Building an e-book service using Raspberry Pi
| Introduction | Caliber 3.0 was recently released, which allows users to read e-books in the browser! Note that Raspbian's repository has not updated it (as of writing). E-books are a great way for teachers, librarians, and others to share books, class materials, or other files with students, as long as you have reliable bandwidth access. But even if you have a slow or no connection, there's a simple solution: Create an e-book server using the open-source Caliber e-book management software that runs on a Raspberry Pi 3. This is what I did and you can too. |
First I downloaded the latest Raspbian Pixel image and installed it on a new 8GB microSD card. I then plugged in the microSD, connected a keyboard, mouse and an HDMI cable to an old LCD TV, and booted up the Pi. After adjusting the Pixel environment resolution on my monitor and connecting to a local network, I was ready to get started. I opened a terminal and typed
sudo apt-get update
to get the latest updates for your operating system.
Updating Raspbian Pixel
Next, I type
in the terminalsudo apt-get install calibre
To install Caliber.
Installing Caliber
I started Caliber from the command line (note it can also be started from the GUI). Caliber's interface is very intuitive. When you start it for the first time, you will see the Welcome to Caliber wizard. I changed the default "Caliber Library" to "CaliberLibrary" (one word) because this is easier when starting the content server.
After selecting the location for my Caliber content, I'm ready to start downloading the book.
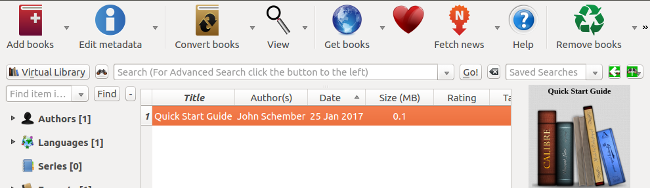
Caliber's interface
I selected the Get Books option from the menu, where it was easy to enter my search terms and select the ebook providers I was interested in. I was looking for DRM-free material, so I chose Project Gutenberg as my source. (Caliber's disclaimer states that ebook transactions are between you and the individual content provider.) I entered "Mark Twain" into the author field and got 10 results.
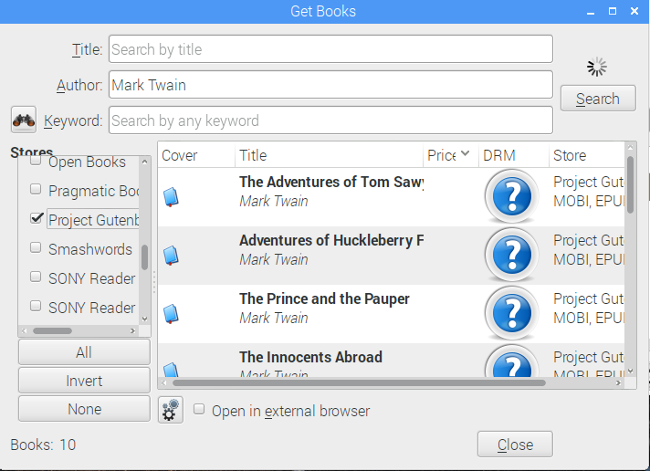
Searching for e-books
I chose the book Adventures of Huckleberry Finn. On the next page, I can choose between the two ebook formats MOBI and EPUB. I chose EPUB and the book downloaded very quickly.
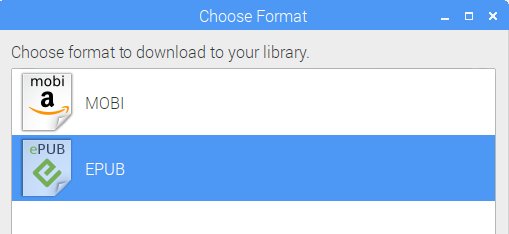
Choosing the e-book format
You can also add books to the library from other content providers instead of adding them to Caliber's list. For example, teachers can share open educational resources in e-book format with students through this content server. To load content, use the "Add Books" option on the far left side of the interface.
Depending on the size of your library, you may need to increase the size of your microSD card.
