Steps to configure static IP in Linux bridge mode
| Introduction | I have been using NAT mode before. During the test, when the android terminal remotely accessed the mysql of the virtual machine, I found that it could not connect. However, I successfully accessed the mysql of the virtual machine Linux copied by my classmate. I thought about the reason because it was set by him. bridge mode. |
Regarding the difference between the two modes, you can search a lot of articles on the Internet. In layman's terms, in NAT mode, the virtual machine is subordinate to the host, that is, access to the external network must be accessed through the host, so the IP of the virtual machine is only Only the host can identify it. In bridge mode, the virtual machine and the host are in a parallel relationship, share a network card (using multiple interfaces of the network card), and can directly access the external network. Therefore, if you want to remotely access the MySQL of the virtual machine, you need to use bridge mode instead of NAT mode. However, the IP in bridge mode generally changes. In order to avoid resetting the IP for each remote connection, it is set to a static IP here.
The first step is to check the IP under Linux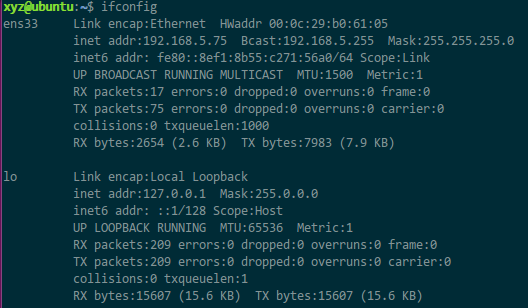 This is Ubuntu 16.04. There are 2 items here. The lower one is lo (local loopback) and can be ignored. The upper one needs to be configured. Note that my virtual network card here is ens33, and the one I will modify later is also ens33. There are many configuration tutorials on the Internet where the network card name of their Linux system is not ens33 (for example, some are eth0).
The second step is to set up the virtual network
In the VMware menu, Edit->Virtual Network Editor
This is Ubuntu 16.04. There are 2 items here. The lower one is lo (local loopback) and can be ignored. The upper one needs to be configured. Note that my virtual network card here is ens33, and the one I will modify later is also ens33. There are many configuration tutorials on the Internet where the network card name of their Linux system is not ens33 (for example, some are eth0).
The second step is to set up the virtual network
In the VMware menu, Edit->Virtual Network Editor
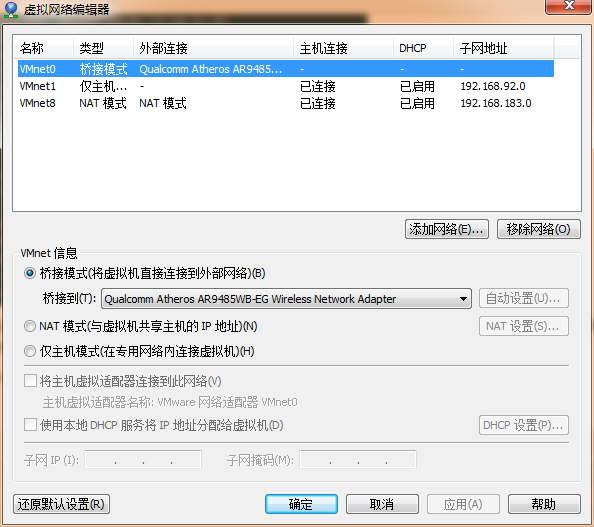 Modify "Bridge to" in the VMnet information to the network card adapter. The default is automatic.
The third step is to check the IP information of the host (here is windows)
The command is ipconfig /all. The reason why the /all option is added at the end is to view the description of the network card.
Modify "Bridge to" in the VMnet information to the network card adapter. The default is automatic.
The third step is to check the IP information of the host (here is windows)
The command is ipconfig /all. The reason why the /all option is added at the end is to view the description of the network card.
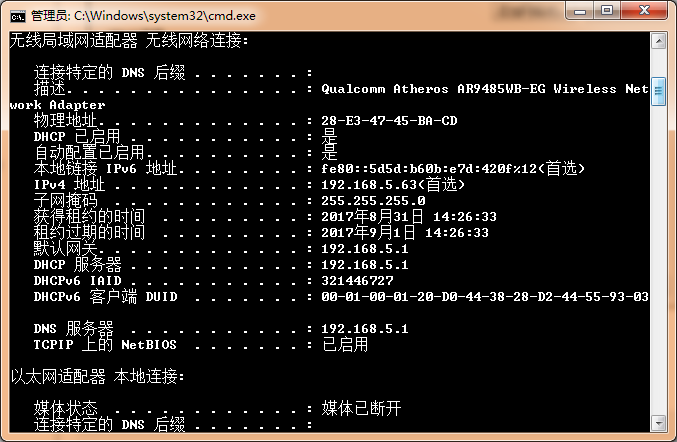 Note that the description here of Qualcomm Atheros is the same as the name of the network card selected in the second step. Remember the three important items of the host.
