementation of finite state machines, there are generally the following methods. I will introduce their advantages and disadvantages one by one.
1. Finite state machine implemented using if/else if statements
Using if/else if statements to implement finite state machines is the simplest and easiest to understand method. Just use a large number of if/else if statements to determine the current status and perform corresponding logical processing.
The following is a simple state machine example. We use a large number of if/else if statements to implement it, perform corresponding operations according to different states, and implement state transitions.
enum
{
GET_UP,
GO_TO_SCHOOL,
HAVE_LUNCH,
GO_HOME,
DO_HOMEWORK,
SLEEP,
};
int
main()
{
int
state = GET_UP;
//小明的一天
while
(
1
)
{
if
(state == GET_UP)
{
GetUp
();
//具体调用的函数
state = GO_TO_SCHOOL;
//状态的转移
}
else
if
(state == GO_TO_SCHOOL)
{
Go2School
();
state = HAVE_LUNCH;
}
else
if
(state == HAVE_LUNCH)
{
HaveLunch
();
}
...
else
if
(state == SLEEP)
{
Go2Bed
();
state = GET_UP;
}
}
return
0
;
}
After reading the above example, what do you think? Do you feel that although the program is simple and easy to understand, it uses a large number of if judgment statements, which makes the code very low-end and the code is bloated. This state machine has only a few states, and the code expansion is not obvious. However, if there are dozens of states that we need to process, the code of this state machine will be difficult to read.
2. Use switch to implement FSM
The structure of FSM implemented using switch statements has become clearer, and its shortcomings are also obvious: although this design method is simple and processed through a lot of judgments, it is suitable for small-scale state switching processes, but if the scale Expansion is difficult to expand and maintain.
int
state = GET_UP;
//小明的一天
while
(
1
)
{
switch
(state)
{
case
GET_UP:
GetUp
();
//具体调用的函数
state = GO_TO_SCHOOL;
//状态的转移
break
;
case
GO_TO_SCHOOL:
Go2School
();
state = HAVE_LUNCH;
break
;
case
HAVE_LUNCH:
HaveLunch
();
state = GO_HOME;
break
;
...
default
:
break
;
}
}
return
0
;
}
3. Use function pointers to implement FSM
The idea of using function pointers to implement FSM: establish the corresponding state table and action query table, locate the corresponding action processing function according to the state table, event, and action table, and then switch the state after the execution is completed.
当然使用函数指针实现的 FSM 的过程还是比较费时费力,但是这一切都是值得的,因为当你的程序规模大时候,基于这种表结构的状态机,维护程序起来也是得心应手。
下面给出一个使用函数指针实现的 FSM 的框架:
我们还是以 “小明的一天” 为例设计出该 FSM。
先给出该 FSM 的状态转移图:
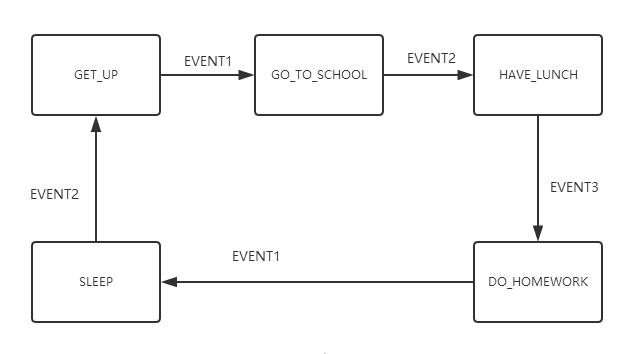
下面讲解关键部分代码实现
首先我们定义出小明一天的活动状态:
//比如我们定义了小明一天的状态如下
enum
{
GET_UP,
GO_TO_SCHOOL,
HAVE_LUNCH,
DO_HOMEWORK,
SLEEP,
};
我们也定义出会发生的事件
{
