Designing personalized payment options in OpenCart: Part 3
If you have been following this series, you should be familiar with the type of file structure we set up on the backend for custom payment methods. If you haven't read the previous parts of this series, I highly recommend reading them before continuing with this series.
We will also use a similar file setup for the front-end part.
Controller settings
Go ahead and create the controller file in catalog/controller/ payment/custom.php. Paste the following content into the newly created controller file custom.php.
<?php
class ControllerPaymentCustom extends Controller {
protected function index() {
$this->language->load('payment/custom');
$this->data['button_confirm'] = $this->language->get('button_confirm');
$this->data['action'] = 'https://yourpaymentgatewayurl';
$this->load->model('checkout/order');
$order_info = $this->model_checkout_order->getOrder($this->session->data['order_id']);
if ($order_info) {
$this->data['text_config_one'] = trim($this->config->get('text_config_one'));
$this->data['text_config_two'] = trim($this->config->get('text_config_two'));
$this->data['orderid'] = date('His') . $this->session->data['order_id'];
$this->data['callbackurl'] = $this->url->link('payment/custom/callback');
$this->data['orderdate'] = date('YmdHis');
$this->data['currency'] = $order_info['currency_code'];
$this->data['orderamount'] = $this->currency->format($order_info['total'], $this->data['currency'] , false, false);
$this->data['billemail'] = $order_info['email'];
$this->data['billphone'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['telephone'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['billaddress'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['payment_address_1'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['billcountry'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['payment_iso_code_2'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['billprovince'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['payment_zone'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');;
$this->data['billcity'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['payment_city'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['billpost'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['payment_postcode'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliveryname'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_firstname'] . $order_info['shipping_lastname'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliveryaddress'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_address_1'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliverycity'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_city'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliverycountry'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_iso_code_2'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliveryprovince'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_zone'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliveryemail'] = $order_info['email'];
$this->data['deliveryphone'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['telephone'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliverypost'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_postcode'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
if (file_exists(DIR_TEMPLATE . $this->config->get('config_template') . '/template/payment/custom.tpl')){
$this->template = $this->config->get('config_template') . '/template/payment/custom.tpl';
} else {
$this->template = 'default/template/payment/custom.tpl';
}
$this->render();
}
}
public function callback() {
if (isset($this->request->post['orderid'])) {
$order_id = trim(substr(($this->request->post['orderid']), 6));
} else {
die('Illegal Access');
}
$this->load->model('checkout/order');
$order_info = $this->model_checkout_order->getOrder($order_id);
if ($order_info) {
$data = array_merge($this->request->post,$this->request->get);
//payment was made successfully
if ($data['status'] == 'Y' || $data['status'] == 'y') {
// update the order status accordingly
}
}
}
}
?>
As you can see, there are two different methods. The index method will be responsible for setting the data when the form is submitted to the third-party payment gateway, while the callback method is used to handle the response data from the third-party payment gateway. Having said that, you can define more methods if your payment gateway requires it. In this example, we keep the process as simple as possible.
Let’s understand each part in detail. We'll start with the index method.
First, we loaded the language file and set the value of the Confirm button. We also set the action attribute, which will be used by the payment submission form. You should change this setting according to your payment gateway.
$this->language->load('payment/custom');
$this->data['button_confirm'] = $this->language->get('button_confirm');
$this->data['action'] = 'https://yourpaymentgatewayurl';
Next, we load the order information from the user's active session.
$this->load->model('checkout/order');
$order_info = $this->model_checkout_order->getOrder($this->session->data['order_id']);
If the order information is available, we will proceed to set the data of the hidden variables that will be used to submit the form to the payment gateway URL. If you pay close attention to the code, you'll notice that we also use the custom parameters text_config_one and text_config_two, which we set in the admin configuration form in the previous part of this series.
Another important variable to note here is callbackurl, which holds the URL used by the payment gateway to redirect the user back to our store after the payment process. Yes, looking at the URL payment/custom/callback should indicate that it will call the callback method, as we will see at this point.
