Install Apache Hadoop on CentOS!
| Introduction | The Apache Hadoop software library is a framework that allows distributed processing of large data sets on a computer cluster using a simple programming model. Apache™ Hadoop® is open source software for reliable, scalable, distributed computing. |
The project includes the following modules:
- Hadoop Common: Common tools that support other Hadoop modules.
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS™): A distributed file system that provides support for high-throughput access to application data.
- Hadoop YARN: Job scheduling and cluster resource management framework.
- Hadoop MapReduce: A YARN-based parallel processing system for large data sets.
This article will help you step by step to install hadoop on CentOS and configure a single-node hadoop cluster.
Install JavaBefore installing hadoop, please make sure Java is installed on your system. Use this command to check the installed version of Java.
java -version java version "1.7.0_75" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_75-b13) Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.75-b04, mixed mode)
To install or update Java, please refer to the step-by-step instructions below.
The first step is to download the latest version of java from the Oracle official website.
cd /opt/ wget --no-cookies --no-check-certificate --header "Cookie: gpw_e24=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.oracle.com%2F; oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" "http://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/7u79-b15/jdk-7u79-linux-x64.tar.gz" tar xzf jdk-7u79-linux-x64.tar.gz
Requires setup to use a newer version of Java as an alternative. Use the following command to do this.
cd /opt/jdk1.7.0_79/ alternatives --install /usr/bin/java java /opt/jdk1.7.0_79/bin/java 2 alternatives --config java There are 3 programs which provide 'java'. Selection Command ----------------------------------------------- * 1 /opt/jdk1.7.0_60/bin/java + 2 /opt/jdk1.7.0_72/bin/java 3 /opt/jdk1.7.0_79/bin/java Enter to keep the current selection[+], or type selection number: 3 [Press Enter]
Now you may also need to use the alternatives command to set the javac and jar command paths.
alternatives --install /usr/bin/jar jar /opt/jdk1.7.0_79/bin/jar 2 alternatives --install /usr/bin/javac javac /opt/jdk1.7.0_79/bin/javac 2 alternatives --set jar /opt/jdk1.7.0_79/bin/jar alternatives --set javac /opt/jdk1.7.0_79/bin/javac
The next step is to configure environment variables. Use the following commands to set these variables correctly.
Set JAVA_HOME variable:
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/jdk1.7.0_79
Set the JRE_HOME variable:
export JRE_HOME=/opt/jdk1.7.0_79/jre
Set the PATH variable:
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/jdk1.7.0_79/bin:/opt/jdk1.7.0_79/jre/bin
After setting up the java environment. Start installing Apache Hadoop.
The first step is to create a system user account for the hadoop installation.
useradd hadoop passwd hadoop
Now you need to configure the ssh key for user hadoop. Use the following command to enable password-less ssh login.
su - hadoop ssh-keygen -t rsa cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys chmod 0600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys exit
Now download the latest available version of hadoop from the official website hadoop.apache.org.
cd ~ wget http://apache.claz.org/hadoop/common/hadoop-2.6.0/hadoop-2.6.0.tar.gz tar xzf hadoop-2.6.0.tar.gz mv hadoop-2.6.0 hadoop
The next step is to set the environment variables used by hadoop.
Edit ~/.bashrc and add the following values at the end of the file.
export HADOOP_HOME=/home/hadoop/hadoop export HADOOP_INSTALL=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_COMMON_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_HDFS_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_COMMON_LIB_NATIVE_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/lib/native export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin:$HADOOP_HOME/bin
Apply changes in the current running environment.
source ~/.bashrc
Edit $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh and set the JAVA_HOME environment variable.
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/jdk1.7.0_79/
Now, start by configuring a basic hadoop single-node cluster.
