 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 770 million parameters, exceeding 540 billion PaLM! UW Google proposes 'step-by-step distillation', which only requires 80% of training data | ACL 2023
770 million parameters, exceeding 540 billion PaLM! UW Google proposes 'step-by-step distillation', which only requires 80% of training data | ACL 2023
770 million parameters, exceeding 540 billion PaLM! UW Google proposes 'step-by-step distillation', which only requires 80% of training data | ACL 2023
Large language models excel in performance and are able to solve new tasks with zero- or few-shot hints. However, in actual application deployment, LLM is not very practical because its memory utilization efficiency is low and it requires a large amount of computing resources. For example, running a language model service with 175 billion parameters requires at least 350GB of video memory. Most of the current most advanced language models have more than 500 billion parameters. Many research teams do not have enough resources to run them, and they cannot meet the low-latency performance in real applications.
There are also some studies using manually labeled data or distillation using LLM-generated labels to train smaller, task-specific models, but fine-tuning and distillation require a large amount of training data to achieve comparable performance to LLM.
In order to solve the problem of resource requirements for large models, the University of Washington and Google collaborated to propose a new distillation mechanism called "Distilling Step-by-Step". Through step-by-step distillation, the size of the distilled model is smaller than the original model, but the performance is better, and less training data is required during the fine-tuning and distillation process

The distribution distillation mechanism extracts the prediction reason from LLM (rationale ) as additional supervisory information for training small models within a multi-task framework.
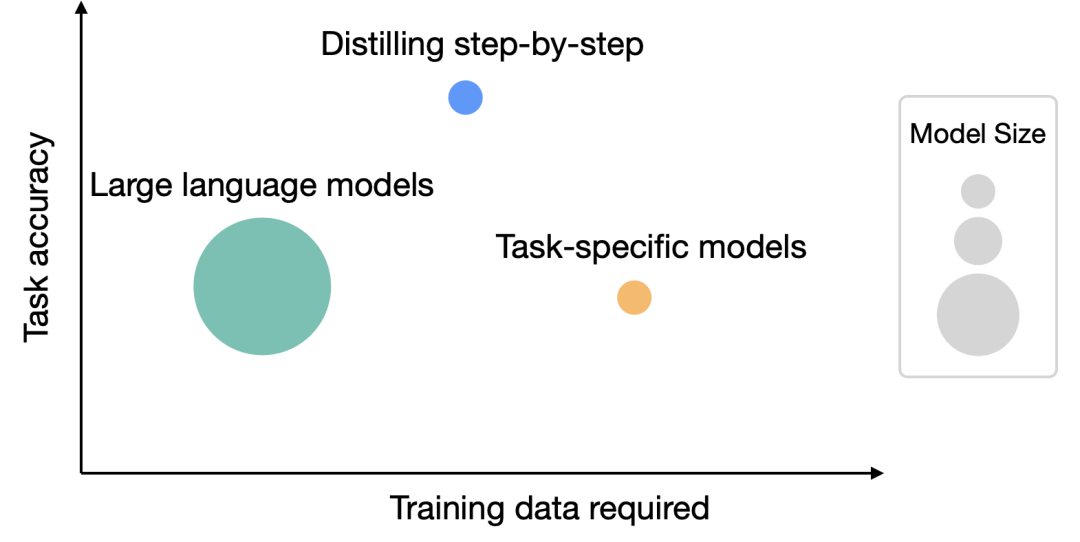 After experiments on 4 NLP benchmarks, we found:
After experiments on 4 NLP benchmarks, we found:
1. Compared with fine-tuning and distillation, this mechanism uses less Training samples achieve better performance;
Compared with few-sample prompt LLM, this mechanism uses smaller size models to achieve better performance
3. At the same time, it reduces the model size and The data volume can also achieve better performance than LLM.
In the experiment, the 770M T5 model after fine-tuning was better than the 540B PaLM model with few sample hints in the benchmark test using only 80% of the available data, while the T5 model with the same standard fine-tuning even used 100% Data sets are also difficult to match.
