 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Golang
Golang
 Performance impact and optimization of coroutine synchronization in Golang
Performance impact and optimization of coroutine synchronization in Golang
Performance impact and optimization of coroutine synchronization in Golang
Performance impact and optimization of coroutine synchronization in Golang
Introduction:
With the continuous improvement of computer hardware, the popularity of multi-core processors and large-scale concurrency As the demand for programming increases, coroutines, as a lightweight thread solution, have been widely used in Golang. However, when using coroutines for concurrent programming, we need to pay attention to the performance impact of coroutine synchronization and combine appropriate optimization strategies to improve program efficiency.
1. Performance impact of coroutine synchronization
Goroutine is the basic concurrency unit in Golang. It can execute concurrently with other coroutines and communicate through channels. However, in the process of concurrent scheduling of multiple coroutines and communication between coroutines, there will be some additional overhead, which will affect the performance of the program.
- Race Condition (Race Condition)
When multiple coroutines access and modify shared data at the same time, a race condition will occur. Race conditions can lead to data inconsistency and uncertainty in program execution results, so we need to use mutexes (Mutex) or other synchronization primitives to protect critical sections.
The use of mutex locks will introduce additional overhead: the process of acquiring the lock, releasing the lock, and waiting for the lock takes time. In high-concurrency scenarios, frequent lock competition will lead to coroutine switching and resource waste, thereby reducing program performance.
- Channel synchronization
Channel is an important mechanism for communication between coroutines. It provides a synchronization method to realize information transfer and data sharing between coroutines. However, channel operation also brings some performance impacts.
The sending and receiving operations of the channel will introduce an internal lock mechanism to ensure the synchronization and order of information. Therefore, when the amount of concurrency is high, coroutine waiting and channel competition can also cause potential performance problems.
2. Optimization strategies
When facing the above performance problems, we can adopt some optimization strategies to improve program efficiency.
- Reduce lock competition
In multi-threaded programming, reducing the use of locks is one of the important means to improve performance. Lock competition can be reduced in the following ways: - Fine-grained locks: Split large locks (locking the entire shared data structure) into small locks, and only lock the parts that need to be modified.
- Read-write lock: allows multiple coroutines to read shared data at the same time, but only allows one coroutine to perform write operations.
- Lock-free data structure: Use lock-free data structures, such as atomic operations, atomic pointers, etc., to avoid using locks.
- Using unbuffered channels
Unbuffered channels can achieve synchronization between coroutines without introducing additional queues or buffers. Using unbuffered channels can force coroutines to wait, thereby avoiding frequent coroutine switching and resource waste. In some scenarios, unbuffered channels may be more efficient than buffered channels. - Batch operations and concurrency control
For many IO-intensive tasks, batch operations can be used to reduce the overhead of system calls. For example, multiple tasks can be merged into a batch and IO operations can be performed at one time, thereby reducing the overhead of IO scheduling context switching.
In addition, for some scenarios with limited concurrent resources, the performance of the program can be improved by controlling the concurrency. For example, limiting the number of coroutines running simultaneously can avoid excessive coroutine switching and resource competition.
Conclusion:
In coroutine programming, coroutine synchronization will have an impact on the performance of the program. In order to improve the efficiency of the program, we can reduce lock competition, use unbuffered channels, and adopt optimization strategies such as batch operations and concurrency control. Ultimately, through reasonable design and optimization, the advantages of Golang coroutine concurrent programming can be fully utilized and the performance of the program can be improved.
The above is the detailed content of Performance impact and optimization of coroutine synchronization in Golang. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1242
1242
 24
24
 The parent-child relationship between golang functions and goroutine
Apr 25, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
The parent-child relationship between golang functions and goroutine
Apr 25, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
There is a parent-child relationship between functions and goroutines in Go. The parent goroutine creates the child goroutine, and the child goroutine can access the variables of the parent goroutine but not vice versa. Create a child goroutine using the go keyword, and the child goroutine is executed through an anonymous function or a named function. A parent goroutine can wait for child goroutines to complete via sync.WaitGroup to ensure that the program does not exit before all child goroutines have completed.
 Application of concurrency and coroutines in Golang API design
May 07, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
Application of concurrency and coroutines in Golang API design
May 07, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
Concurrency and coroutines are used in GoAPI design for: High-performance processing: Processing multiple requests simultaneously to improve performance. Asynchronous processing: Use coroutines to process tasks (such as sending emails) asynchronously, releasing the main thread. Stream processing: Use coroutines to efficiently process data streams (such as database reads).
 C++ program optimization: time complexity reduction techniques
Jun 01, 2024 am 11:19 AM
C++ program optimization: time complexity reduction techniques
Jun 01, 2024 am 11:19 AM
Time complexity measures the execution time of an algorithm relative to the size of the input. Tips for reducing the time complexity of C++ programs include: choosing appropriate containers (such as vector, list) to optimize data storage and management. Utilize efficient algorithms such as quick sort to reduce computation time. Eliminate multiple operations to reduce double counting. Use conditional branches to avoid unnecessary calculations. Optimize linear search by using faster algorithms such as binary search.
 The relationship between Golang coroutine and goroutine
Apr 15, 2024 am 10:42 AM
The relationship between Golang coroutine and goroutine
Apr 15, 2024 am 10:42 AM
Coroutine is an abstract concept for executing tasks concurrently, and goroutine is a lightweight thread function in the Go language that implements the concept of coroutine. The two are closely related, but goroutine resource consumption is lower and managed by the Go scheduler. Goroutine is widely used in actual combat, such as concurrently processing web requests and improving program performance.
 How to control the life cycle of Golang coroutines?
May 31, 2024 pm 06:05 PM
How to control the life cycle of Golang coroutines?
May 31, 2024 pm 06:05 PM
Controlling the life cycle of a Go coroutine can be done in the following ways: Create a coroutine: Use the go keyword to start a new task. Terminate coroutines: wait for all coroutines to complete, use sync.WaitGroup. Use channel closing signals. Use context context.Context.
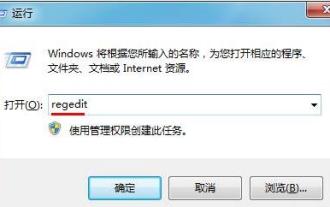 How to optimize the startup items of WIN7 system
Mar 26, 2024 pm 06:20 PM
How to optimize the startup items of WIN7 system
Mar 26, 2024 pm 06:20 PM
1. Press the key combination (win key + R) on the desktop to open the run window, then enter [regedit] and press Enter to confirm. 2. After opening the Registry Editor, we click to expand [HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorer], and then see if there is a Serialize item in the directory. If not, we can right-click Explorer, create a new item, and name it Serialize. 3. Then click Serialize, then right-click the blank space in the right pane, create a new DWORD (32) bit value, and name it Star
 What are some ways to resolve inefficiencies in PHP functions?
May 02, 2024 pm 01:48 PM
What are some ways to resolve inefficiencies in PHP functions?
May 02, 2024 pm 01:48 PM
Five ways to optimize PHP function efficiency: avoid unnecessary copying of variables. Use references to avoid variable copying. Avoid repeated function calls. Inline simple functions. Optimizing loops using arrays.
 How to implement parallel processing using Go coroutines?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:07 PM
How to implement parallel processing using Go coroutines?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:07 PM
How to use Go coroutines to implement parallel processing? Create a coroutine to calculate the Fibonacci sequence in parallel. Coroutines transfer data through channels to achieve parallel computing. The main coroutine receives and processes the results of parallel calculations.