First edit the hadoop configuration file and make the following changes.
cd /home/hadoop/hadoop/etc/hadoop
Let’s edit core-site.xml.
fs.default.name hdfs://localhost:9000
Then edit hdfs-site.xml:
dfs.replication 1 dfs.name.dir file:///home/hadoop/hadoopdata/hdfs/namenode dfs.data.dir file:///home/hadoop/hadoopdata/hdfs/datanode
And edit mapred-site.xml:
mapreduce.framework.name yarn
Last edit yarn-site.xml:
yarn.nodemanager.aux-services mapreduce_shuffle
Now format the namenode using the following command:
hdfs namenode -format
To start all hadoop services, use the following command:
cd /home/hadoop/hadoop/sbin/ start-dfs.sh start-yarn.sh
To check whether all services start normally, use the jps command:
jps
You should see output like this.
26049 SecondaryNameNode 25929 DataNode 26399 Jps 26129 JobTracker 26249 TaskTracker 25807 NameNode
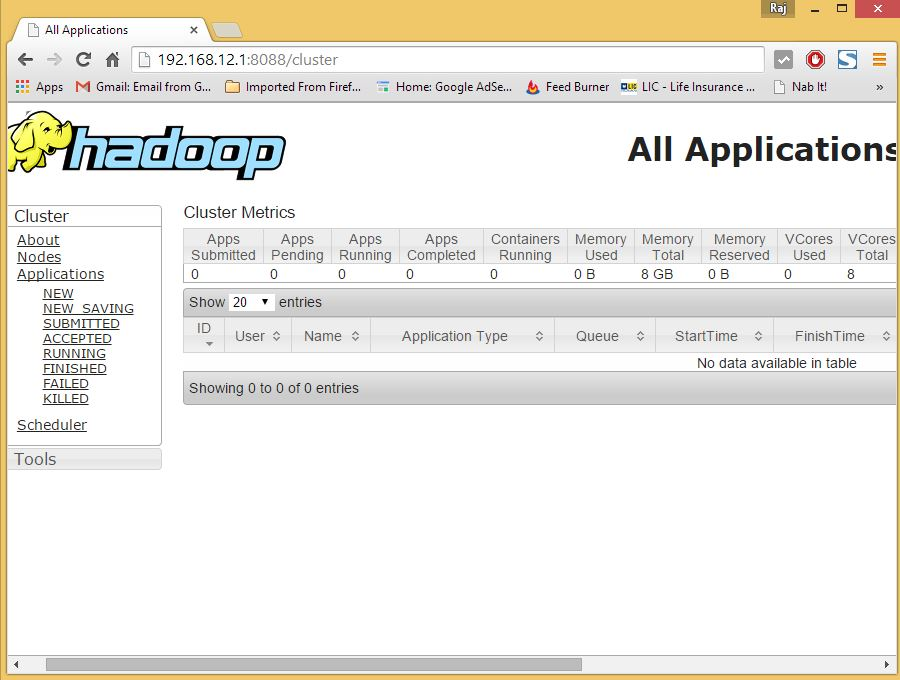
Now, you can access the Hadoop service in your browser: http://your-ip-address:8088/.
hadoop
The above is the detailed content of Install Apache Hadoop on CentOS!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1655
1655
 14
14
 1414
1414
 52
52
 1307
1307
 25
25
 1253
1253
 29
29
 1227
1227
 24
24
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
VS Code One-step/Next step shortcut key usage: One-step (backward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl ←; macOS: Cmd ←Next step (forward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl →; macOS: Cmd →
 vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
Causes and solutions for the VS Code terminal commands not available: The necessary tools are not installed (Windows: WSL; macOS: Xcode command line tools) Path configuration is wrong (add executable files to PATH environment variables) Permission issues (run VS Code as administrator) Firewall or proxy restrictions (check settings, unrestrictions) Terminal settings are incorrect (enable use of external terminals) VS Code installation is corrupt (reinstall or update) Terminal configuration is incompatible (try different terminal types or commands) Specific environment variables are missing (set necessary environment variables)
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.