Distillation method
The key idea of distribution distillation is to gradually extract information-rich prediction reasons described in natural language, that is, intermediate reasoning steps, to explain the connection between the input problem and the model output , and use these data to train small models more efficiently
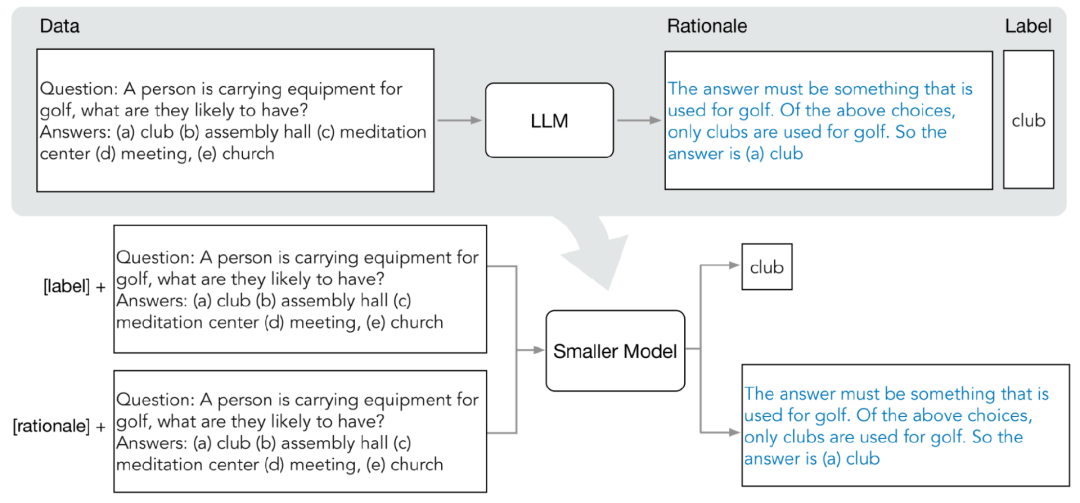 Distribution distillation mainly includes two stages:
Distribution distillation mainly includes two stages:
1. From Extraction principle (rationale) in LLMResearchers use the few-sample Chain of Thinking (CoT) prompt to extract the prediction intermediate steps from LLM.
After determining the target task, first prepare several samples in the LLM input prompt. Each example consists of a triplet, including input, principle and output
 After inputting prompts, LLM can imitate the triplet demonstration to generate other new problems. Prediction principle, for example, in the common sense question and answer task, given
After inputting prompts, LLM can imitate the triplet demonstration to generate other new problems. Prediction principle, for example, in the common sense question and answer task, given
Sammy wants to go to a place where crowds gather. Where will he choose? The options are: (a) densely populated area, (b) race track, (c) desert, (d) apartment, (e) roadblock
(Sammy wanted to go to where the people are. Where might he go? Answer Choices: (a) populated areas, (b) race track, (c) desert, (d) apartment, (e) roadblock)After gradual refinement, LLM You can give the correct answer to the question "(a) Densely populated area" and provide a reason for answering the question "The answer must be a place with many people. Among the above choices, only densely populated areas have many people." After gradual refinement, LLM was able to conclude that the correct answer is "(a) densely populated area" and provided the reason for answering the question "The answer must be a place with many people. Among the above choices, only densely populated areas have many people." people."
By providing CoT examples paired with rationales in prompts, the contextual learning capability allows LLM to generate appropriate answer reasons for unencountered question types
2. Training Mini Model
By constructing the training process as a multi-task problem, the reasons for prediction can be extracted and incorporated into the training small model
In addition to the standard label prediction task In addition, the researchers also used a new reason generation task to train a small model, so that the model can learn to generate intermediate reasoning steps for prediction, and guide the model to better predict the result label.
Distinguish label prediction and reason generation tasks by adding the task prefixes "label" and "rationale" to the input prompt.
Experimental results
In the experiment, the researchers selected the PaLM model with 540 billion parameters as the LLM baseline, and used the T5 model as the task-related downstream small model.
In this study, we conducted experiments on four benchmark datasets, namely e-SNLI and ANLI for natural language reasoning, CQA for common sense question answering, and SVAMP for Application problems in arithmetic and mathematics. We conducted experiments on these three different NLP tasks
Less training data
The stepwise distillation method performs better than Standard fine-tuning is better and requires less training data
On the e-SNLI dataset, better performance than standard fine-tuning is achieved when using 12.5% of the full dataset, on ANLI, Only 75%, 25% and 20% of the training data are required on CQA and SVAMP respectively.
