 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C++
C++
 In the C program, translate the following content into Chinese: Program to find the nth node from the bottom of a linked list
In the C program, translate the following content into Chinese: Program to find the nth node from the bottom of a linked list
In the C program, translate the following content into Chinese: Program to find the nth node from the bottom of a linked list
Given n nodes, the task is to print the nth node at the end of the linked list. The program must not change the order of the nodes in the list, but should only print the nth node from the last node of the linked list.
Example
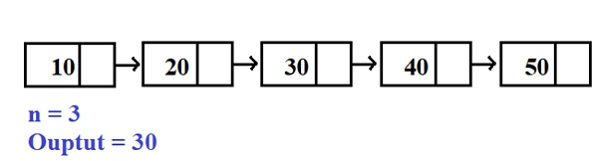
Input -: 10 20 30 40 50 60 N=3 Output -: 40
In the above example, starting from the first node, traverse to count-n nodes, that is, 10,20 30,40, 50,60, so the last Three nodes are 40.
Instead of traversing the entire list so efficiently one can follow -
- Get a temporary pointer to, say, a temp# of node type ##Set this temporary pointer to the first node head pointer pointed to Set the counter to the number of nodes in the list Move temp to temp → next until count -nDisplay temp → data
th Starting at position 10, the result up to 20 is in the 1st position, and the 30th position is in the second position. So with this approach, there is no need to iterate through the entire list until the end, which will save space and memory.
AlgorithmStart
Step 1 -> create structure of a node and temp, next and head as pointer to a structure node
struct node
int data
struct node *next, *head, *temp
End
Step 2 -> declare function to insert a node in a list
void insert(int val)
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node))
newnode->data = val
IF head= NULL
set head = newnode
set head->next = NULL
End
Else
Set temp=head
Loop While temp->next!=NULL
Set temp=temp->next
End
Set newnode->next=NULL
Set temp->next=newnode
End
Step 3 -> Declare a function to display list
void display()
IF head=NULL
Print no node
End
Else
Set temp=head
Loop While temp!=NULL
Print temp->data
Set temp=temp->next
End
End
Step 4 -> declare a function to find nth node from last of a linked list
void last(int n)
declare int product=1, i
Set temp=head
Loop For i=0 and i<count-n and i++
Set temp=temp->next
End
Print temp->data
Step 5 -> in main()
Create nodes using struct node* head = NULL
Declare variable n as nth to 3
Call function insert(10) to insert a node
Call display() to display the list
Call last(n) to find nth node from last of a list
StopCopy after login
Example Live demonstrationStart
Step 1 -> create structure of a node and temp, next and head as pointer to a structure node
struct node
int data
struct node *next, *head, *temp
End
Step 2 -> declare function to insert a node in a list
void insert(int val)
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node))
newnode->data = val
IF head= NULL
set head = newnode
set head->next = NULL
End
Else
Set temp=head
Loop While temp->next!=NULL
Set temp=temp->next
End
Set newnode->next=NULL
Set temp->next=newnode
End
Step 3 -> Declare a function to display list
void display()
IF head=NULL
Print no node
End
Else
Set temp=head
Loop While temp!=NULL
Print temp->data
Set temp=temp->next
End
End
Step 4 -> declare a function to find nth node from last of a linked list
void last(int n)
declare int product=1, i
Set temp=head
Loop For i=0 and i<count-n and i++
Set temp=temp->next
End
Print temp->data
Step 5 -> in main()
Create nodes using struct node* head = NULL
Declare variable n as nth to 3
Call function insert(10) to insert a node
Call display() to display the list
Call last(n) to find nth node from last of a list
Stop#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//structure of a node
struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}*head,*temp;
int count=0;
//function for inserting nodes into a list
void insert(int val){
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->data = val;
newnode->next = NULL;
if(head == NULL){
head = newnode;
temp = head;
count++;
} else {
temp->next=newnode;
temp=temp->next;
count++;
}
}
//function for displaying a list
void display(){
if(head==NULL)
printf("no node ");
else {
temp=head;
while(temp!=NULL) {
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp=temp->next;
}
}
}
//function for finding 3rd node from the last of a linked list
void last(int n){
int i;
temp=head;
for(i=0;i<count-n;i++){
temp=temp->next;
}
printf("</p><p>%drd node from the end of linked list is : %d" ,n,temp->data);
}
int main(){
//creating list
struct node* head = NULL;
int n=3;
//inserting elements into a list
insert(1);
insert(2);
insert(3);
insert(4);
insert(5);
insert(6);
//displaying the list
printf("</p><p>linked list is : ");
display();
//calling function for finding nth element in a list from last
last(n);
return 0;
}linked list is : 1 2 3 4 5 6
3rd node from the end of linked list is : 4
Copy after login
linked list is : 1 2 3 4 5 6 3rd node from the end of linked list is : 4
The above is the detailed content of In the C program, translate the following content into Chinese: Program to find the nth node from the bottom of a linked list. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Find the nth node from the last linked list in C++ using recursive method
Sep 15, 2023 pm 05:53 PM
Find the nth node from the last linked list in C++ using recursive method
Sep 15, 2023 pm 05:53 PM
Given a singly linked list and a positive integer N as input. The goal is to find the Nth node from the end of the given list using recursion. If the input list has nodes a→b→c→d→e→f and N is 4, then the 4th node from the last will be c. We will first traverse until the last node in the list and when returning from the recursive (backtracking) increment count. When count equals N, a pointer to the current node is returned as the result. Let's look at various input and output scenarios for this - Input - List: -1→5→7→12→2→96→33N=3 Output − The Nth node from the last is: 2 Explanation − The third node is 2 . Input − List: -12→53→8→19→20→96→33N=8 Output – Node does not exist