IPv4 address: 192.168.5.63 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 Default gateway: 192.168.5.1
Step 4: Modify the Linux network interface configuration
$ sudo vim /etc/network/interfaces
Modify the file (the specific path varies with the system) and set ens33 to a new IP under the same network segment. Here I set it to 192.168.5.64. (The IP calculation method for the same network segment is that the IP and subnet mask AND operation results are consistent. For example, if 192.168.5.63 and 255.255.255.0 are ANDed, 192.168.5.0 is obtained. For specific knowledge, please refer to the IP part of the computer network textbook)
Note that the description here of Qualcomm Atheros is the same as the name of the network card selected in the second step. Remember the three important items of the host.
IPv4 address: 192.168.5.63 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 Default gateway: 192.168.5.1
Step 4: Modify the Linux network interface configuration
$ sudo vim /etc/network/interfaces
Modify the file (the specific path varies with the system) and set ens33 to a new IP under the same network segment. Here I set it to 192.168.5.64. (The IP calculation method for the same network segment is that the IP and subnet mask AND operation results are consistent. For example, if 192.168.5.63 and 255.255.255.0 are ANDed, 192.168.5.0 is obtained. For specific knowledge, please refer to the IP part of the computer network textbook)
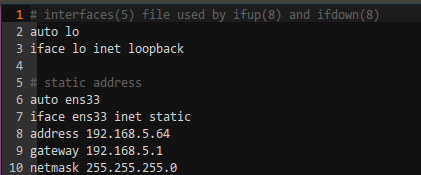 Lines 5 to 10 were manually edited by me. You can see that the gateway and netmask are the same as those on the host, and only the address has been modified.
Step 5: Set DNS
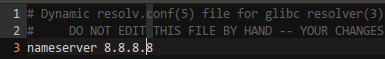
xyz@ubuntu:~$ sudo vim /etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/head
Lines 5 to 10 were manually edited by me. You can see that the gateway and netmask are the same as those on the host, and only the address has been modified.
Step 5: Set DNS
xyz@ubuntu:~$ sudo vim /etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/head
 Then restart the virtual machine network service (practice has proven that this step is useless, although I don’t know why, just restart the system honestly.)
xyz@ubuntu:~$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart
[ ok ] Restarting networking (via systemctl): networking.service.
Now check if the configuration is correct.
Check the IP and it has changed to the set 192.168.5.64
Then restart the virtual machine network service (practice has proven that this step is useless, although I don’t know why, just restart the system honestly.)
xyz@ubuntu:~$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart
[ ok ] Restarting networking (via systemctl): networking.service.
Now check if the configuration is correct.
Check the IP and it has changed to the set 192.168.5.64
 Try pinging a URL:
Try pinging a URL:
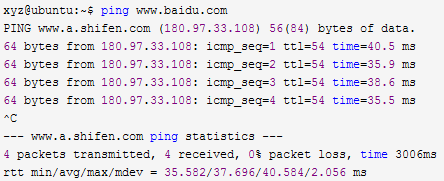 Try the host pinging the virtual machine:
Try the host pinging the virtual machine:
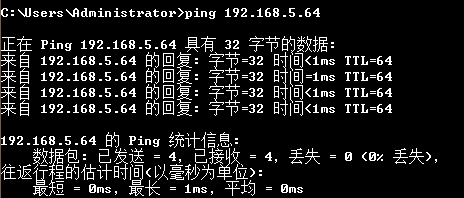 But the virtual machine failed to ping the host:
But the virtual machine failed to ping the host:
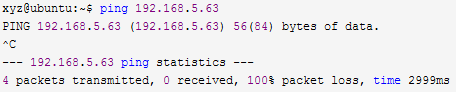 The reason is that the firewall is turned on on the host and the firewall on the public network is turned off.
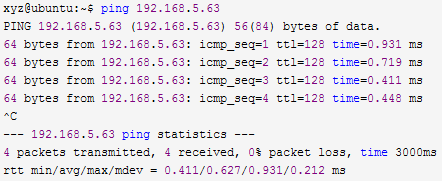
Pinging the host again is successful:
The reason is that the firewall is turned on on the host and the firewall on the public network is turned off.
Pinging the host again is successful:
The above is the detailed content of Steps to configure static IP in Linux bridge mode. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.