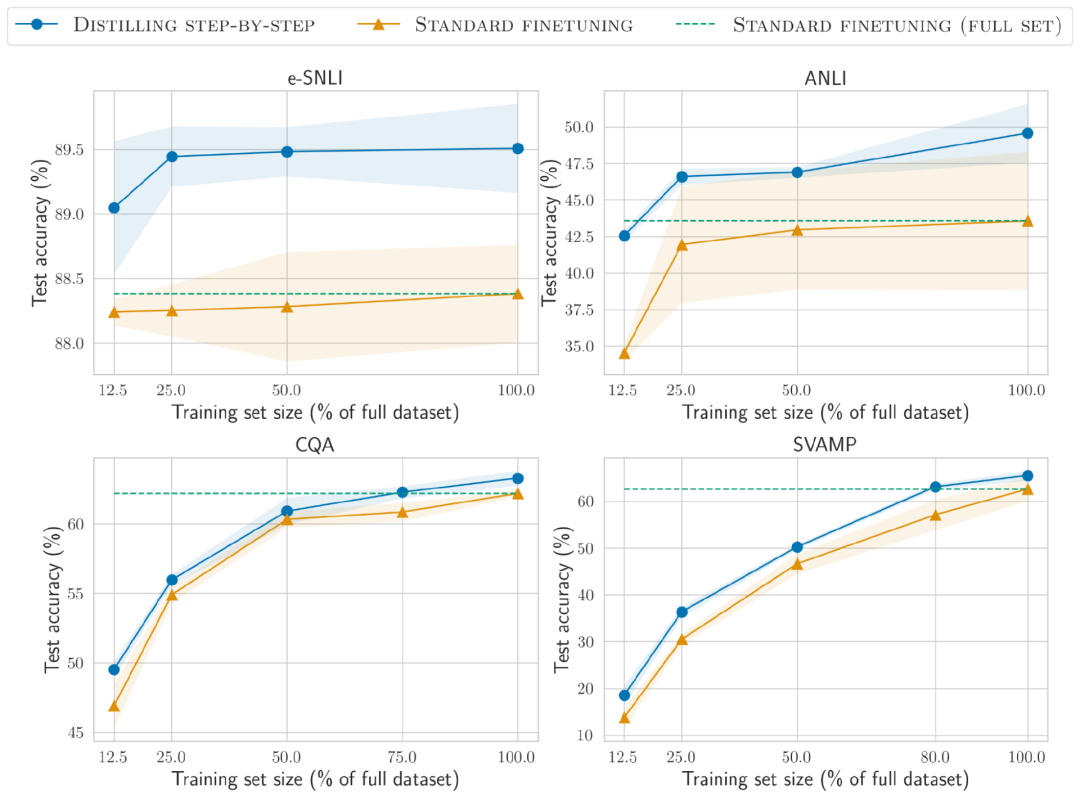
Compared to standard fine-tuning using a 220M T5 model on manually labeled datasets of varying sizes, distribution distillation is superior when using fewer training examples across all datasets. Distribution compared to LLM prompted by few-shot CoT Distillation results in a model that is much smaller in size but performs better.
On the e-SNLI data set, using the 220M T5 model achieves better performance than the 540B PaLM; on ANLI, using the 770M T5 model achieves better performance than the 540B PaLM. Model size is only 1/700Smaller model, less data
While reducing model size and training data , we successfully achieved performance exceeding few-shot PaLM
In ANLI, outperforming 540B PaLM using a 770M T5 model, while using only 80% of the full dataset
It has been observed that standard fine-tuning cannot reach the performance level of PaLM even with the complete 100% data set, indicating that stepwise distillation can simultaneously reduce the model size and the amount of training data, thereby achieving Performance beyond LLMThe above is the detailed content of 770 million parameters, exceeding 540 billion PaLM! UW Google proposes 'step-by-step distillation', which only requires 80% of training data | ACL 2023. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1665
1665
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1321
1321
 25
25
 1269
1269
 29
29
 1249
1249
 24
24
 How to use the chrono library in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the chrono library in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Using the chrono library in C can allow you to control time and time intervals more accurately. Let's explore the charm of this library. C's chrono library is part of the standard library, which provides a modern way to deal with time and time intervals. For programmers who have suffered from time.h and ctime, chrono is undoubtedly a boon. It not only improves the readability and maintainability of the code, but also provides higher accuracy and flexibility. Let's start with the basics. The chrono library mainly includes the following key components: std::chrono::system_clock: represents the system clock, used to obtain the current time. std::chron
 How to understand DMA operations in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
How to understand DMA operations in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
DMA in C refers to DirectMemoryAccess, a direct memory access technology, allowing hardware devices to directly transmit data to memory without CPU intervention. 1) DMA operation is highly dependent on hardware devices and drivers, and the implementation method varies from system to system. 2) Direct access to memory may bring security risks, and the correctness and security of the code must be ensured. 3) DMA can improve performance, but improper use may lead to degradation of system performance. Through practice and learning, we can master the skills of using DMA and maximize its effectiveness in scenarios such as high-speed data transmission and real-time signal processing.