$this->data['text_config_one'] = trim($this->config->get('text_config_one'));
$this->data['text_config_two'] = trim($this->config->get('text_config_two'));
$this->data['orderid'] = date('His') . $this->session->data['order_id'];
$this->data['callbackurl'] = $this->url->link('payment/custom/callback');
$this->data['orderdate'] = date('YmdHis');
$this->data['currency'] = $order_info['currency_code'];
$this->data['orderamount'] = $this->currency->format($order_info['total'], $this->data['currency'] , false, false);
$this->data['billemail'] = $order_info['email'];
$this->data['billphone'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['telephone'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['billaddress'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['payment_address_1'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['billcountry'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['payment_iso_code_2'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['billprovince'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['payment_zone'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');;
$this->data['billcity'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['payment_city'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['billpost'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['payment_postcode'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliveryname'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_firstname'] . $order_info['shipping_lastname'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliveryaddress'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_address_1'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliverycity'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_city'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliverycountry'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_iso_code_2'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliveryprovince'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_zone'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliveryemail'] = $order_info['email'];
$this->data['deliveryphone'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['telephone'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
$this->data['deliverypost'] = html_entity_decode($order_info['shipping_postcode'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
Finally, we assign the custom template file custom.tpl and render the view.
if (file_exists(DIR_TEMPLATE . $this->config->get('config_template') . '/template/payment/custom.tpl')){
$this->template = $this->config->get('config_template') . '/template/payment/custom.tpl';
} else {
$this->template = 'default/template/payment/custom.tpl';
}
$this->render();
Let's review the code of the callback method. This method is called when the user returns to the store from the payment gateway site.
First, we check if the orderid variable is available before proceeding. If it is not available, we will stop further processing.
if (isset($this->request->post['orderid'])) {
$order_id = trim(substr(($this->request->post['orderid']), 6));
} else {
die('Illegal Access');
}
Next, we load the order information from the database. Finally, we will check if there is a success indicator in the payment gateway response. If so, we will continue to update order status information accordingly.
$this->load->model('checkout/order');
$order_info = $this->model_checkout_order->getOrder($order_id);
if ($order_info) {
$data = array_merge($this->request->post,$this->request->get);
//payment was made succ
if ($data['status'] == 'Y' || $data['status'] == 'y') {
// update the order status accordingly
}
}
This is the controller settings. Pretty simple, isn't it?
Traditional Model
As you probably know, OpenCart has its own set of conventions and standards for dealing with the inner workings of your store. This is the case for the model setup for payment method detection. You just set it up according to the convention and it will be picked up automatically.
Go ahead and create the model file in catalog/model/ payment/custom.php. Paste the following content into the newly created model file custom.php.
<?php
class ModelPaymentCustom extends Model {
public function getMethod($address, $total) {
$this->load->language('payment/custom');
$method_data = array(
'code' => 'custom',
'title' => $this->language->get('text_title'),
'sort_order' => $this->config->get('custom_sort_order')
);
return $method_data;
}
}
OpenCart will use this class when listing valid payment methods during the checkout process. During this process, OpenCart collects a list of valid payment methods from the backend, and for each method, it checks whether the appropriate model class is available. Payment methods are only listed if the associated model class is available.
The most important thing in this setting is the value of the code variable. In our case we defined it as custom which means when you select your payment method and press continue it will call payment/custom Internal URL that ultimately sets up the form for our payment gateway.
In short, we can say that it is a mandatory file for front-end payment method detection and normal working.
Language and template files
Now, we just need to create the language and view the files. Go ahead and create the language file in catalog/language/english/ payment/custom.php. Paste the following content into the newly created language file custom.php.
<?php $_['text_title'] = 'Custom Payment Method'; $_['button_confirm'] = 'Confirm Order'; ?>
Pretty easy to understand: we just set up the tags that will be used on the frontend during checkout.
Go ahead and create the template file in catalog/view/theme/default/template/ payment/custom.tpl. Paste the following content into the newly created template file custom.tpl.
<form action="<?php echo $action; ?>" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="text_config_one" value="<?php echo $text_config_one; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="text_config_two" value="<?php echo $text_config_two; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="orderid" value="<?php echo $orderid; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="callbackurl" value="<?php echo $callbackurl; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="orderdate" value="<?php echo $orderdate; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="currency" value="<?php echo $currency; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="orderamount" value="<?php echo $orderamount; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="billemail" value="<?php echo $billemail; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="billphone" value="<?php echo $billphone; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="billaddress" value="<?php echo $billaddress; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="billcountry" value="<?php echo $billcountry; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="billprovince" value="<?php echo $billprovince; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="billcity" value="<?php echo $billcity; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="billpost" value="<?php echo $billpost; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="deliveryname" value="<?php echo $deliveryname; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="deliveryaddress" value="<?php echo $deliveryaddress; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="deliverycity" value="<?php echo $deliverycity; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="deliverycountry" value="<?php echo $deliverycountry; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="deliveryprovince" value="<?php echo $deliveryprovince; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="deliveryemail" value="<?php echo $deliveryemail; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="deliveryphone" value="<?php echo $deliveryphone; ?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="deliverypost" value="<?php echo $deliverypost; ?>" />
<div class="buttons">
<div class="right">
<input type="submit" value="<?php echo $button_confirm; ?>" class="button" />
</div>
</div>
</form>
As you may have guessed, this is the form that will be submitted when the user clicks the Confirm Order button. We have just set the hidden variables and their values, which were previously defined in the index method of the controller.