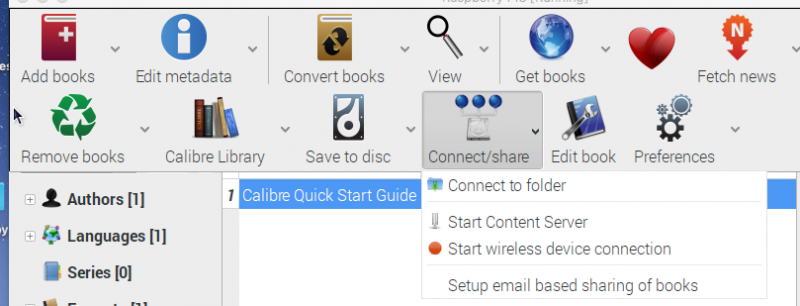
start_the_server.png
Once you add content to the eBook server, you can share the content with others on your network. By typing
in the terminalifconfig
Get your Raspberry Pi IP address. I'm using a wireless network, so I used the results from wlan0 in the example below. Click on the far right side of the interface and expand the menu. Then click “Connect and Share” and start the server.
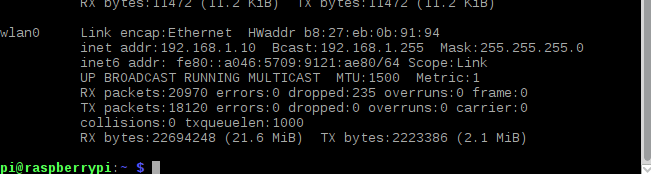
Identifying the IP address with ipconfig
My next step is to access the e-book I added via my computer client connected to the Raspberry Pi. I opened a browser on the client and entered the address of the Raspberry followed by the port :8080. In my case it is http://192.168.1.10:8080 (Adapt it according to the address of your Pi).
You will see the home page in your browser:
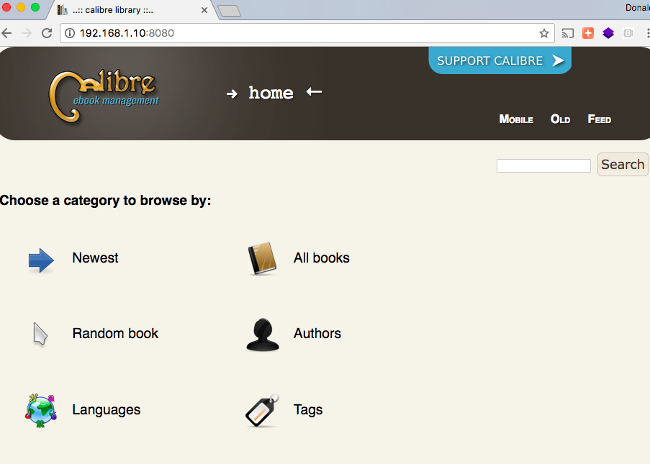
Caliber's client homepage
I have tested and can easily connect to the server using iPhone, Linux, and MacOS computers.
You can explore the options from this home page, or click All Books to display all content on the server.
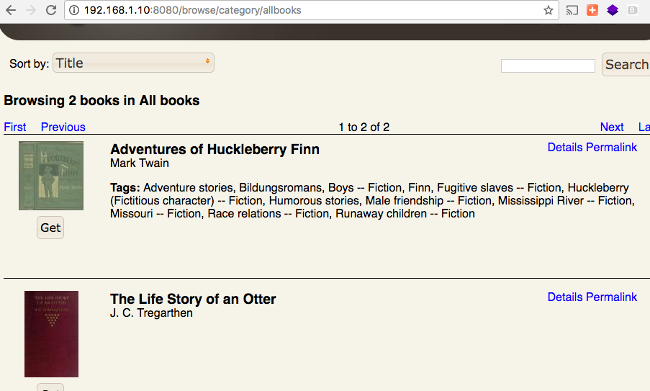
Browsing e-books
From here, you can download the book to your device and read it offline.
Have you not set up an e-book server yet? Or are you considering setting up one yourself? Share your suggestions or questions in the comments.
The above is the detailed content of Building an e-book service using Raspberry Pi. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1418
1418
 52
52
 1311
1311
 25
25
 1261
1261
 29
29
 1234
1234
 24
24
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
VS Code One-step/Next step shortcut key usage: One-step (backward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl ←; macOS: Cmd ←Next step (forward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl →; macOS: Cmd →
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
To install Laravel, follow these steps in sequence: Install Composer (for macOS/Linux and Windows) Install Laravel Installer Create a new project Start Service Access Application (URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000) Set up the database connection (if required)
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version