 How to handle high DPI display in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
How to handle high DPI display in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
Handling high DPI display in C can be achieved through the following steps: 1) Understand DPI and scaling, use the operating system API to obtain DPI information and adjust the graphics output; 2) Handle cross-platform compatibility, use cross-platform graphics libraries such as SDL or Qt; 3) Perform performance optimization, improve performance through cache, hardware acceleration, and dynamic adjustment of the details level; 4) Solve common problems, such as blurred text and interface elements are too small, and solve by correctly applying DPI scaling.
 What is real-time operating system programming in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
What is real-time operating system programming in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
C performs well in real-time operating system (RTOS) programming, providing efficient execution efficiency and precise time management. 1) C Meet the needs of RTOS through direct operation of hardware resources and efficient memory management. 2) Using object-oriented features, C can design a flexible task scheduling system. 3) C supports efficient interrupt processing, but dynamic memory allocation and exception processing must be avoided to ensure real-time. 4) Template programming and inline functions help in performance optimization. 5) In practical applications, C can be used to implement an efficient logging system.
 How to measure thread performance in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to measure thread performance in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Measuring thread performance in C can use the timing tools, performance analysis tools, and custom timers in the standard library. 1. Use the library to measure execution time. 2. Use gprof for performance analysis. The steps include adding the -pg option during compilation, running the program to generate a gmon.out file, and generating a performance report. 3. Use Valgrind's Callgrind module to perform more detailed analysis. The steps include running the program to generate the callgrind.out file and viewing the results using kcachegrind. 4. Custom timers can flexibly measure the execution time of a specific code segment. These methods help to fully understand thread performance and optimize code.
 Steps to add and delete fields to MySQL tables
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:15 PM
Steps to add and delete fields to MySQL tables
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:15 PM
In MySQL, add fields using ALTERTABLEtable_nameADDCOLUMNnew_columnVARCHAR(255)AFTERexisting_column, delete fields using ALTERTABLEtable_nameDROPCOLUMNcolumn_to_drop. When adding fields, you need to specify a location to optimize query performance and data structure; before deleting fields, you need to confirm that the operation is irreversible; modifying table structure using online DDL, backup data, test environment, and low-load time periods is performance optimization and best practice.
 Quantitative Exchange Ranking 2025 Top 10 Recommendations for Digital Currency Quantitative Trading APPs
Apr 30, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Quantitative Exchange Ranking 2025 Top 10 Recommendations for Digital Currency Quantitative Trading APPs
Apr 30, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
The built-in quantization tools on the exchange include: 1. Binance: Provides Binance Futures quantitative module, low handling fees, and supports AI-assisted transactions. 2. OKX (Ouyi): Supports multi-account management and intelligent order routing, and provides institutional-level risk control. The independent quantitative strategy platforms include: 3. 3Commas: drag-and-drop strategy generator, suitable for multi-platform hedging arbitrage. 4. Quadency: Professional-level algorithm strategy library, supporting customized risk thresholds. 5. Pionex: Built-in 16 preset strategy, low transaction fee. Vertical domain tools include: 6. Cryptohopper: cloud-based quantitative platform, supporting 150 technical indicators. 7. Bitsgap:
 How to use string streams in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
How to use string streams in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The main steps and precautions for using string streams in C are as follows: 1. Create an output string stream and convert data, such as converting integers into strings. 2. Apply to serialization of complex data structures, such as converting vector into strings. 3. Pay attention to performance issues and avoid frequent use of string streams when processing large amounts of data. You can consider using the append method of std::string. 4. Pay attention to memory management and avoid frequent creation and destruction of string stream objects. You can reuse or use std::stringstream.