 Query the minimum weight in the subtree starting from node X and distance at most D
Aug 25, 2023 am 11:25 AM
Query the minimum weight in the subtree starting from node X and distance at most D
Aug 25, 2023 am 11:25 AM
When doing computer programming, sometimes it is necessary to find the minimum weight of a subtree originating from a specific node, provided that the subtree cannot contain nodes that are more than D units away from the specified node. This problem arises in various fields and applications, including graph theory, tree-based algorithms, and network optimization. A subtree is a subset of a larger tree structure, with the specified node serving as the root node of the subtree. A subtree contains all descendants of the root node and their connecting edges. A node's weight refers to a specific value assigned to that node, which can represent its importance, significance, or other relevant metrics. In this problem, the goal is to find the minimum weight among all nodes in a subtree while limiting the subtree to nodes that are at most D units away from the root node. In the following article, we will delve into the complexity of mining minimum weights from subtrees
 PHP SPL data structures: Inject speed and flexibility into your projects
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:00 PM
PHP SPL data structures: Inject speed and flexibility into your projects
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:00 PM
Overview of the PHPSPL Data Structure Library The PHPSPL (Standard PHP Library) data structure library contains a set of classes and interfaces for storing and manipulating various data structures. These data structures include arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, and sets, each of which provides a specific set of methods and properties for manipulating data. Arrays In PHP, an array is an ordered collection that stores a sequence of elements. The SPL array class provides enhanced functions for native PHP arrays, including sorting, filtering, and mapping. Here is an example of using the SPL array class: useSplArrayObject;$array=newArrayObject(["foo","bar","baz"]);$array
 Comparison of algorithm time complexity of PHP arrays and linked lists
May 07, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
Comparison of algorithm time complexity of PHP arrays and linked lists
May 07, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
Comparison of the algorithm time complexity of arrays and linked lists: accessing arrays O(1), linked lists O(n); inserting arrays O(1), linked lists O(1)/O(n); deleting arrays O(1), linked lists O(n) (n); Search array O(n), linked list O(n).
 Add 1 to a number represented by a linked list
Aug 29, 2023 pm 09:17 PM
Add 1 to a number represented by a linked list
Aug 29, 2023 pm 09:17 PM
A linked list representation of a number is provided like this: All nodes of the linked list are considered to be one digit of the number. Nodes store numbers such that the first element of the linked list holds the most significant digit of the number, and the last element of the linked list holds the least significant digit of the number. For example, the number 202345 is represented in the linked list as (2->0->2->3->4->5). To add 1 to this linked list representing numbers, we must check the value of the least significant bit in the list. If it's less than 9 it's ok, otherwise the code will change the next number and so on. Now let us see an example to understand how to do this, 1999 is represented as (1->9->9->9) and adding 1 should change it
 How to implement the node copy and cut functions of mind maps through Vue and jsmind?
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
How to implement the node copy and cut functions of mind maps through Vue and jsmind?
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
How to implement the node copy and cut functions of mind maps through Vue and jsmind? Mind map is a common thinking tool that can help us organize our thoughts and sort out our thinking logic. The node copy and cut functions are commonly used operations in mind maps, which allow us to reuse existing nodes more conveniently and improve the efficiency of thinking organization. In this article, we will use the two tools Vue and jsmind to implement the node copy and cut functions of the mind map. First, we need to install Vue and jsmind and create
 PHP data structure: the charm of linked lists, exploring dynamic data organization
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:53 PM
PHP data structure: the charm of linked lists, exploring dynamic data organization
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:53 PM
A linked list is a data structure that uses a series of nodes with data and pointers to organize elements, and is particularly suitable for processing large data sets and frequent insertion/deletion operations. Its basic components include nodes (data and pointers to the next node) and head nodes (pointing to the first node in the linked list). Common linked list operations include: addition (tail insertion), deletion (specific value) and traversal.
 Python program: add elements to first and last position of linked list
Aug 23, 2023 pm 11:17 PM
Python program: add elements to first and last position of linked list
Aug 23, 2023 pm 11:17 PM
In Python, a linked list is a linear data structure that consists of a sequence of nodes, each node containing a value and a reference to the next node in the linked list. In this article, we will discuss how to add elements to the first and last position of a linked list in Python. LinkedList inPython A linked list is a reference data structure used to store a set of elements. It is similar to an array in a way, but in an array, the data is stored in contiguous memory locations, whereas in a linked list, the data is not subject to this condition. This means that the data is not stored sequentially but in a random manner in memory. Thisraisesonequestionthatis,howwecanac