Let’s take a look at the front end:
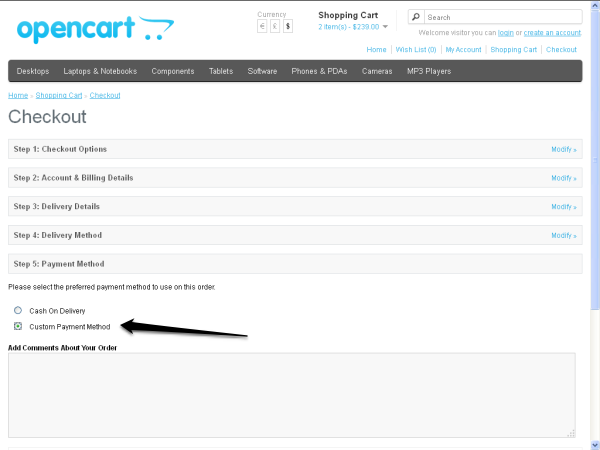
Let’s take a quick look at the entire process:
- First, you must set up the model file for your payment method so that it can be listed in the Step 5: Payment Methods tag.
- Next, when the user selects Custom payment method in the fifth tab and clicks the Continue button, OpenCart will internally call
payment /customURL, ultimately calling theindexmethod and rendering thecustom.tplfile in the sixth tab.
- Finally, when the user clicks on the Confirm Order button, the form will be submitted and the user will be taken to the payment gateway website, where the payment process will begin. After the payment process is completed, the user will be redirected back to our website due to the
callbackurlhidden variable. Of course, if everything works as expected, the order status will be updated as part of thecallbackmethod.
in conclusion
In this series, I explain how to set up almost any payment method by creating your own payment method module. I hope you enjoyed this series and learned something useful.
Creating custom content for any framework is always fun, isn't it? Remember, you can always leave comments and questions using the comment form below.
The above is the detailed content of Designing personalized payment options in OpenCart: Part 3. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1248
1248
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 Explain secure password hashing in PHP (e.g., password_hash, password_verify). Why not use MD5 or SHA1?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Explain secure password hashing in PHP (e.g., password_hash, password_verify). Why not use MD5 or SHA1?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:06 AM
In PHP, password_hash and password_verify functions should be used to implement secure password hashing, and MD5 or SHA1 should not be used. 1) password_hash generates a hash containing salt values to enhance security. 2) Password_verify verify password and ensure security by comparing hash values. 3) MD5 and SHA1 are vulnerable and lack salt values, and are not suitable for modern password security.
 PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is widely used in e-commerce, content management systems and API development. 1) E-commerce: used for shopping cart function and payment processing. 2) Content management system: used for dynamic content generation and user management. 3) API development: used for RESTful API development and API security. Through performance optimization and best practices, the efficiency and maintainability of PHP applications are improved.
 How does PHP handle file uploads securely?
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:37 AM
How does PHP handle file uploads securely?
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:37 AM
PHP handles file uploads through the $\_FILES variable. The methods to ensure security include: 1. Check upload errors, 2. Verify file type and size, 3. Prevent file overwriting, 4. Move files to a permanent storage location.
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
PHP is still dynamic and still occupies an important position in the field of modern programming. 1) PHP's simplicity and powerful community support make it widely used in web development; 2) Its flexibility and stability make it outstanding in handling web forms, database operations and file processing; 3) PHP is constantly evolving and optimizing, suitable for beginners and experienced developers.
 How does PHP type hinting work, including scalar types, return types, union types, and nullable types?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:25 AM
How does PHP type hinting work, including scalar types, return types, union types, and nullable types?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP type prompts to improve code quality and readability. 1) Scalar type tips: Since PHP7.0, basic data types are allowed to be specified in function parameters, such as int, float, etc. 2) Return type prompt: Ensure the consistency of the function return value type. 3) Union type prompt: Since PHP8.0, multiple types are allowed to be specified in function parameters or return values. 4) Nullable type prompt: Allows to include null values and handle functions that may return null values.
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.