EVENT1 =
1
,
EVENT2,
EVENT3,
};
定义状态表的数据结构
typedef
struct
FsmTable_s
{
int
event
;
//事件
int
CurState
;
//当前状态
void
(*eventActFun)();
//函数指针
int
NextState
;
//下一个状态
}
FsmTable_t
;
接下来定义出最重要 FSM 的状态表,我们整个 FSM 就是根据这个定义好的表来运转的。
FsmTable_t
XiaoMingTable
[] =
{
//{到来的事件,当前的状态,将要要执行的函数,下一个状态}
{ EVENT1, SLEEP,
GetUp
, GET_UP },
{ EVENT2, GET_UP,
Go2School
, GO_TO_SCHOOL },
{ EVENT3, GO_TO_SCHOOL,
HaveLunch
, HAVE_LUNCH },
{ EVENT1, HAVE_LUNCH,
DoHomework
, DO_HOMEWORK },
{ EVENT2, DO_HOMEWORK,
Go2Bed
, SLEEP },
//add your codes here
};
状态机的注册、状态转移、事件处理的动作实现
/*状态机注册*/
void
FSM_Regist(
FSM_t
* pFsm,
FsmTable_t
* pTable)
{
pFsm->
FsmTable
= pTable;
}
/*状态迁移*/
void
FSM_StateTransfer(
FSM_t
* pFsm,
int
state)
{
pFsm->curState = state;
}
/*事件处理*/
void
FSM_EventHandle(
FSM_t
* pFsm,
int
event
)
{
FsmTable_t
* pActTable = pFsm->
FsmTable
;
void
(*eventActFun)() = NULL;
//函数指针初始化为空
int
NextState
;
int
CurState
= pFsm->curState;
int
flag =
0
;
//标识是否满足条件
int
i;
/*获取当前动作函数*/
for
(i =
0
; iif
(
event
== pActTable[i].
event
&&
CurState
== pActTable[i].
CurState
)
{
flag =
1
;
eventActFun = pActTable[i].eventActFun;
NextState
= pActTable[i].
NextState
;
break
;
}
}
if
(flag)
//如果满足条件了
{
/*动作执行*/
if
(eventActFun)
{
eventActFun();
}
//跳转到下一个状态
FSM_StateTransfer(pFsm,
NextState
);
}
else
{
// do nothing
}
}
主函数我们这样写,然后观察状态机的运转情况。
int
main()
{
FSM_t
fsm;
InitFsm
(&fsm);
int
event
= EVENT1;
//小明的一天,周而复始的一天又一天,进行着相同的活动
while
(
1
)
{
printf(
"event %d is coming...\n"
,
event
);
FSM_EventHandle(&fsm,
event
);
printf(
"fsm current state %d\n"
, fsm.curState);
test(&
event
);
sleep(
1
);
//休眠1秒,方便观察
}
return
0
;
}
看一看该状态机跑起来的状态转移情况:
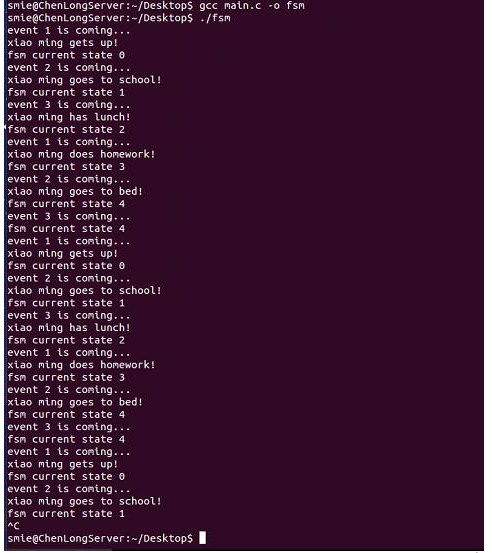
上面的图可以看出,当且仅当在指定的状态下来了指定的事件才会发生函数的执行以及状态的转移,否则不会发生状态的跳转。这种机制使得这个状态机不停地自动运转,有条不絮地完成任务。
与前两种方法相比,使用函数指针实现 FSM 能很好用于大规模的切换流程,只要我们实现搭好了 FSM 框架,以后进行扩展就很简单了(只要在状态表里加一行来写入新的状态处理就可以了)。
The above is the detailed content of Understanding and Implementation of Finite State Machine FSM in Linux Programming. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1421
1421
 52
52
 1315
1315
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.
 laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
To install Laravel, follow these steps in sequence: Install Composer (for macOS/Linux and Windows) Install Laravel Installer Create a new project Start Service Access Application (URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000) Set up the database connection (if required)
 git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Installing Git software includes the following steps: Download the installation package and run the installation package to verify the installation configuration Git installation Git Bash (Windows only)
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version



